Summary
The cellular distribution (apicalvs. basolateral) of parathyroid hormone (PTH) signal transduction systems in opossum kidney (OK) cells was evaluated by measuring the action of PTH on apically located transport processes (Na/Pi cotransport and Na/H exchange) and on the generation of intracellular messengers (cAMP and IP3).
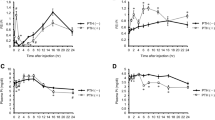
PTH application led to immediate inhibition of Na/H-exchange without a difference in dose/response relationships between apical and basolateral cell-surface hormone addition (halfmaximal inhibition at ≈5×10−10 m). PTH required 2–3 hr for maximal inhibition of Na/Pi cotransport with a half-maximal inhibition occurring at ≈×10−12 m for apical application. PTH addition to either side of the monolayer produced a dose-dependent production of both cAMP and IP3. Half-maximal activation of IP3 was at about 7×10−12 m PTH and displayed no differences between apical and basolateral hormone addition, while cAMP was produced with a half maximal concentration of 7×10−9 m for apical PTH application and 10−9 m for basolateral administration.
The PTH analog [nle8.18, tyr34]PTH(3-34), (nlePTH), produced partial inhibition of Na/Pi cotransport (agonism) with no difference between apical and basolateral application. When applied as a PTH antagonist, nlePTH displayed dose-dependent antagonism of PTH inhibition of Na/Pi cotransport on the apical surface, failing to have an effect on the basolateral surface. Independent of addition to the apical or basolateral cell surface, nlePTH had only weak stimulatory effect on production of cAMP, whereas high levels of IP3 could be measured after addition of this PTH analog to either cell surface. Also an antagonistic action of nlePTH on PTH-dependent generation of the internal messengers, cAMP and IP3, was observed; at the apical and basolateral cell surface nlePTH reduced PTH-dependent generation of cAMP, while PTH-dependent generation of IP3 was only reduced by nlePTH at the apical surface.
Pertussis toxin (PT) preincubation produced an attenuation of both PTH-dependent inhibition of Na/Pi cotransport and IP3 generation while producing an enhancement of PTH-dependent cAMP generation; these effects displayed no cell surface polarity, suggesting that PTH action through either adenylate cyclase or phospholipase C was transduced through similar sets of G-proteins at each cell surface.
It is concluded that apparent receptor activities with high and low affinity for PTH exist on both cell surfaces; those with apparent high affinity seem to be coupled preferentially to phospholipase C and those with apparent low affinity to adenylate cyclase. The differences in apparent affinity of receptor events coupled to adenylate cyclase and the differences in PTH/nlePTH interaction on the two cell surfaces are suggestive of the existence of differences in apparent PTH-receptor activities on the two cell surfaces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpern, R.J. 1990. Cell mechanisms of proximal tubule acidification.Physiol. Rev. 70:79–114
Bredt, D.S., Mourey, R.J., Snyder, S.H. 1989. A simple, sensitive and specific radioreceptor assay for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in biological tissues.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 159:976–982
Brown, B.L., Ekins, R.P., Albano, J.D.M. 1972., Saturation assay for cAMP using endogenous binding protein.Adv. Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 2:25–40
Caulfield, M.P., Rosenblatt, M. 1990. Parathyroid hormone-receptor interactions.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1:164–168
Cole, J.A., Carnes, D.L., Forte, L.R., Eber, S., Poelling, R.E., Thorne, P.K. 1989. Structure-activity relationship of parathyroid hormone analogs in the opossum kidney cell line.J. Bone Miner. Res. 4:723–730
Cole, J.A., Eber, S.L., Poelling, R.E., Thorne, P.K., Forte, L.R. 1987. A dual mechanism for regulation of kidney phosphate transport by parathyroid hormone.Am. J. Physiol. 253:E221-E227
Cole, J.A., Forte, L.R., Eber, S., Thorne, P.K., Poelling, R.E. 1988. Regulation of sodium-dependent phosphate transport by parathyroid hormone in opossum kidney cells: Adenosine 3′, 5′-monophosphate-dependent and-independent mechanisms.Endocrinology 122:2981–2989
Dean, N.M., Beaven, M.A. 1989. Methods for the analysis of inositol phosphates.Anal Biochem. 183:199–209
Dunlay, R., Hruska, K. 1990. PTH receptor coupling to phospholipase C is an alternate pathway of signal transduction in bone and kidney.Am. J. Physiol. 258:F223-F231
