Abstract
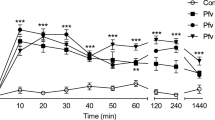
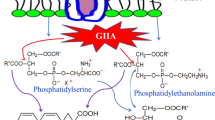
Paw edema was produced in CD-1 mice by the injection of 0.3 μg of snake venom PLA2 (A.p. piscivorus D-49) into the hind paw. Edema peaked at 10 min, remained elevated until 60 min, and then declined slowly. The PLA2 inhibitors, luffariellolide and aristolochic acid, reduced the edema but only when coinjected with the PLA2. The histamine/serotonin antagonists were the most effective drug class against PLA2-induced paw edema. The PAF antagonists, CV-6202 (iv) and kadsurenone (coinjected) reduced the PLA2-induced edema, whereas high doses of the corticosteroids, dexamethasone and hydrocortisone, were also effective. NSAIDs only partially inhibited the paw edema. The LO/CO inhibitors yielded varying activities, with only BW755C and NDGA inhibiting the edema. These results suggest that PLA2 induces paw edema in the mouse via the action of several classes of inflammatory mediators.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Vadas, E. Stefanski and W. Bruzanski,Characterization of extra-cellular phospholipase A 2 in rheumatoid synovial fluid. Life Sciences36, 579–587 (1985).
S. Steinder and K. Tramposch,Assay method for the detection of phospholipase A 2 inhibition. 3rd International Conference Inflammation Research Association, White Haven, PA (Abstract) 1986.
S. P. Peters, M. I. Segel, A. Kagey-Sobotka and L. M. Lichtenstein,Lipoxygenase products modulate histamine release in human basophils. Nature292, 455–457 (1981).
G. Marone, A. Kagey-Sobotka and L. M. Lichtenstein,Possible role of phospholipase A 2 in triggering histamine secretion from human basophils in vitro. Clin. Immunol. Immunopath.20, 231–239 (1981).
K. F. Albizati, T. Homan, D. J. Faulkner, K. B. Glaser and R. S. Jacobs,Luffariellolide, an antiinflammatory sesterterpine from the marine sponge luffariella sp. Experimentia43, 949–950 (1987).
S. B. Vishwanath and T. Gowda,Interaction of aristolochic acid with vipera russelli phospholipase A 2:Its effect on enzymatic and pathological activities. Toxicon.25, 929–937 (1987).
S. B. Vishwanath, A. A. Fawzy and R. C. Franson,Edemainducing activity of phospholipase A 2 purified from human synovial fluid and inhibition by aristolochic acid. Inflammation (in press).
J. Benveniste and M. Chignard,A role for PAP-acether (platelet-activating factor) in platelet-dependent vascular diseases? Circulation72, 713–717 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calhoun, W., Yu, J., Sung, A. et al. Pharmacologic modulation of D-49 phospholipase A2-induced paw edema in the mouse. Agents and Actions 27, 418–421 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972839
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972839