Abstract
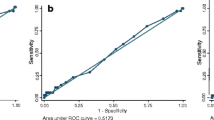
A rapid immunoblotting technique based on the IgM response to a major immunogenic protein is described for the diagnosis ofMycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Using results of the complement fixation test as the criterion for diagnosis, the rapid immunoblot method was positive in 95.7 % of patients. The sensitivity was reduced to 81.9 % if the test was performed on either single sera or acute sera only from serum pairs. Although the few sera that failed to demonstrate a positive IgM response were more likely to be from older patients, there was a consistent IgM response recorded for both younger (<20 years) and older (≥20 years) patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ponka A, Ponka T, Sarna S, Penttinen K: Questionable specificity of lipid antigen in theMycoplasma pneumoniae complement fixation test. Journal of Infection 1981, 3: 332–338.
Cimolai N, Schryvers A, Bryan LE, Woods DE: Culture-amplified immunological detection ofMycoplasma pneumoniae in clinical specimens. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 1988, 9: 207–212.
Kok TW, Varkanis G, Marmion BP, Martin J, Esterman A: Laboratory diagnosis ofMycoplasma pneumoniae infection. I. Direct detection of antigen in respiratory exudates by enzyme immunoassay. Epidemiology and Infection 1988, 101: 669–684.
Dular R, Kajioka R, Kasatiya S: Comparison of Gen-Probe commercial kit and culture techniques for the diagnosis ofMycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1988, 26: 1068–1069.
Tilton RC, Dias F, Kidd H, Ryan RW: DNA probe versus culture for detection ofMycoplasma pneumoniae in clinical specimens. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 1988, 10: 109–112.
Harris R, Marmion BP, Varkanis G, Kok T, Lunn B, Martin J: Laboratory diagnosis ofMycoplasma pneumoniae infection. II. Comparison of methods for direct detection of specific antigen or nucleic acid sequences in respiratory exudates. Epidemiology and Infection 1988, 101: 685–694.
Brunner H, Schaeg W, Bruck U, Schummer U, Szielgoleit D, Schiefer H: Determination of IgG, IgM, and IgA antibodies toMycoplasma pneumoniae by an indirect staphylococcal radioimmunoassay. Medical Microbiology and Immunology 1978, 165: 29–41.
Dussaix E, Slim A, Tournier P: Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and complement fixation test for detection ofMycoplasma pneumoniae antibodies. Journal of Clinical Pathology 1983, 36: 228–232.
Moule JH, Caul ED, Wreghitt TG: The specific IgM response toMycoplasma pneumoniae infection: interpretation and application to early diagnosis. Epidemiology and Infection 1987, 99: 685–692.
Rousseau SA, Tettmar RE: The serologic diagnosis ofMycoplasma pneumoniae infection: a comparison of complement fixation, haemagglutination and immunofluorescence. Journal of Hygiene 1985, 95: 345–352.
Van Griethuysen AJA, de Graaf R, Van Druten JAM, Heessen FWA, Van der Logt JTM, Van Loon AM: Use of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the early diagnosis ofMycoplasma pneumoniae infection. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1984, 3: 116–121.
Vikerfors T, Brodin G, Grandien M, Hirschberg L, Krook A, Pettersson C: Detection of specific IgM antibodies for the diagnosis ofMycoplasma pneumoniae infections: a clinical evaluation. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1988, 20: 601–610.
Vu AC, Foy HM, Cartwright FD, Kenny GE: The principal protein antigens of isolates ofMycoplasma pneumoniae as measured by levels of immunoglobin G in human serum are stable in strains collected over a 10-year period. Infection and Immunity 1987, 55: 1830–1836.
Jacobs E, Bennewitz A, Bredt W: Reaction pattern of human anti-Mycoplasma pneumoniae antibodies in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and immunoblotting. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1986, 23: 517–522.
Cimolai N, Bryan LE, To M, Woods DE: Immunological cross-reactivity ofMycoplasma pneumoniae membrane-associated protein antigen withMycoplasma genitalium andAcholeplasma laidlawii. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1987, 25: 2126–2139.
Jacobs E, Fuchte K, Bredt W: A 168-kilodalton protein ofMycoplasma pneumoniae used as antigen in a dot enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1986, 5: 435–440.
Papierok G, Defives C, Daunizeau A, Wattre P, Derieux JC: Preparative electroelution of specific protein antigens fromMycoplasma pneumoniae: Use in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Annales de Microbiologie 1988, 139: 589–603.
Clyde WA, Hu PC: Antigenic determinants of the attachment protein ofMycoplasma pneumoniae shared by other pathogenicMycoplasma species. Infection and Immunity 1986, 51: 690–692.
Baseman JB, Dallo SF, Tully JG, Rose DL: Isolation and characterization ofMycoplasma genitalium strains from the human respiratory tract. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1988, 26: 2266–2269.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cimolai, N., Mah, D., Thomas, E. et al. Rapid immunoblot method for diagnosis of acuteMycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 9, 223–226 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01963844
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01963844