Abstract
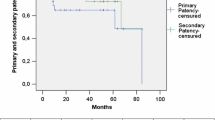
Ninety-eight patients with aortic infection or aortoenteric fistula were treated by axillobifemoral bypasses and aortic exclusion by 22 surgical teams. Early mortality was 24%. Primary patency at two and five years was 62% and 55%, respectively. Actuarial primary patency at two and five years was 82% and 65%, respectively. The actuarial rate of limb salvage at two and five years was 90% and 82%, respectively. Eight aortic stumps ruptured in less than eight months, postoperatively. Two of these ruptures were treated with success. Infection of the axillobifemoral bypasses was observed in seven cases, six of which were treated successfully. Eight patients had axillary complications, all treated successfully without upper limb sequelae. In eight cases, the axillobifemoral bypass was replaced by a thoracic aortic bypass. Early mortality was higher after emergency operation (30%) than after elective operation (14%). Mortality after cure of primary infection (7%) was lower than after secondary infection (27%). The rate of infection in polytetrafluoroethylene axillobifemoral bypass (3%) was lower than in Dacron axillobifemoral bypass (13%). The rate of occlusion of polytetrafluoroethylene axillobifemoral bypass and Dacron axillobifemoral bypass was identical. The rate of occlusion in ringed reinforced grafts was lower (9%) than in the nonreinforced grafts (22%). The rate of occlusion was significantly higher after ablation of graft for occlusive lesions (38%) than after graft for aneurysms (7.9%) (p<0.01).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BACOURT F, GOEAU-BRISSONIERE O, KOSKAS F. Fermeture du moignon aortique: une nouvelle méthode.Ann Chir Vasc 1986;1:271–272.
ALEXANDER RH, SELBY JH. Axillo femoral bypass grafts using polytetrafluoroethylene.South Med J 1980;73:1325–1332.
ALLISON HF, TERBLANCHE J, IMMELMAN EJ, et al. Axillofemoral bypass. A 2 decade experience reviewed.S Afr Med J 1985;68:559–562.
BROOME A, CHRISTENSON JT, EKELOF B, et al. Axillofemoral bypass reconstructions in sixty-one patients with leg ischemia.Surgery 1980;88:673–676.
BURRELL MJ, WHEELER JR, GREGORY RT, et al. Axillofemoral bypass.Ann Surg 1982;195:796–797.
EUGENE J, GOLDSTONE J, MOORE WS. Fifteen year experience with subcutaneous bypass. Grafts for lower extremity ischemia.Ann Surg 1977;186:177–183.
HEPP W, JONGE K, PALLUA N. Late results following extraanatomic bypass procedures for chronic aortoiliac occlusive disease.J Cardiovasc Surg 1988;29:181–185.
LIVESAY JJ, ATKINSON JB, BAKER JD, et al. Late results of extra-anatomic bypass.Arch Surg 1979;114:1260–1267.
LOGERFO FW, JOHNSON WC, CORSON JD, et al. A comparison of the late patency rates of axillobilateral femoral and axillounilateral femoral grafts.Surgery 1977;81:33–40.
MOORE WS, HALL AD, BLAISDELL FW. Late results of axillary-femoral bypass grafting.Am J Surg 1971;122:148–154.
NAYLOR AR, AH-SEE AK, ENGESET J. Axillo-femoral bypass as a limb salvage in high risk patients with aorto iliac disease.Br J Surg 1990;77:659–661.
RAY LI, O'CONNOR JB, DAVIS CC, et al. Axillofemoral bypass: a critical reappraisal of its role in the management of aortoiliac occlusive disease.Am J Surg 1979;138:117–128.
REILLY LM, STONEY RJ, GOLDSTONE J, et al. Improved management of aortic graft infection: the influence of operation sequence and staging.J Vasc Surg 1987;5:421–431.
WARD RE, HOLCROFT JW, CONTI S, et al. New concepts in the use of axillofemoral bypass grafts.Arch Surg 1983;118(5:573–576.
BUNT TJ. Synthetic vascular graft infections. I. Graft infections.Surgery 1983;93:733–746.
ELLIOT JP, SMITH RF, SZILAGYI DE. Aortoenteric and paraprosthetic enteric fistulas.Arch Surg 1974;108:479–490.
O'HARA PJ, HERTZER NR, BEVEN EF, et al. Surgical management of infected abdominal aortic grafts: review of a 25 year experience.J Vasc Surg 1986;3:725–731.
QUINONES-BALDRICH WJ, HERNANDEZ JJ, MOORE WS. Long term results following surgical management of aortic graft infection.Arch Surg 1991;126:507–511.
