Abstract
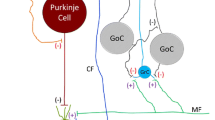
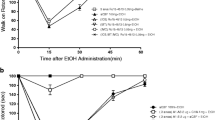
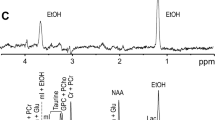
Chronic ethanol ingestion results in an “up-regulation” of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) subtype of glutamate receptor in mouse brain. This increase in receptors is associated with ethanol withdrawal seizures, which can be attenuated by NMDA receptor antagonists. Chronic exposure to ethanol (3 days) of rat cerebellar granule cells in primary culture also produces an increase in NMDA receptor number and function, which leads to enhanced susceptibility to glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. Antagonists acting at various sites on the NMDA receptor can block glutamate excitotoxicity in both control and ethanol-exposed cells. These results suggest the possibility of developing agents that will ameliorate ethanol withdrawal seizures as well as withdrawal-induced neuronal damage. In addition, acute (2 hr) or chronic (3 day) exposure of cerebellar granule cells to ganglioside GM1 protects control and ethanol-treated cells against glutamate neurotoxicity. However, while the acute GM1 treatment does not interfere with the initial response to glutamate (increase in intracellular Ca2+), this response is “down-regulated” after chronic ganglioside treatment. These findings suggest that the mechanism by which acute and chronic ganglioside treatments protect against glutamate neurotoxicity may differ. Furthermore, chronic ganglioside treatment during ethanol exposure has the potential to prevent the ethanol-induced up-regulation of NMDA receptors that underlies withdrawal seizures and increased susceptibility to excitotoxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballenger, J.C. and Post, R.M. (1978). Kindling as a model for alcohol withdrawal syndromes.Br. J. Psych. 133:1–14.
Becker, H.C. and Hale, R.L. (1993). Repeated episodes of ethanol withdrawal potentiate the severity of subsequent withdrawal seizures: an animal model of alcohol withdrawal “kindling”.Alcoholism: Clin. Exp. Res. 17:94–98.
Cadete-Leite, A., Brandao, F., Madeira, M.D., and Paula-Barbarosa, M.M. (1991). Effects of GM1 ganglioside upon neuronal degeneration during withdrawal from alcohol.Alcohol 8:417–423.
Charness, M.E. (1993). Brain lesions in alcoholics.Alcoholism: Clin. Exp. Res. 17:2–11.
Chen, L. and Huang, L.-Y.M. (1992). Protein kinase C reduces Mg2+ block of NMDA-receptor channels as a mechanism of modulation.Nature 356:521–523.
Choi, D.W. (1992). Excitotoxic cell death.J. Neurobiol. 23:1261–1276.
Collingridge, G.L. and Lester, R.A.J. (1989). Excitatory amino acid receptors in the vertebrate central nervous system.Pharmacol. Rev. 40:143–210.
Courtney, M.J. and Nicholls, D.G. (1992). Interactions between phospholipase C-coupled and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in cultured cerebellar granule cells: protein kinase C mediated inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate responses.J. Neurochem. 59:983–992.
Didier, M., Heaulme, M., Soubrié, P., Bockaert, J., and Pin, J.-P. (1990). Rapid, sensitive, and simple method for quantification of both neurotoxic and neurotrophic effects of NMDA on cultured cerebellar granule cells.J. Neurosci. Res. 27:25–35.
Dubinsky, J.M. and Rothman, S.M. (1991). Intracellular calcium concentrations during “chemical hypoxia” and excitotoxic neuronal injury.J. Neurosci. 11:2545–2551.
Favaron, M., Manev, H., Alho, H., Bertolino, M., Ferret, B., Guidotti, A., and Costa, E. (1988). Gangliosides prevent glutamate and kainate neurotoxicity in primary neuronal cultures of neonatal rat cerebellum and cortex.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:7351–7355.
