Abstract
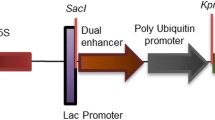
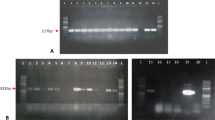
The range of sap-sucking insect pests to which GNA, (the mannose specific lectin from snowdrops (Galanthus nivalis) has been shown to be insecticidal in artificial diets has been extended to include the peach potato aphid (Myzus persicae). A gene construct for constitutive expression of GNA from the CaMV35S gene promoter has been introduced into tobacco plants. A transgenic tobacco line which expresses high levels of GNA has been shown to have enhanced resistance toM. persicae in leaf disc and whole plant bioassays,demonstrating the potential for extending transgenic plant technology to the control of sap-sucking insect pests.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, W.S. (1925) A method for computing the effectiveness of an insecticide.J. Econom. Entomol. 18, 265–7.
Barton, K.A. and Miller, M.J. (1993) inTransgenic Plants Vol. 1 (Kung, S. & Wu, R. eds). New York. Academic Press: pp. 297–315.
Barton, K.A., Whiteley, H. and Yang, N. (1987)Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin in transgenicNicotiana tabacum provides resistance to lepidopteran insects.Pl. Physiol. 85, 1103–9.
Baulcombe, D.A., Saunders, G.R., Bevan, W., Mayo, M.A. and Harrison, B.D. (1986) Expression of biologically active viral satellite RNA from the nuclear genome of transformed plants.Nature 321, 446–9.
Boulter, D., Edwards, G.A., Gatehouse, A.M.R., Gatehouse, J.A. and Hilder, V.A. (1990) Additive protective effects of different plant-derived insect resistance genes in transgenic tobacco plants.Crop Protection 9, 351–4.
Bradford, M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–54.
Fischhoff, D.A., Bowdish, K.S., Perlak, F.J., Marrone, P.G., McCormick, S.M., Niedermeyer, J.G., Dean, D.A., Kusano-Kretzmer, K., Mayer, E.J., Rochester, D.E., Rogers, S.G. and Fraley, R.T. (1987) Insect tolerant transgenic tomato plants.Bio/Technology 5, 807–13.
Hilder, V.A., Gatehouse, A.M.R. and Boulter, D. (1990) Genetic engineering of crops for insect resistance using genes of plant origin. In Lycett, G. and Grierson, D. edsGenetic Engineering of Crop plants, pp. 51–66. London: Butterworths.
Hilder, V.A., Gatehouse, A.M.R. and Boulter, D. (1993) Transgenic plants conferring insect tolerance: protease inhibitor approach. In Kung, S. and Wu, R. edsTransgenic Plants Vol. 1, pp. 317–38. New York: Academic Press.
Hilder, V.A., Brough, C., Gatehouse, A.M.R., Gatehouse, L.N., Powell, K.S., Shi, Y. and Hamilton, W.D.O. (1992) Genes for protecting transgenic crops from chewing and sapsucking insect pests. InProceedings of the Brighton Crop Protection Conference: Pests and Diseases 1992. Vol. 2. pp. 731–40. Lavenham: Lavenham Press.
Hilder, V.A., Gatehouse, A.M.R., Sheerman, S.E., Barker, R.F. and Boulter, D. (1987) A novel mechanism of insect resistance engineered into tobacco.Nature 330, 160–3.
Hill, D.S. (1987)Agricultural Insect Pests of Temperate Regions and Their Control. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Hoffman, M.P., Zalom, F.G., Wilson, L.T., Smilanick, J.M., Malyj, L.D., Kiser, J., Hilder, V.A. and Barnes, W.M. (1992) Field evaluation of transgenic tobacco containing genes encodingBacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin or cowpea trypsin inhibitor: efficacy againstHelicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).J. Econom. Entomol. 85, 2516–22.
Horsch, R.B., Fry, J.E., Hoffman, N.L., Wallroth, M., Eichholtz, D., Rogers, S.G. and Fraley, R.T. (1985) A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants.Science 227, 1229–31.
Johnson, R., Narvaez, J., An, G. and Ryan, C. (1989) Expression of proteinase inhibitors I and II in transgenic tobacco plants: effects on natural defence againstManduca sexta larvae.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 86, 9871–5.
Lis, H. and Sharon, N. (1972) Soy bean (Glycine max) agglutinin.Meths. Enz. 28, 360–8.
Mittler, T.E. and Dadd, R.H. (1962) Artificial feeding and rearing of the aphid,Myzus persicae (Sulzer) on a completely defined synthetic diet.Nature 195, 404.
Mitsuhashi, J. (1974) Methods for rearing leafhoppers and planthoppers on artificial diets.Rev. Pl. Protect. Res. 7, 57–67.
Peferoen, M. (1992) Engineering of insect-resistant plants withBacillus thuringiensis crystal protein genes. In Gatehouse, A.M.R., Hilder, V.A. and Boulter, D. edsPlant Genetic Manipulation for Crop Protection, pp. 135–53. Wallingford: CAB International.
Powell, K.S., Gatehouse, A.M.R., Hilder, V.A. and Gatehouse, J.A. (1993) Antimetabolic effects of plant lectins and plant and fungal enzymes on the nymphal stages of two important rice pests,Nilaparvata lugens andNephotettix cinciteps.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 66, 119–26.
Read, S.M. and Northcote, D.H. (1983) Subunit structure and interactions of the phloem proteins ofCucurbita maxima (Pumpkin).Eur. J. Biochem. 134, 561–9.
Shi, Y., Wang, M.B., Powell, K.S., Van Damme, E., Hilder, V.A., Gatehouse, A.M.R., Boulter, D. and Gatehouse, J.A. (1994) Use of the rice sucrose synthase-1 promoter to direct phloem-specific expression of β-glucuronidase and snowdrop lectin genes in transgenic tobacco plants.J. Exp. Bot. 45, 623–31.
Vaeck, M., Reynaerts, A., Hofte, H., Jansens, S., De Beuckeleer, M., Dean, C., Zabeau, M., Van Montagu, M. and Leemans, J. (1987) Transgenic plants protected from insect attack.Nature 327, 33–7.
Van Damme, E.J.M., DeClercq, N., Claessens, F., Hemschoote, K., Peeters, B. and Peumans, W.J. (1991) Molecular cloning and characterisation of multiple isoforms of the snowdrop (Galanthus nivalis L.) lectin.Planta 186, 35–43.
Wang, M., Boulter, D. and Gatehouse, J.A. (1992) A complete sequence of the rice sucrose synthase-1 (RSs-1) gene.Pl. Mol. Biol. 19, 881–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hilder, V.A., Powell, K.S., Gatehouse, A.M.R. et al. Expression of snowdrop lectin in transgenic tobacco plants results in added protection against aphids. Transgenic Research 4, 18–25 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01976497
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01976497