Abstract
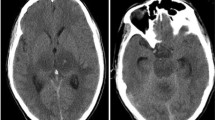
A newborn infant is described who presented with septicaemia and meningoencephalitis caused byPlesiomonas shigelloides, a Gram-negative rod belonging to the family Vibrionaceae. The patient in this case, the first to be documented in Europe, developed multilocular lysis of the brain despite immediate treatment with antibiotics active in vitro. A cranial CT revealed garland-like calcifications and a large amount of medullary necrosis was seen on MRI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelbaum PC, Bowen AJ, Adhikari (1978) Neonatal septicemia and meningitis due toAeromonas shigelloides. J Pediatr 92:676–677
Arai T, Ikeiima N, Itoh T, Sakai S, Shimada T, Sakazaki R (1980) A survey ofPlesiomonas shigelloides from aquatic environments, domestic animals, pets and humans. J Hyg (Long) 84:203–211
Bhat P, Shanthakumarik S, Rajan D (1974) The characterization and significance ofPlesiomonas shigelloides andAeromonas hydrophila isolated from an epidemic of diarrhea. Indian J Med Res 62:1051–1060
Bauer AW, Kirby WMM, Sherris KC, Turck M (1966) Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardised single disc method. Am J Clin Pathol 45:493–496
Claessen BE, Holmlund DE, Lindhagen CA, Maetzsch TW (1984)Plesiomonas shigelloides in acute cholecystitis: a case report. J Clin Microbiol 5:985–987
Dahm LJ, Weinberg AG (1980)Plesiomonas (Aeromonas) shigelloides septicemia and meningitis in a neonate. South Med J 73:393–394
Dudley AG, Mays W, Sale L (1982)Plesiomonas (Aeromonas) shigelloides meningitis in a neonate: a case report. South Med Assoc Ga 71:775–776
Eddy PB, Carpenter KP (1964) Further studies onAeromonas and C27 strains. J Appl Bacteriol 27:96–109
Ewing WH, Hugh R, Johnson JG (1974) Studies on theAeromonas group, Atlanta. U. S. Department of Health. Education and Welfare Public Health Service, p 13
Ferguson WW, Henderson ND (1947) Description of strain C27: a motile organism with the major antigen of Shigella sonnei Phase I. J Bacteriol 54:179–181
Gooal V, Burns FE (1991) Cellulitis and compartment syndrome due toPlesiomonas shigelloides: a case report. Milit Med 156:43
Gordon DL, Philpot CR, McGuire G (1983)Plesiomonas shigelloides septic arthritis complicating rheumatoid arthritis. Aust NZ J Med 13:275–276
Graevenitz A von, Mensch AH (1968) The genusAeromonas in human bacteriology: report of 30 cases and review of the literature. N Engl J Med 278:245–249
Holmberg SD, Farmer JJ (1984)Aeromonas hydrophila andPlesiomonas shigelloides as causes of intestinal infection. Rev Infect Dis 6:633–639
Ingram CE, Morrison AJ Jr, Levitz RE (1987) Gastroenteritis, sepsis, and osteomyelitis caused byPlesiomonas shigelloides in an immunocompetent host: case report and review of the literature. J Clin Microbiol 25/9:1791–1793
Kain KC, Kelly MT (1989) Antimicrobial susceptibility ofPlesiomonas shigelloides from patients with diarrhea. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 33:1609–1610
McCracken AW, Bareley R (1972) Isolation ofAeromonas species from clinical sources. J Clin Pathol 25:970–975
Nolte FS, Poole RM, Murphy GW, Clark C, Panner BJ (1988) Proctitis and fatal septicemia caused byPlesiomonas shigelloides in a bisexual man. J Clin Microbiol 26:388–391
Overman TL, Kessler JF, Seabolt JP (1985) Comparison of API 20E, API rapid, and API rapid NFT for identification of members of the family Vibrionaceae. J Clin Microbiol 22:778–781
Pathak A, Custer JR, Levy J (1983) Neonatal septicemia and meningitis due toPlesiomonas shigelloides. Pediatrics 71:389–391
Rutala WA, Sarubbi FA, Finch CS (1982) Oyster-associated outbreak of diarrheae disease possibly caused byPlesiomonas shigelloides (letter). Lancet I:739
Su S, Ee CK (1981)Plesiomonas shigelloides meningitis in newborn. Singapore Pediatr 23:156–158
Van Damme LR, Vandepitte J (1980) Frequent isolation of Edwardsiella tarda andPlesiomonas shigelloides from healthy Zairese freshwater fish: a possible source of sporadic diarrhea in the tropics. Appl Environ Microbiol 39:475–479
Vandepitte J, Makulu A, Gatti F (1974)Plesiomonas shigelloides: survey and possible association with diarrhea in Zaire. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop 54:503–513
Wadstroem T, Liungh A (1991) Aeromonas and Plesiomonas as food- and waterborne pathogens. Int J Food Microbiol 12:303–311
Waecker NJ, Davis CE, Bernstein G, Spector SA (1988)Plesiomonas shigelloides septicemia and meningitis in a newborn. Pediatr Infect Dis 7:877–879
Zakhariev ZA (1971)Plesiomonas shigelloides isolated from sea water. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol 15:402–404
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terpeluk, C., Goldmann, A., Bartmann, P. et al. Plesiomonas shigelloides sepsis and meningoencephalitis in a neonate. Eur J Pediatr 151, 499–501 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957753
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957753