Grant, K.A., Snell, L.D., Rogawski, M.I., Thurkauf, A., and Tabakoff, B. (1992). Comparison of the effects of the uncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist (±)-5-aminocarbonyl-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5,10-imine (ADCI) with its structural analogs dizocilpine (MK-801) and carbamazepine on ethanol withdrawal seizures.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 260:1017–1022.
Grant, K.A., Valverius, P., Hudspith, M., and Tabakoff, B. (1990). Ethanol withdrawal seizures and the NMDA receptor complex.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 176:289–296.
Gulya, K., Grant, K.A., Valverius, P., Hoffman, P.L., and Tabakoff, B. (1991). Brain regional specificity and time course of changes in the NMDA receptor-ionophore complex during ethanol withdrawal.Brain Res. 547:129–134.
Hartley, D.M., Kurth, M.C., Bjerkness, L., Weiss, J.H., and Choi, D.W. (1993). Glutamate receptor-induced45Ca2+ accumulation in cortical cell culture correlates with subsequent neuronal degeneration.J. Neurosci. 13:1993–2000.
Hoffman, P.L. (1995). The effects of alcohol on excitatory amino acid receptor function. In: H. Kranzler, (ed.),Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, Vol. 114, The Pharmacology of Alcohol Abuse. Springer, Heidleberg (in press).
Hoffman, P.L., Iorio, K.R., Snell, L.D., and Tabakoff, B. (1995). Attenuation of glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in chronically ethanol-exposed cerebellar granule cells by NMDA receptor antagonists and ganglioside GM1.Alcoholism: Clin. Exp. Res. (in press).
Iorio, K.R., Reinlib, L., Tabakoff, B., and Hoffman, P.L. (1992). Chronic exposure of cerebellar granule cells to ethanol results in increased NMDA receptor function.Mol. Pharmacol. 41:1142–1148.
Iorio, K.R., Tabakoff, B., and Hoffman, P.L. (1993). Glutamate-induced neurotoxicity is increased in cerebellar granule cells exposed chronically to ethanol.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 248:209–212.
Javitt, D.C. and Zukin, S.R. (1989). Biexponential kinetics of [3H]MK-801 binding: evidence for access to closed and open N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels.Mol. Pharmacol. 35:387–393.
Kutsuwada, T., Kashiwabuchi, N., Mori, H., Sakimura, K., Kushiya, E., Araki, K.,et al. (1992). Molecular diversity of the NMDA receptor channel.Nature 358:36–41.
Liljequist, S. (1991). The competitive NMDA receptor antagonist, CGP 39551, inhibits ethanol withdrawal seizures.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 192:197–198.
Michaels, R.L. and Rothman, S.M. (1990). Glutamate neurotoxicityin vitro: antagonist pharmacology and intracellular calcium concentrations.J. Neurosci. 10:283–292.
Momoi, T. (1986). Activation of protein kinase C by ganglioside GM3 in the presence of calcium and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 138:865–871.
Morrisett, R.A., Rezvani, A.H., Overstreet, D., Janowsky, D.S., Wilson, W.A., and Swartzwelder, H.A. (1990). MK-801 potently inhibits alcohol withdrawal seizures in rats.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 176:103–105.
Snell, L.D., Iorio, K.R., Tabakoff, B., and Hoffman, P.L. (1994). Protein kinase C activation attenuates N-methyl-D-aspartate induced increases in intracellular calcium in cerebellar granule cells.J. Neurochem. 62:1783–1789.
Vaccarino, F., Guidotti, A., and Costa, E. (1987). Ganglioside inhibition of glutamate-mediated protein kinase C translocation in primary cultures of cerebellar neurons.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:8707–8711.
Williams, K., Dichter, M.A., and Molinoff, P.B. (1992). Up-regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on cultured cortical neurons after exposure to antagonists.Mol. Pharmacol. 42:147–151.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffman, P.L. Glutamate receptors in alcohol withdrawal-induced neurotoxicity. Metab Brain Dis 10, 73–79 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01991784
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01991784