Summary
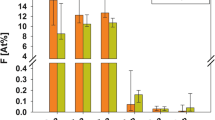
Sixteen 58-day-old male rats of Wistar strain, with a mean body weight of 179 g, were divided into two equal groups. Each group of eight animals was maintained for 70 days on drinking water, ad lib., containing no fluorine (control group) and 100 ppm of fluorine (experimental group). All specimens examined were obtained from the incisal portions of the incisors. The following types of enamel specimens were prepared for scanning electron microscopy: (1) acid-etched specimens; (2) acid-etched specimens followed by low temperature microincineration; and (3) fractured specimens. The enamel formed during high fluoride exposure showed marked hypocalcification, that is, the crystallite density in the prism core and interprismatic region was lower than that of control animals. The organic substances appeared to increase in these regions. These changes were prominent in the outer and middle enamel layers. Such changes following fluoride administration appear to indicate an inhibition of enamel maturation, that is, an inhibition of the mineral deposition and/or an inhibition of organic matrix withdrawal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth, N.J.: Mottled teeth. Brit. Dent. J.55, 233–250 (1933)
Allan, J.H.: Observations on the development of dental enamel in acute experimental fluorosis. In: Advances in fluorine research and dental caries prevention (J.L. Hardwick, J.P. Dustin, H.R. Held, eds.), Vol. 1, pp. 41–52. Oxford, London, New York, and Paris: Pergamon Press 1963
Bhussry, B.R.: Chemical and physical studies of enamel from human teeth. IV. Density and nitrogen content of mottled enamel. J. Dent. Res.38, 369–373 (1959)
Bowes, J.H., Murray, M.M.: A chemical study of “Mottled teeth” from Maldon, Essex. Br. Dent. J.60, 556–562 (1936)
Boyde, A.: Electron microscopic observations relating to the nature and development of prism decussation in mammalian dental enamel. Bull. Group. Int. Rech. Sc. Stomat.12, 151–207 (1969)
Brudevold, F.: The role of fluorides in tooth chemistry and in the prevention of dental caries. In: Handbook of experimental pharmacology (O. Eichler, A. Farah, H. Herken, A.D. Welch, eds.), Vol. XX/1, pp. 173–230. Berlin, Heidelberg, and New York: Springer 1966
Darling, A.I., Brooks, A.W.: Some observations on the mottled enamel of fluorosis. J. Dent. Res.38, 1226–1227 (1959)
Eanes, E.D., Zipkin, I., Harper, R.A., Posner, A.S.: Small-angle X-ray diffraction analysis of the effect of fluoride on human bone apatite. Arch. Oral Biol.10, 161–173 (1965)
Eastoe, J.E.: The changing nature of developing dental enamel. Br. Dent. J.121, 451–454 (1966)
Fejerskov, O., Johnson, N.W., Silverstone, L.M.: The ultrastructure of fluorosed human dental enamel. Scand. J. Dent. Res.82, 357–372 (1974)
Fejerskov, O., Silverstone, L.M., Melsen, B., Møller, I.J.: Histological features of fluorosed human dental enamel. Caries Res.9, 190–210 (1975)
Frazier, P.D., Little, M.F., Casciani, F.S.: X-ray diffraction analysis of human enamel containing different amount of fluoride. Arch. Oral Biol.12, 35–42 (1967)
Frazier, P.D., Brown, F.J., Rose, L.S., Fowler, B.O.: Radiofrequency oxygen excitation apparatus for low-temperature ashing. J. Dent. Res.46, 1098–1101 (1967)
Gleit, C.E., Holland, W.D.: Use of electrically excited oxygen for the low temperature decomposition of organic substances. Anal. Chem.34, 1454–1457 (1962)
Gustafson, A.G.: The histology of fluorosed teeth. Arch. Oral Biol.4, 67–69 (1961)
Hasegawa, K.: Studies on the formative disturbances of the enamel in experimental chronic fluorosis. Jpn. J. Oral Biol.13, 239–254 (1971)
Ijuin, N.: Effects of the fluoride on rat incisal enamel organ in acute experimental fluorosis. Jpn. J. Oral Biol.13, 39–61 (1971)
Ishida, T.: Observations on the development of rat incisal enamel in acute experimental fluorosis. Jpn. J. Oral Biol.12, 88–107 (1970)
Ishiki, T.: The histologic changes in the tooth and the salivary gland of the rat in the experimental fluorosis. J. Jpn. Stomatol. Soc.24, 1–18 (1957)
