Abstract
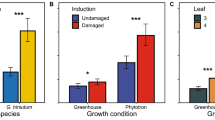
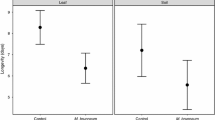
Cotton,Gossypium hirsutum L., has been shown to exhibit systemic induced resistance to arthropods under certain conditions. We conducted experiments to determine the effects of previous feeding ofSpodoptera exigua Hübner andSpodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) larvae on feeding behavior, growth, and survival of larvae subsequently feeding on cotton. In one feeding choice test,S. exigua larvae preferred young leaves from undamaged control plants to undamaged young leaves from a previously damaged plant. Feeding deterrence was noticeable after only 6 hr of initial feeding damage by larvae, and there was almost complete deterrence after 30 and 54 hr of continuous feeding. In a second feeding choice test,S. littoralis larvae fed more on mature leaves from undamaged control plants than on undamaged mature leaves from previously damaged plants. In no-choice tests, third instars ofS. littoralis fed undamaged young leaves from damaged plants did not gain weight and died by the seventh day, whereas larvae fed young leaves from undamaged control plants gained weight and pupated within 11 days. Sixth instars ofS. littoralis fed either old damaged leaves, old undamaged leaves, or young undamaged leaves all from previously damaged plants gained weight slowly and took more than 12 days to pupate, whereas larvae fed young leaves from undamaged plants gained weight rapidly and pupated within five days of the beginning of the experiment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin, I. T. 1991. Damaged-induced alkaloids in wild tobacco, pp. 47–70,in D. W. Tallamy and M. J. Raupp (eds.). Phytochemical Induction by Herbivores, Wiley & Sons, New York.
Benedict, J. H., andChang, J. F. 1991. Bacterially induced changes in the cotton plant-boll weevil paradigm, pp. 379–410,in D. W. Tallamy and M. J. Raupp (eds.). Phytochemical Induction by Herbivores. Wiley & Sons, New York.
Croxford, A. C., Edwards, P. J., andWratten, S. D. 1989. Temporal and spatial variation in palatability of soybean and cotton leaves following wounding.Oecologia 79:520–525.
Edwards, P. J., Wratten, S. D., andCox, H. 1985. Wound-induced changes in the acceptability of tomato to larvae ofSpodoptera littoralis: A laboratory bioassay.Ecol. Entomol. 10:155–158.
Feeny, P. 1977. Plant apparency and chemical defense.Recent Adv. Phytochem. 10:1–40.
Fowler, S. V., andLawton, J. H. 1985. Rapidly induced defenses and talking trees: the devil's advocate position.Am. Nat. 126:181–195.
Green, T. R., andRyan, C. A. 1972. Wound-induced proteinase inhibitor in plant leaves: Possible defense mechanism against insects.Science 175:776–777.
Harrison, S., andKarban, R. 1986. Behavioural response of spider mites (Tetranychus urticae) to induced resistance of cotton plants.Ecol. Entomol. 11:181–188.
Hedin, P. A., Jenkins, J. N., Collum, D. H., White, W. H., andParrott, W. L. 1983. Multiple factors in cotton contributing to resistance to the tobacco budworm,Heliothis virescens F., pp. 347–365,in P. A. Hedin (ed.). Plant Resistance to Insects. ACS Symposium Series 208, American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C.
Hedin, P. A., Parrott, W. L., andJenkins, J. N. 1992. Relationships of glands, cotton square terpenoid aldehydes, and other allelochemicals to larval growth ofHeliothis virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).J. Econ. Entomol. 85:359–364.
Hinks, C. F., andByers, J. R. 1976. Biosystematics of the genusEuxoa (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). V. Rearing procedures and life cycles of 36 species.Can. Entomol. 108:1345–1357.
Karban, R. 1987. Environmental conditions affecting the strength of induced resistance against mites in cotton.Oecologia 73:414–419.
Karban, R. 1988. Resistance to beet armyworms (Spodoptera exigua) induced by exposure to spider mites (Tetranychus turkestani) in cotton.Midl. Nat. 119:77–82.
Karban, R. 1991a. Induced resistance ofGossypium australe against its most abundant folivore,Buccalatrix gossypii.Aust. J. Ecol. 16:501–506.
Karban, R. 1991b. Inducible resistance in agricultural systems, pp. 402–429,in D. W. Tallamy and M. J. Raupp (eds.). Phytochemical Induction by Herbivores. Wiley & Sons, New York.
Karban, R., andCarey, J. R. 1984. Induced resistance of cotton seedlings to mites.Science 225:53–54.
Karban, R., andMyers, J. H. 1989. Induced plant responses to herbivory.Annu. Rev. Entomol. 20:331–348.
King, E. G., andLeppla, N. C. 1984. Advances and Challenges in Insect Rearing. Agriculture Research Service, USDA, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C.
Kogan, M., andPaxton, J. 1983. Natural inducers of plant resistance to insects, pp. 153–171,in P. A. Hedin (ed.). Plant Resistance to Insects. ACS Symposium Series 208, American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C.
Lin, H., andKogan, M. 1990. Influence of induced resistance in soybean on development and nutrition of the soybean looper and the Mexican bean beetle.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 55:131–138.
Niles, G. A. 1980. Breeding cotton for resistance to insect pests, pp. 337–370,in F. G. Maxwell and P. R. Jennings (eds.). Breeding Plants Resistant to Insects, Wiley & Sons, New York.
Schultz, J. C. 1993. Signaling in plant responses to herbivory, pp. 93–101.in J. C. Schultz and I. Raskin (eds.). Plant Signals in Interactions with Other Organisms. Current Topics in Plant Physiology: An American Society of Plant Physiologists Series, Vol. 11, Rockville, Maryland.
Stipanovic, R. D., Williams, H. J., andSmith, L. A. 1986. Cotton terpenoid inhibition ofHeliothis virescens development, pp. 79–94,in M. B. Green and P. A. Hedin (eds.). Natural Resistance of Plants to Pests: Roles of Allelochemicals. ACS Symposium Series 296. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
Tallamy, D. W., andRaupp, M. J. (eds.). 1991. Phytochemical Induction by Herbivores. Wiley & Sons, New York.
Turlings, T. C. J., Tumlinson, J. H., andLewis, W. J. 1990. Exploitation of herbivore-induced plant odors by host-seeking parasitic wasps.Science 250:1251–1253.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alborn, H.T., Röse, U.S.R. & McAuslane, H.J. Systemic induction of feeding deterrents in cotton plants by feeding ofSpodoptera SPP. Larvae. J Chem Ecol 22, 919–932 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02029945
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02029945