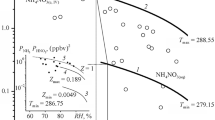
Summary
Following a recent hypothesis on the role of activated sodium chloride particles as potential nuclei of atmospheric precipitation, further analysis is made of average annual data due toC. Junge on the chemical composition of rainwater salts, and correlation of some parameters with the total amount of rainfall is attempted. It is found that the results obtained are in agreement with the proposed role of activated sodium chloride as a nucleus of a substantial part of the atmospheric precipitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papée H. M.:Activated salt surfaces in ice nucleation and growth and the formation of droplets. J. Meteor., 16, 217 (1959).
Papée H. M.:On the chemical composition of atmospheric aerosols. Part. I:Some stoichiometric aspects of the problem. Geofisica pura e applicata. This Volume, pp. 191–203.
Papée H. M.:Microcalorimetry of adsorption of water vapor on sodium chloride which has been treated in electric discharges. J. Meteor. 16, 295 (1959).
Szaynok A.:Measurements of electric charge created when NaClis dispersed. Zeszyty Nauk. Polit. Wrocl. 4. Chem. I, 47 (1954).
Szaynok A.:Creation of electric charge in powdered NaClcrystals as affected by lattice defects. Zeszyty Nauk Polit. Wrocl. 25. Chem., 5, 2 (1958).
Simon H. &Suhrmann R.:Der Lichtelektrische Effekt und seine Anwendungen. Springer Verlag, Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg (1958).
Woodcock A. H.:Atmospheric salt in nuclei and in raindrops. In: «Artificial Stimulation of Rain». Pergamon Press, N. York, 204 (1957).
Papée H. M. & Smith A. C.:On the Chemical composition of atmospheric aerosols, Part. II:Trends between some chemical components of rainwater, and physical variables over the United States. Geofisica pura e applicata, This Volume, pp. 204–215.
Junge C. E.:The concentration of chloride, sodium, potassium, calcium and sulfate in rainwater over the United States. J. Meteor., 15, 417 (1958).
Woodcock A. H.:Atmospheric salt particles and raindrops. J. Meteor. 9, 200 (1952).
Schaefer V. J.:The formation of ice crystals in the laboratory and in the atmosphere. Chemical Reviews, 44, 291 (1949).
Braham R. R. &Sievers R. J.:Overseeding of cumulus clouds. In: «Artificial Stimulation of Rain». Pergamon Press. N. Y. (1957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papée, H.M., Smith, A.C. On the chemical composition of atmospheric aerosols — Part III: Trends of the total annual precipitation with respect to the chemical content of rainwater over the United States. Geofisica Pura e Applicata 44, 216–223 (1959). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01997649
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01997649