YEAGER RA, McCONNELL DB, SASAKI TM, et al. Aortic and peripheral prosthetic graft infection differential management and causes of mortality.Am J Surg 1985;150:36–43.
SCHMITT DD, SEABROOK GR, BANDYK DF. Graft excision and extra-anatomic reconstruction. The treatment of choice for the septic aortic prosthesis.J Cardiovasc Surg 1990;31:327–332.
REILLY LM, ALTMAN H, LUSBY RJ, et al. Late results following surgical management of vascular graft infection.J Vasc Surg 1984;1:36–44.
DAUGHERTY M, SHEARER GR, ERNST CB. Primary aortoduodenal fistula. Extra-anatomic vascular reconstruction not required for successful management.Surgery 1979;86:399–401.
HOLLIER L. In discussion: TROUT HH, KOZLOFF L, GIORDANO JM. Priority of revascularization in patients with graft enteric fistulas, infected arteries, or infected arterial prostheses.Ann Surg 1984;199:669–683.
BAHNINI A, KOSKAS F, MARTIN-MONDIERE C, et al. Traitement des infections aortiques post-opératoires par allogreffe artérielle in situ: résultats précoces chez onze malades.Ann Chir Vasc In press 1992.
WALKER WE, COOLEY DA, DUNCAN JM, et al. The management of aorto-duodenal fistula by in situ replacement of the infected abdominal aortic graft.Ann Surg 1987;205:727–732.
JACOBS MJHM, REUL GJ, GREGORIC I, et al. In situ replacement and extra-anatomic bypass for the treatment of infected abdominal aortic grafts.Eur J Vasc Surg 1991;5:83–86.
BANDYK DF, BERGAMINI TM, KINNEY EV, et al. In situ replacement of vascular prosthesis infected by bacterial biofilms.J Vasc Surg 1991;13:575–583.
TROUT HH, KOZLOFF L, GIORDANO JM. Priority of revascularization in patients with graft enteric fistulas, infected arteries, or infected arterial prostheses.Ann Surg 1984;199:669–683.
DU TOIT DF, MARITZ J, KLOMPJE J, et al. Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm associated with an aorto-enteric fistula.S Afr Med J 1983;64:216–217.
PICCONE AL, GREEN RM, RICOTTA JR, et al. Spinal cord ischemia following operations on the abdominal aorta.J Vasc Surg 1986;3:94–103.
MACBETH GA, RUBIN JR, MCINTYRE KE, et al. The relevance of arterial wall microbiology to the treatment of prosthetic graft infections: graft infection vs. arterial infection.J Vasc Surg 1984;1:750–756.
RUTHERFORD RB, PATT A, PEARCE WH. Extraanatomic bypass: a closer view.J Vasc Surg 1987;5:437–446.
ASCER E, VEITH FJ, GUPTA SK, et al. Comparison of axillounifemoral and axillobifemoral bypass operations.Surgery 1985;97:169–174.
TRICOT JF, KIEFFER E, MARAVAL M, et al. Pontages axillo-fémoraux. Technique. Complications. Résultats. (92 patients)J Chir (Paris) 1978;115:329–336.
GOEAU-BRISSONNIERE O, LEPORT C, GUIDOIN R, et al. Experimental colonization of a PTFE vascular graft with staphylococcus aureus: a quantitative and morphologic study.J Vasc Surg 1987;5:743–748.
BANDYK DF, THIELE BL, RADKE HM. Upper-extremity emboli secondary to axillofemoral graft thrombosis.Arch Surg 1981;116:393–395.
DIMARIA G, REY Cl, GALLON JP. Les complications au membre supérieur des pontages axillo-fémoraux.Chirurgie 1984;110:546–551.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Additional information
the French University Association for Research in Surgery, Paris, France: Bernard Andréassian, MD, François Bacourt, MD, Xavier Barral, MD, A. Barret, MD, Jean-Pierre Becquemin, MD, Alain Branchereau, MD, R. Brenot, MD, Jean-Michel Chevalier, MD, M. David, MD, J.P. Dereume, MD, Jean-Michel Fichelle, MD, G. Fievé, MD, C. Gautier, MD, H. Giudicelli, MD, Bernard Habozit, MD, Edouard Kieffer, MD, P. Lagneau, MD, J.L. Magne, MD, Dominique Maiza, MD, H. Mary, MD, Philippe Piquet, MD, J.P. Ribal, MD, J.M. Serisé, MD, C. Stankowiak, MD, J. Testard, MD, J. Watelet, MD.
About this article
Cite this article
Bacourt, F., Koskas, F. & the French University Association for Research in Surgery. Axillobifemoral bypass and aortic exclusion for vascular septic lesions: A multicenter retrospective study of 98 cases. Annals of Vascular Surgery 6, 119–126 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02042731
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02042731