Abstract
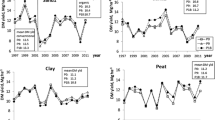
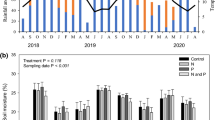
In order to propose consistent decision rules for fertilizer supply, a study was made on the effect of additions of N and P fertilizers and of their interaction on the above-ground dry matter yield of pastures during spring. The interaction between N and P could occur through nutrient acquisition or nutrient efficiency for growth. We therefore characterised the herbage N and P status (N and P index) from previously established critical curves of herbage mineral content according to above-ground dry matter. First we studied the effect of N and P addition on herbage nutrient status. Secondly, we expressed the above-ground dry matter as a function of the herbage nutrient status. This study consisted of four treatments applied to four permanent pastures which had a low phosphorus availability. The results showed a positive effect of P supply on the herbage nitrogen status, which may be due to an increase of organic matter mineralization or root growth. The P herbage status decreased only if N was supplied without P. The dry matter yield was positively related to the herbage nitrogen status, but a low P herbage status reduced the slope of the relationship. For the pastures studied, the indirect effect of P supply on above-ground dry matter, revealed by an increase in N index, was greater than its direct effect. This methodology allows us to distinguish the direct and indirect effects of N and P addition on herbage growth at field level. It could be used to propose consistent rules to manage jointly both N and P supplies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bélanger G, Gastal F and Lemaire, G (1992) Growth analysis of a tall fescue sward fertilized with different rates of nitrogen. Crop Sci, 32, 6, 1371–1376
Callot G, Chamayou, Maertens C and Salsac L (1982) Les interactions sol-racine. Incidence sur la nutrition minérale. INRA, 325 p
Duru M (1992) Diagnostic de la nutrition minérale de prairies permanentes au printemps. I Etablissement de références. agronomie, 12, 219–233
Duru M, Thélier L (1997) N and P-K status of herbage: use for diagnosis of grasslands. In Diagnostic procedures for crop N management and decision making. Sciences Update, ed INRA (in press)
Duru M, Colomb B, Cransac Y, Fardeau JC, Julien JL, Rozière m (1993) Pédoclimat, fertilisation et croissance des prairies permanentes au printemps. I-Variabilité de la nutrition minérale. Fourrages, 133, 23–41
Duru M, Ducrocq H and Tirilly V (1995) Modeling growth of cocks-foot (Dactylis glomerata L.) and tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea schreb.) at the end of spring in relation to herbage nitrogen status. Journal of plant nutrition, 18 (10), 2033–2047
Fardeau JC and Jappe J (1988) Valeurs caractéristiques des cinétiques de dilution isotopique des ions phosphate dans les systèmes sol-solution. In Phosphore et potassium dans les relations sol-plante. Ed INRA, 79–100
Fleming GA (1973) Mineral composition of herbage. In GW Butler and RW Bailey (ed.) Chemistry and biochemistry of herbage, vol 1, pp 529–566, Academic press
Greenwood DJ, Gastal F, Lemaire G, Draycott A, Millard P and Neeteson JJ (1991) Growth rate an N% of field grown crops: theory and experiments. Ann Bot 67 (2), 181–190
Haynes RJ and Swift RS (1988) Effects of lime and phosphate additions on changes in enzyme activities, microbial biomass and levels of extractable nitrogen, sulphur and phosphorus in an acid soil Biol Fertil Soils, 6, 153–158
Kamprath EJ (1987) Enhanced phosphorus status of maize resulting from nitrogen fertilization of high phosphorus soils. Soil Sci Am J, 51, 1522–1526
Kendall MG and Stuart A (1958) The advances theory of statistics, vol. 1, ed C Griffin, London.
Langer RHM (1959) Growth and nutrition of timothy (Phleum pratense L.) V Growth and flowering at different levels of nitrogen. Ann appl Biol, 4, 740–751
Lemaire G, Gastal F and Salette J (1989) Analysis of the effect of N nutrition on dry matter yield of a sward by reference to potential yield and optimum N content. XVI International Grassland Congress, Nice, Fr, 179–180
MacLeod LB (1969) Effects of N, P and K and their interactions on the yield and kernel weight of barley in hydroponic culture. Agron J, 61, 26–29
Martin WE and Matocha JE (1972) Plant analysis as an aid in the fertilization of forage crops. Soil Sc Soc of Am J, 393–425
Mengel K and Kirby EA (1987) Principles of plant nutrition. Ed. Int. Potash Inst. Berne, 3rd ed., 655 p
Munevar F and Wollum AG (1977) Effects of the addition of phosphorus and inorganic nitrogen on carbon and nitrogen mineralization in Andepts from Colombia. Soil Sci Soc Am J 41, 540–545
Pedgel DM (1987) Soil fertility and the composition of semi-natural grasslands. In disturbance in grasslands. J Van Andelet al. (eds), 51–66
Rorison IH (1968) The response to phosphorus of some ecologically distinct plant species. I-Growth rates and phosphorus absorption. New Phytol, 67, 913–923
Salette J (1982) The role of fertilizers in improving herbage quality and optimization of its utilization. Proceeding of the12th Int Potash Symp. Berne: Inst. potash Institute, 117–144
Salette J (1990) The effect of level of nitrogen nutrition upon mineral content and removal in grasses and wheat. Fertiliser Research, 26, 229–235
Salette J, Huché L (1991) Diagnostic de l'état de nutrition minérale d'une prairie par l'analyse minérale du végétal: principes, mise en oeuvre, exemples. Fourrages, 125, 3–18
Tate KR, Speir TW, Ross DJ, Parfitt KN, Whale KN and Cowling JC (1991) Temporal variations in some plant and soil P pools in two pasture soils of widely different P fertility status Plant and soil, 132, 219–232
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duru, M., Ducrocq, H. A nitrogen and phosphorus herbage nutrient index as a tool for assessing the effect of N and P supply on the dry matter yield of permanent pastures. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 47, 59–69 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01985719
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01985719