Garcia, J.C., McConkey, C.L., Stokes, T.J., Betts, C.R., Martin, K.J. 1989. Influence of pertussis toxin on parathyroid hormone stimulated cyclic AMP production and phosphate transport in opossum kidney cells.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 114:691–696
Haggerty, J.G., Agarwal, N., Reilly, R.F., Adelberg, E.A., Slayman, C.W. 1990. Pharmacologically different Na/H antiporters on the apical and basolateral surfaces of cultured kidney cells (LLC-PK1)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:6797–6801
Helmle-Kolb, C., Montrose, M.H., Murer, H. 1990a. Parathyroid hormone regulation of Na+/H+ exchange in opossum kidney cells: Polarity and mechanisms.Pfluegers Arch. 416:615–623
Helmle-Kolb, C., Strange, G., Montrose, M.H., Murer, H. 1990b. Regulation of Na/H-exchange in opossum kidney cells by parathyroid hormone, cAMP and phorbol esters.Pfluegers Arch. 415:461–470
Koyama, H.C., Goodpasture, C., Miller, M.M., Teplitz, R.L., Riggs, A.D. 1978. Establishment and characterization of a cell line from the American opossum (Didelphys virginia).In Vitro 14:239–246
Liu, F.Y., Cogan, M.G. 1988. Angiotensin II stimulation of hydrogen ion secretion in the rat proximal tubule. Modes of action, mechanism and kinetics.J. Clin. Invest. 82:601–607
Malmström, K., Murer, H. 1986. Parathyroid hormone inhibits phosphate transport in OK-cells but not in LLC-PK1 and JTC-12.P3-cells.Am. J. Physiol. 251:C23-C31
Malmström, K., Stange, G., Murer, H. 1988. Intracellular cascades in the parathyroid-hormone-dependent regulation of Na/phosphate cotransport in OK cells.Biochem. J. 251:207–213
Miyauchi, A., Dobre, V., Rickmeyer, M., Cole, J., Forte, L.R., Hruska, K.A. 1990. Stimulation of transient elevations of Ca2+ is related to inhibition of Pi-transport in OK-cells.Am. J. Physiol. 259:F485-F493
Muff, R., Caulfield, M.P., Fischer, J.A. 1990. Dissociation of cAMP accumulation and phosphate uptake in opossum kidney (OK) cells with parathyroid hormone (PTH) and, parathyroid hormone related protein PTHrP).Peptides 11:945–949
Murer, H., Werner, A., Reshkin, S., Wuarin, F., Biber, J. 1991. Cellular mechanisms in proximal tubular reabsorption of inorganic phosphate.Am. J. Physiol. 260:C885-C889
Nibbering, P.H., Zomerdijk, T.P.L., van Haastert, P.J.M., van Furth, R. 1990. A competition binding assay for determination of the inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate content of human leucocytes.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 170:755–762
Nissenson, R.A., Klein, R.F. 1987. Parathyroid hormone receptors.In: Peptide Hormone Receptors. M.Y. Kalimi and J.R. Hubbard, editors. pp. 481–517. de Gruyter, Berlin
Quamme, G., Pfeilschifter, J., Murer, H. 1989. Parathyroid hormone inhibition of Na/phosphate cotransport in OK cells: Generation of second messengers in the regulatory cascade.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 158:951–957
Reshkin, S.J., Forgo, J., Murer, H. 1990a. Functional asymmetry of phosphate transport and its regulation in opossum kidney cells: Phosphate transport.Pfluegers Arch. 416:554–560
Reshkin, S.J., Forgo, J., Murer, H. 1990b. Functional asymmetry of phosphate transport and its regulation in opossum kidney cells: Parathyroid hormone inhibition.Pfluegers Arch. 416:624–631
Reshkin, S.J., Murer, H. 1991. Parathyroid hormone, regulation in OK-cells:In situ protein phosphorylation reactions involving PKA, PKC and GTP-binding protein.Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 1:143–159
Rizzoli, R., Bonjour, J.-P. 1988. Effect of pertussis toxin on parathyroid hormone-stimulated cyclic AMP production in cultured kidney cells.J. Bone Miner. Res. 3:605–611
Segal, J.H., Pollock, J.S. 1990. Transfection-mediated expression of cAMP-resistant phenotype in the opossum (OK) cell line prevents parathyroid hormone-induced inhibition of Na-phosphate cotransport.J. Clin. Invest. 86:1442–1450
Spiegel, A.M. 1990. Receptor-effector coupling by G-proteins: Implications for endocrinology.Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1:72–76
Teitelbaum, I., Strasheim, A., Berl, T. 1989. Adrenergic control of cAMP generation in rat inner medullary collecting tubule cells.Kidney Int. 35:647–653
Teitelbaum, I., Strasheim, A., Berl, T. 1990. Epidermal growth factor-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in cultured rat inner medullary collecting tubule cells.J. Clin. Invest. 85:1044–1050
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reshkin, S.J., Forgo, J. & Murer, H. Apical and basolateral effects of PTH in OK cells: Transport inhibition, messenger production, effects of pertussis toxin, and interaction with a PTH analog. J. Membrain Biol. 124, 227–237 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01994356
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01994356