Johnson, N.W., Poole, D.F.G., Tyler, J.E.: Factors affecting the differential dissolution of human enamel in acid and EDTA. A scanning electron microscope study. Arch. Oral Biol.16, 385–396 (1971)
Kato, Y., Ogura, H.: Low-temperature ashing of bovine dentine. Calcif. Tissue Res.18, 141–148 (1975)
Kruger, B.J.: Ultrastructural changes in ameloblasts from fluoride treated rats. Arch. Oral Biol.13, 969–977 (1968)
Kruger, B.J.: The effect of different levels of fluoride on the ultrastructure of ameloblasts in the rat. Arch. Oral Biol.15, 109–114 (1970)
Kruger, B.J.: Scanning electron microscopy of sections of fluorosed rat enamel. J. Dent. Res.50, 1685 (1971)
Montelius, G., McIntosh, J.F., Ma, Y.C.: Chemical investigations of mottled enamel and brown stain. J. Dent. Res.13, 73–79 (1933)
Motoyama, S.: On the interprismatic substance of the human enamel. A scanning electron microscopic study. Jpn. J. Oral Biol.15, 31–50 (1973)
Newbrun, E.: Studies on the physical properties of fluorosed enamel — II. Microhardness. Arch. Oral Biol.2, 21–27 (1960)
Newbrun, E., Brudevold, F.: Studies on the physical properties of fluorosed enamel — I. Microradiographic studies. Arch. Oral Biol.2, 15–20 (1960)
Otake, T.: Pathohistological and histochemical studies on the formative disturbances of the enamel in experimental fluorosis. Odontology48, 1–54 (1960)
Pindborg, J.J., Weinmann, J.P.: Morphologic and functional correlations in the enamel organ of the rat incisor during amelogenesis. Acta Anat. (Basel)36, 367–381 (1959)
Poole, D.F.G., Johnson, N.W.: The effects of different demineralising agents on human enamel surfaces studied by scanning electron microscopy. Arch. Oral Biol.12, 1621–1634 (1967)
Poole, D.F.G., Tolidis, T.: Electron microscopy of fluorosed enamel from human permanent teeth. Yrbk. Sch. Dent. Univ. Thesaloniki, pp. 75–82 (1973)
Posner, A.S., Eanes, E.D., Zipkin, I.: X-ray diffraction of the effect of fluoride on bone. In: Proc. second European symposium on calcified tissues (L.J. Richelle, M.J. Dallemagne, eds.), pp. 79–88. Liège: Universitè de Liège 1965
Schour, I., Smith, M.C.: Mottled teeth: An experimental and histologic analysis. J. A. Dent. Assoc.22, 796–813 (1935)
Schraer, H., Posner, A.S., Schraer, R., Zipkin, I.: Effect of fluoride on bone crystallinity in the growing rat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta64, 565–567 (1962)
Shinoda, H.: Effect of long-term administration of fluoride on physico-chemical properties of the rat incisor enamel. Calcif. Tissue Res.18, 91–100 (1975)
Silness, J., Gustavsen, F.: Some observations on the fine structure on fluorosed dental enamel. Acta Odontol. Scand.28, 701–720 (1970)
Simmelink, J.W., Nygaard, V.K., Scott, D.B.: Theory for the sequence of human and rat enamel dissolution by acid and by EDTA: A correlated scanning and transmission electron microscope study. Arch. Oral Biol.19, 183–197 (1974)
Smith, M.C., Lantz, E., Smith, H.V.: The cause of mottled enamel. J. Dent. Res.12, 149–159 (1932)
Suga, S.: Histochemical observation of proteolytic enzyme activity in the developing dental hard tissues of the rat. Arch. Oral Biol.15, 555–558 (1970)
Tamaki, S.: Effects of fluoride on crystallinity of synthetic and biological apatites. J. Osaka Univ. Dent. Soc.12, 95–110 (1967)
Thomas, R.S., Greenawalt, J.W.: Microincienration, electron microscopy, and electron diffraction of calcium phosphateloaded mitochondria. J. Cell Biol.39, 55–76 (1968)
Walton, R.E., Eisenmann, D.R.: Ultrastructural examination of various stages of amelogenesis in the rat following parenteral fluoride administration. Arch. Oral Biol.19, 171–182 (1974)
Yaeger, J.A.: The effect of high fluoride diet on developing enamel and dentine in the incisors of rats. Am. J. Anat.118, 665–684 (1966)
Zipkin, I., Posner, A.S., Eanes, E.C.: The effect of fluoride on the X-ray diffraction pattern of the aptite of human bone. Biochim. Biophys. Acta59, 255–258 (1962)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinoda, H., Ogura, H. Scanning electron microscopical study on the fluorosis of enamel in rats. Calc. Tis Res. 25, 75–83 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02010754
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02010754