Abstract
Electron microscopy of ultrathin sections of leaves ofNicotiana clevelandii infected with sharka virus revealed several types of cytoplasmic inclusions. Pinwheels and lamellar aggregates were frequent. Pinwheels showed a central core with a threadlike structure in the middle. Lamellar aggregates showed a striation with a periodicity of 55 Å on their surface and they were associated with the endoplasmic reticulum. Irregular crystalline structures were found less frequently. Microbodies were common in the cytoplasm of sharka virus infectedN. clevelandii plants, but they also abounded in healthy controls.
Nuclear inclusions were present only for short periods after infection.
In leaf extracts irregularly shaped inclusions were found. They had a regular striation of 55 Å. Sometimes nearly parallel stripes were seen on their surface, always at an angle of 80 degrees with the striation.
Samenvatting
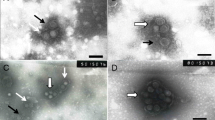
In ultradunne coupes van bladeren vanNicotiana clevelandii, geïnfecteerd met het sharkavirus bleken schoepenradvormige insluitsels (‘pinwheels’) en lamellaire aggregaten algemeen voor te komen. De schoepenradvormige insluitsels vertoonden een centrale holte met daarin een draadvormige structuur (Fig. 2). De lamellaire aggregaten vertoonden een streping met een periodiciteit van 55±5 Å, zowel in ultradunne coupes als in bladextracten (Fig. 1). De lamellaire aggregaten bleken vaak geassociëerd met het endoplasmatisch reticulum (Fig. 3). Kristallijne structuren (Fig. 4) werden slechts incidenteel waargenomen. ‘Microbodies’ waren wel algemeen, maar zij kwamen ook voor in gezonde controleplanten (Fig. 5).
Kerninsluitsels werden met de elektronenmicroscoop aangetoond gedurende de periode, dat zij ook lichtmicroscopisch zichtbaar zijn (Fig. 6). Zij bezaten een duidelijke structuur (Fig. 7).
Gewezen wordt op een mogelijke relatie tussen de kerninsluitsels en de kristallijne structuren in het cytoplasma. Wellicht zijn de naaldvormige insluitsels, die met de lichtmicroscoop in de kern en het cytoplasma kunnen worden waargenomen, identiek aan de elektronenmicroscopisch waargenomen kerninsluitsels en kristallijne structuren in het cytoplasma.
In bladextracten van planten vanNicotiana clevelandii, geïnfecteerd met het sharkavirus, werden onregelmatig gevormde insluitsels gevonden. Ze vertoonden een fijne, precies evenwijdige streping met een periodiciteit van 55±5 Å. Soms bevonden zich op het oppervlak van het insluitsel ook nog wat onregelmatige, grovere strepen. Beide strepingen vormden steeds een hoek van 80 graden (Fig. 1).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnott, H. J. & Smith, K. M., 1967. Electron microscopy of virus infected sunflower leaves. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 19: 173–195.
Bovey, R. 1971. Etude au microscope électronique de quelques altérations de structure produites par le virus de la sharka (plum pox virus) dans les cellules infectées. Annls Phytopath. (numéro hors série) 225–232.
Edwardson, J. R., Purcifull, D. E. & Christie, R. G., 1968. Structure of cytoplasmic inclusions in plants infected with rod-shaped viruses. Virology 34: 250–263.
Frederick, S. E. & Newcomb, E. H., 1969. Cytochemical localization of catalase in leaf microbodies (peroxisomes). J. Cell Biol. 43: 343–353.
Harrison, B. D. & Roberts, I. M., 1971. Pinwheels and crystalline structures induced byAtropa mild mosaic virus, a plant virus with particles 925 nm long. J. gen. Virol. 10: 71–78.
Hoefert, L. L., 1969. Proteinaceous and viruslike inclusions in cells infected with beet mosaic virus. Virology 37: 598–601.
Kim, K. S. & Fulton, J. P., 1969. Electron microscopy of pokeweed mosaic virus. Virology 37: 297–308.
Macovei, A., 1971. Electron microscopic evidence of cytoplasmic inclusions inNicotiana clevelandii Gray cells infected with sharka (plum pox) virus. Annls Phytopath. (numéro hors série): 221–224.
Oosten, H. J. van & Bakel, C. H. J. van, 1970. Inclusion bodies in plants infected with sharka (plum pox) virus. Neth. J. Pl. Path. 76: 313–319.
Pleše, N., Rilović, M. & Wrischer, M., 1969. (Neue Wirtspflanzen und intrazelluläre Einschlusskörper des Scharka-Virus). Zašt. Bilja 20: 143–150.
Purcifull, D. E., Edwardson, J. R., & Christie, S. R., 1970. A morphological comparison of inclusions induced by tobacco etch and potato Y viruses. Phytopathology 60: 779–782.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Bakel, C.H.J., van Oosten, H.J. Additional data on the ultrastructure of inclusion bodies evoked by sharka (plum pox) virus. Netherlands Journal of Plant Pathology 78, 160–167 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01976549
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01976549