Summary
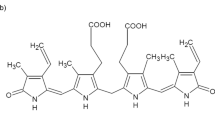
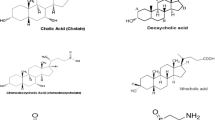
Freshly precipitated uncojugated bilirubin (UCB) is solubilized rapidly and to a large extent by the sodium salts of di- and trihydroxy bile acids. The solubilization effect depending on bile salt concentration, pH and ionic strength is based on micellar mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. T. G. Overbeeck, C. L. J. Vink and H. Deenstra, Recl Trav. chim.74, 81, (1955).
R. C. Burnstine and R. Schmid, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.109, 356 (1962).
T. J. Devers, D. Gallo and J. D. Ostrow, Gastroenterology69, 816 (1975).
T. J. Devers, D. Gallo and J. D. Ostrow, in: The Liver. Quantitative Aspects of Structure and Function, p. 429. Aulendorf 1976.
S. Yamamoto, Acta med. (Fukuoka)28, 28 (1958).
L. Jendrassik and P. Gròf, Biochem. Z.297, 81 (1938).
R. Paul and P. Balaram, Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.81, 850 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wosiewitz, U., Schroebler, S. Solubilization of unconjugated bilirubin by bile salts. Experientia 35, 717–718 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01968199
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01968199