Abstract
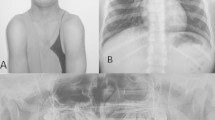
We report on nine patients with craniofrontonasal dysplasia (CFND). Seven classical cases had facial features suggestive of frontonasal dysplasia and coronal craniosynostosis. Extracranial abnormalities such as brittle nails with prominent longitudinal grooves or syndactyly of fingers and toes were observed in individual patients. In two families the father of classical cases showed a milder pattern of abnormalities, consistent with the diagnosis. We present a 2- to 13-year follow-up on our patients. Hypotonia and laxity of joints are common and may necessitate supportive measures. Mild developmental delay was noted in three out of six classical cases studied in detail. Unlike almost all other X-linked disorders, clinical expression in CFND is generally much more severe in females than in males. In contrast to previous reports of this condition, one of our severely affected cases is a male.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CFND:
-
craniofrontonasal dysplasia
- OFC:
-
orofrontal circumference
References
Bommelburg T, Lenz W, Eusterbrock T (1987) Median cleft face syndrome in association with hydrocephalus, agenesis of the corpus callosum, holoprosencephaly and choanal atresia. Eur J Pediatr 146:301–302
Cohen MM (1979) Craniofrontonasal dysplasia. Birth Defects XV (5B): 85–89
Cohen MM, (1986) Syndromes with craniosynostosis. In: Cohen MM (ed) Craniosynostosis. Diagnosis, evaluation and management. Raven Press, New York, pp 413–590
Cohen MM Jr (1988) Craniosynostosis update 1987. Am J Med Genet [Suppl] 4:99–148
Cohen MM Jr, Kreiborg S (1990) The central nervous system in the Apert syndrome. Am J Med Genet 36:36–45
David DJ, Poswillo D, Simpson D (1982) The craniosynostoses. Causes, natural history, and management. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 223–226
De Moor MMA, Baruch R, Human DG (1987) Frontonasal dysplasia associated with tetralogy of Fallot. J Med Genet 24:107–109
Golabi M, Gonzales MC, Edwards MS (1983) A new syndrome of oculoauriculovertebral dysplasia and midline craniofacial defect: the oculoauriculofrontonasal syndrome. Two new cases in sibs. Birth Defects 19(5):183–184
Gollop R (1981) Frontonasal dysostosis. A new autosomal recessive syndrome. Am J Med Genet 10:409–412
Griffiths R (1954) The Griffiths mental development scale. The Psychological Cooperation, New York
Grutzner E, Gorlin RJ (1988) Craniofrontonasal dysplasia: phenotypic expression in females and males and genetic considerations. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 65:436–444
Hennekam RCM, Beemer FA, Van Merrienboer F, Van Ketel BA, Kramer PPG (1986) Congenital hypothalamic hamartoma associated with severe midline defect: a developmental field defect. Report of a case. Am J Med Genet [Suppl 2]:45–52
Hootnick D, Holmes LB (1972) Familial polysyndactyly and craniofacial anomalies. Clin Genet 3:128–134
Hurst J, Baraitser M (1988) Craniofrontonasal dysplasia. J Med Genet 25:133–134
Kere J, Ritvanen A, Marttinen E, Kaitila I (1990) Craniofrontonasal dysostosis: variable expression in a three-generation family. Clin Genet 38:441–446
Kumar D, Clark JW, Blank CE, Patton MA (1986) A family with craniofrontonasal dysplasia, and fragile site 12q13 segregating independently. Clin Genet 29:530–537
Kwee ML, Lindhout D (1983) Frontonasal dysplasia, coronal synostosis, pre- and postaxial polydactyly and split nails: a new autosomal dominant mutant with reduced penetrance and variable expression. Clin Genet 24:200–205
Michels VV, Derleth DP, Hoffman AD, Goldston AJ (1988) Craniofrontal dysostosis with deafness and axillary pterygia. Am J Med Genet 34:445–450
Morris CA, Palumbos JC, Carey JC (1987) Delineation of the male phenotype in craniofrontonasal syndrome. Am J Med Genet 27:623–631
Prescott KE, Sheridan-Pereira M, Manchester DK, Eilers B, Hall BD (1989) The median cleft face skeletal syndrome (frontonasal dysplasia) a distinct subgroup with nasal agenesis, tibial aplasia, hallucal polydactyly and mental retardation. Am J Med Genet 45 (4):A59
Pruzansky S, Costanos M, Rollnick BR (1982) Radiocephalometric findings in a family with craniofrontonasal dysplasia. Birth Defects 18(1):121–138
Renier D (1989) Intracranial pressure in craniosynostosis: pre- and postoperative recordings — correlation with functional results. In: Pershing JA, Edgerton MT, Jane JA (eds) Scientific foundations and surgical treatment of craniosynostosis. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 263–269
Reynolds JF, Haas RJ, Edgerton MT, Kelly TE (1982) Craniofrontonasal dysplasia in a three-generation kindred. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol 2:233–238
Richieri-Costa A, Colletto GMDD, Gollop TR, Masiero D (1985) A previously undescribed autosomal recessive multiple congential anomalies/mental retardation (MCA/MR) syndrome with frontonasal dysostosis, cleft lip/palate, limb hypoplasia and postaxial polysyndactyly: acro-fronto-facio-nasal dysostosis syndrome. Am J Med Genet 20:631–638
Richieri-Costa A, Montagnoli L, Kamiya TY (1989) Autosomal recessive acro-fronto-facio-nasal dysostosis with genitourinary anomalies. Am J Med Genet 33:121–124
Schroots JJF, Alphen de Veer RJ van (1976) LDT: Leidse Diagnostische Test. Swets and Zeitlinger, Lisse
Sedano HO, Cohen MM Jr, Jirásek J, Gorlin RJ (1970) Frontonasal dysplasia. J Pediatr 76:906–913
Slover R, Sujansky E (1979) Frontonasal dysplasia with coronal craniosynostosis in three sibs. Birth Defects XV (5B):75–83
Smith ACM, Manchester DK, McBogg P (1990) Craniofrontonasal dysplasia (CFND). Continuing evidence for Johnson's metabolic interference hypothesis for an X-linked locus. Am J Med Genet 47(3):A65
Stinissen J, Van der Steen G (1981) WPPSI: Wechsler preschool and primary scale of intelligence. Swets and Zeitlinger, Lisse
Teebi AS (1987) New autosomal dominant syndrome resembling craniofrontonasal dysplasia. Am J Med Genet 28:581–591
Temple IK, Brunner H, Jones B, Burn J, Baraitser M (1990) Midline defects with ocular colobomata. Am J Med Genet 37:23–27
Toriello HV, Radecki LL, Sharda J, Looyenga D, Mann R (1986) Frontonasal “dysplasia”, cerebral anomalies, and polydactyly: report of a new syndrome and discussion from a developmental field perspective. Am J Med Genet [Suppl 2]: 89–96
Van der Meulen BF, Smrkovsky M (1985) MOS 2.5-8.5: McCarthy Ontwikkelingsschalen. Swets and Zeitlinger, Lisse
Van Haassen PP, et al. (1986) WISC-R: Wechsler inteligence scale for children revised. Nederlandstalige uitgave. Swets and Zeitlinger, Lisse
Van Wiechen HJ (1972) Early detection of handicapped infants and toddlers (in Dutch). Huisarts en wetenschap 15:351–354
Verstappen P (1979) Assessment of motor function (in Dutch). EMV, Mechelen
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapusta, L., Brunner, H.G. & Hamel, B.C.J. Craniofrontonasal dysplasia. Eur J Pediatr 151, 837–841 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957936
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957936