Abstract
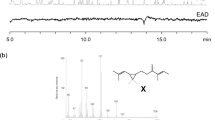
The principal behaviorally active volatile component (ca. 90% +) of the sex pheromone glands ofLutzomyia longipalpis from Jacobina. Brazil, has been isolated and characterized as a novel homosesquiterpene with the structure 3-methyl-α-himachalene (C16H26). A minor component (ca. 10%) of the gland extract has also been identified as the sesquiterpeneα-himachalene (C15H24). This work confirms that there are at least 3 members of theL. longipalpis species complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, W., Chan, Y., Cremer, D., Gauss, J., Scheutzow, D., andSchindler, M. 1987. Spectral and chemical properties of dimethyldioxirane as determined by experiment and ab initio calculations.J. Org. Chem. 52:2800–2803.
Boland, W., andGäbler, A. 1989. Biosynthesis of homoterpenes in higher plants.Helv. Chim. Acta. 72:247–253.
Donath, J., andBoland, W. 1994. Biosynthesis of acyclic homoterpenes in higher plants parallels steroid hormone metabolism.J. Plant Physiol. 143:473–478.
Dougherty, M. J., Guerin, P., andWard, R. D. 1995. Identification of oviposition attractants for the sandflyLutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera: Psychodidae) in volatiles of faeces from vertebrates.Physiol. Entomol. 20:23–32.
Dugdale, J. S. 1990. Reassessment ofCtenopseustis Meyrick andPlanotortrix Dugdale with descriptions of two new genera (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae).N.Z. J. Zool. 17:437–465.
Hamilton, J. G. C., andWard, R. D. 1991. Gas chromatographic analysis ofLutzomyia longipalpis tergal pheromone gland extract.Parassitologia 33 (Suppl 1):283–289.
Hamilton, J. G. C., andWard, R. D. 1994. Chemical analysis of a putative sex pheromone fromLutzomyia pessoai (Diptera:Psychodidae).Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 88(4):405–412.
Hamilton, J. G. C., Doughtery, M. J., andWard, R. D. 1994. Isolation and identification of sex pheromone activity in components of tergal gland extract ofLutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera:Psychodidae) from North East Brazil.J. Chem. Ecol. 20(1):141–151.
Hamilton, J. G. C., Dawson, G. W., andPickett, J. A. 1996a. 9-Methylgermacrene-B: proposed structure for the novel homosesquiterpene sex pheromone ofLutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera:Psychodidae) from Lapinha, Brazil.J. Chem. Ecol. 22(8):1477–1492.
Hamilton, J. G. C., Ward, R. D., Doughtery, M. J., Ponce, C., Ponce, E., Noyes, H., andZeledon, R. 1996b. Comparison of terpene components in extracts ofLutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera: Psychodidae) from areas of visceral and atypical cutaneous leishmaniasis in Honduras and Costa Rica.Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 90(5):533–541.
Krishna Rao, G. S., Dev, S., andGuha, P. C. 1952. Studies in sesquiterpenes. Part XII. Sesquiterpenes of the essential oil from the wood of the Himalayan deodar.J. Indian Chem. Soc. 29(10):721–730.
Lane, R. P., Phillips, A., Molyneux, D. H., Procter, G., andWard, R. D. 1985. Chemical analysis of the abdominal glands of two forms ofLutzomyia longipalpis: Site of a possible sex pheromone?Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 79:225–229.
Lanzaro, G. C., Ostovska, K., Herrero, M. V., Lawyer, P. G., andWarburg, A. 1993.Lutzomyia longipalpis is a species complex: Genetic divergence and interspecific hybrid sterility among three populations.Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 48(6):839–847.
Löfstedt, C., Hansson, B. S., Toth, M., Szöcs, G., Buda, V., Bengtsson, M., Ryrholm, N., Svensson, M., andPriesner, E. 1994. Pheromone differences between sibling taxaDiachrysia chrysitis (Linnaeous, 1758) andD. tutti (Kostrowicki, 1961) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).J. Chem. Ecol. 20(1):91–109.
Morton, I. E., andWard, R. D. 1989. Laboratory response of femaleLutzomyia longipalpis sandflies to a host and male pheromone source over distance.Med. Vet. Entomol. 3:219–223.
NIST 1990. Standard Reference Data Base (Version 3.01). Office of the Standard Reference Data Base. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, Maryland.
Phillips, A., Ward, R. D., Ryan, L., Molyneux, D. H., Lainson, R., andShaw, J. J. 1986. Chemical analysis of compounds extracted from the “tergal” spots ofLutzomyia longipalpis from Brazil.Acta Trop. 43:271–276.
Roelofs, W. L., andCarde, R. T. 1974. Sex pheromones in the reproductive isolation of lepidopterous species, pp. 96–114,in H. C. Birch (ed.). North Holland Publishing, Amsterdam.
Roelofs, W. L., andComeau, A. 1969. Sex pheromone specificity: Taxonomic and evolutionary aspects in Lepidoptera.Science 165:398–400.
Tabacchi, R., Garnero, J., andBuil, P. 1974. Isolement et identification des hydrocarbures sesquiterpéniques de l'huile essentielle de graines d'Anis.Helv. Chim. Acta 57(3):849–851.
Ward, R. D., Ribeiro, A. L., Ready, P. D., andMurtagh, A. 1983. Reproductive isolation between different forms ofLutzomyia longipalpis (Lutz and Neiva), (Diptera: Psychodidae), the vector ofLeishmania donovani chagasi Cunha and Chagas and its significance to Kalaazar distribution in South America.Mem. Inst. Os. Cruz. 78:269–280.
Ward, R. D., Phillips, A., Burnet, B., andMarcondes, C. B. 1988. TheLutzomyia longipalpis complex: reproduction and distribution, pp. 257–269, M. W. Service (ed.)in Biosystematics of Haematophagous Insects. Systematics Association Special Volume 37. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Ward, R. D., Morton, I. E., Lancaster, V., Smith, P., andSwift, A. 1989. Bioassays as an indicator of pheromone communication inLutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera: Psychodidae). NATO ASI Series on Leishmaniasis, Zakinthos, Greece, No. 163. Springer, New York, pp. 239–247.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamilton, J.G.C., Dawson, G.W. & Pickett, J.A. 3-Methyl-α-himachalene: Proposed structure for novel homosesquiterpene sex pheromone ofLutzomyia longipalpis (diptera: Psychodidae) from Jacobina, Brazil. J Chem Ecol 22, 2331–2340 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02029550
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02029550