Abstract
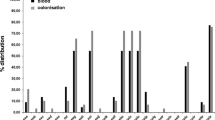
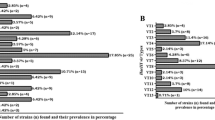
Group A streptococcal isolates (n=53) recovered from 38 erysipelas patients in 1988 and 1990 in Sweden were analysed with respect to serotype, erythrogenic toxin production and polymorphism in theemm gene region. Serotype determination showed a dominance of type T1M1 (28.6 % of the strains), but T type 8 was also prevalent (14.3 %). In the majority of the strains only a low production of erythrogenic toxin A was demonstrated, while both toxin B and C production were high. Polymorphism was detected in theemm gene region of T1M1 strains at a frequency of 64 %. These erysipelas associated group A streptococci were more heterogenic with respect to serotype distribution and polymorphism in theemm gene region compared to previously studied group A streptococci isolated during an outbreak of serious streptococcal infections in Sweden in 1988/1989. The material included isolates from two cases of recurrence, and typing of the isolates indicated that the patients had been infected by the same serotype as in the primary infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jorup Rönström C: Epidemiological, bacteriological and complicating features of erysipelas. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1986, 18: 519–524.
Hugo-Persson M, Nordin K: Erysipelas and group G streptococci. Infection 1987, 15: 184–187.
Bernard P, Bedane C, Mounier M, Denis F, Catanzano G, Bonnetblanc JM: Streptococcal cause of erysipelas and cellulitis in adults. Archives of Dermatology 1989, 125: 779–782.
Breese BB: Streptococcal skin infections. In: Breese BB, Breese Hall C (ed): Beta-hemolytic streptococcal diseases. Houghton Mifflin, 1978, p. 176–211.
Christie AB: Streptococcal infections. In: Christie AB (ed): Infectious diseases: epidemiology and clinical picture. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, 1974, p. 1008–1031.
Jorup Rönström C, Britton S: Recurrent erysipelas: predisposing factors and costs of prophylaxis. Infection 1987, 15: 105–106.
Holm SE, Norrby A, Bergholm AM, Norgren M: Aspects of the pathogenesis in serious group A streptococcal infections in Sweden 1988–1989. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 1992, 100: 31–37.
Norgren M, Norrby A, Holm SE: Genetic diversity in T1M1 group A streptococci in relation to the clinical outcome of the infection. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1992, 166: 1014–1020.
Holm SE, Falsen E: An antigen-free medium for cultivation of β-hemolytic streptococci. Acta Pathologica et Microbiologica Scandinavica 1967, 69: 264–276.
Griffith F: The serological classification ofStreptococcus pyogenes. Journal of Hygiene 1934, 34: 542–584.
Maxted WR, Widdowson JP: The protein antigens of group A streptococci. In: Wannamaker LW, Matsen JM (ed): Streptococci and streptococcal diseases. Academic Press, New York, 1972, p. 256–261.
Lancefield RC: Current knowledge of type-specific M-antigen of group A streptococci. Journal of Immunology 1962, 89: 307–313.
Wadsworth C: A new microtechnique employing a gelchamber compared with other micro- and macroplate techniques for immune diffusion. International Archives of Allergy and Applied Immunology 1962, 21: 131–137.
Birnboim HC, Doly J: A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Research 1979, 7: 1513–1523.
Chassy BM: A gentle method for the lysis of oral streptococci. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communication 1976, 68: 603–608.
Randall KS, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Mulis KB, Erlich HA: Primer directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 1988, 239: 487–491.
Ferretti JJ: Nucleotide sequence of the type A streptococcal exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin) gene fromStreptococcus pyogenes bacteriophage T12. Infection and Immunity 1986, 52: 144–150.
Southern EM: Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. Journal of Molecular Biology 1975, 94: 503–517.
Hollingshead SK, Fishetti VA, Scott JR: Complete nucleotide sequence of type 6 M protein of the group A streptococcus, repetitive structure and membrane anchor. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1986, 261: 1677–1686.
Towbin H, Stachlin T, Gordon J: Electrophoretic transfer from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 1976, 76: 4350–4354.
Dillon HC: Streptococcal infections of the skin and their implications: impetigo and nephritis. In: Wannamaker LW, Matsen JM (ed): Streptococci and streptococcal diseases. Academic Press, New York, 1972, p. 571–578.
Musser JM, Hauser AR, Kim MH, Schlievert PM, Nelson K, Selander RK:Streptococcus pyogenes causing toxic shock-like syndrome and other invasive diseases: clinical diversity and pyrogenic exotoxin expression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 1991, 88: 2668–2672.
Hauser AR, Stevens DL, Kaplan EL, Schlievert PM: Molecular analysis of pyrogenic exotoxins fromStreptococcus pyogenes isolates associated with toxic shocklike syndrome. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1991, 29: 1562–1567.
Gaworzewska E, Colman G: Changes in the pattern of infection caused byStreptococcus pyogenes Epidemiological Infections 1988, 100: 257–269.
Gomi H, Hozumi T, Hattori S, Tagawa C, Kishimob F, Björck L: The gene sequence and some properties of protein H. A novel IgG binding protein. Journal of Immunology 1990, 144: 4046–4052.
Pichichero ME: The rising incidence of penicillin treatment failures in group A streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis: an emerging role for the cephalosporins? Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal, 1991, 10: 50–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norrby, A., Eriksson, B., Norgren, M. et al. Virulence properties of erysipelas-associated group A streptococci. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 11, 1136–1143 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01961132
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01961132