Abstract
Since 1960, gas gangrene has been treated by the administration of pure oxygen at 3 atmospheres absolute (3 ATA).
Small animals are useless for research at this pressure because of oxygen intoxication.
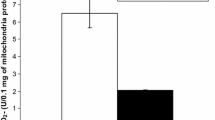
In vitro, the growth ofClostridium perfringens (C. welchii) was not arrested by 1 1/2 hr of hyperbaric oxygen at 3 ATA, but the production of α toxin is inhibited during this period. It is not inhibited at 2 ATA. If the results of the conservative treatment of patients with hyperbaric oxygen depend upon a comparable process, such treatment at less than 3 ATA would probably be ineffective.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boerema, I. 1961. An operating room with high atmospheric pressure. Surgery49: 291–298.
Boerema, I. enBrummelkamp, W. H. 1960. Behandeling van anaërobe infecties met inademing van zuurstof onder een druk van drie atmosferen. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneesk.104: 2548–2550.
van den Brenk, H. A. S. andJamieson, D. 1962. Pulmonary damage due to high pressure oxygen breathing in rats. Australian J. Exptl. Biol. Med. Sci.40: 37–56.
Brooks, M. E., Sterne, M. andWarrack, G. H. 1957. A re-assessment of the criteria used for type differentiation ofClostridium perfringens. J. Pathol. Bacteriol.74: 185–195.
Brummelkamp, W. H., Boerema, I. andHoogendijk, J. L. 1963. Treatment of clostridial infections with hyperbaric oxygen drenching; a report on 26 cases. Lancet1963, 1: 235–238.
Brummelkamp, W. H., Hoogendijk, J. L. andBoerema, I. 1961. Treatment of anaerobic infections (clostridial myositis) by drenching the tissues with oxygen under high atmospheric pressure. Surgery49: 299–302.
Evans, D. G. 1945. The in-vitro production of αtoxin, ϑhaemolysin and hyaluronidase by strains ofCl. welchii type A, and the relationship of in-vitro properties to virulence for guinea-pigs. J. Pathol. Bacteriol.57: 75–85.
Liebegott, G. 1941. Über Organveränderungen bei langer Einwirkung von Sauerstoff mit erhöhtem Partialdruck im Tierexperiment. Beitr. Pathol. Anat. Allgem. Pathol.105: 413–431.
MacLennan, J. D. 1962. The histotoxic clostridial infections of man. Bacteriol. Rev.26: 177–276.
Miles, A. A. andMisra, S. S. 1938. The estimation of the bactericidal power of the blood. J. Hyg. (London)38: 732–748.
Oakley, C. L. andWarrack, G. H. 1953. Routine typing ofClostridium welchii. J. Hyg. (London)51: 102–107.
Pichotka, J. 1941. Über die histologischen Veränderungen der Lunge nach Atmung von hochkonzentrierten Sauerstoff im Experiment. Beitr. Pathol. Anat. Allgem. Pathol.105: 381–412.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Unnik, A.J.M. Inhibition of toxin production inClostridium perfringens in vitro by hyperbaric oxygen. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 31, 181–186 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02045889
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02045889