Abstract
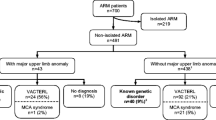
From 1974 until 1995 a total of 264 (141 ♂, 123 ♀) patients born with an anorectal malformation (ARM) were referred to the University Hospital Nijmegen in the Netherlands. All additional congenital defects (ACDs) were registered. Special attention was paid to whether the ACDs take part in associations, syndromes, or sequences. One or more ACDs were observed in 67% of the patients. In decreasing order the defects concerned the uro-genital tract (43%), skeleton (38%), gastrointestinal tract (24%), circulation (21%), extremities (16%), face (16%), central nervous system (15%), respiratory tract (5%), and remaining defects (5%). Associations were observed in 49% of the patients, mostly (in 44%) the Vertebral, Anorectal, Cardial, Tracheo-Esophageal, Renal and Limb association. In 5% of the patients syndromes were recognized. Sequences were seen in 2% of the patients. Remarkable is the combination of trisomy 21 and ARM without a fistula. The combination of ARM and the Zellweger syndrome has not been reported before.
Conclusion
Almost all combinations of ARM and ACDs can be classified as an association, syndrome or sequence. ARM-causing agents affect males and females in equal numbers but lead to different expression in the sexes. The origin of the Omphalocele, Extrophia of the bladder, Imperforate anus, Sacral anomalies complex probably differs from that of other forms of ARM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACD :
-
additional congenital defect
- ARM :
-
anorectal malformation
- OEIS :
-
omphalocele extrophia of the bladder, imperforate anus, sacral anomalies
- VACTERL :
-
vertebral, anorectal, cardial, tracheo-esophageal, renal, limb
References
Black CT, Sherman JO (1989) The association of low imperforate anus and Down's Syndrome. J Pediatr Surg 24: 92–94
Boocock GR, Donnai D (1987) Anorectal malformation: familial aspects and associated anomalies. Arch Dis Child 62: 57–579
Briard ML, Feingold J, Kaplan J et al (1975) Epidemiologie et génétique des malformation ano-rectales. J Génét Hum 23: 177–186
Cattarius U, Bardenhewer A, Hofmann-v.Kap-herr S (1983) Begleitfehlbildungen bei anorektalen Anomalien im Mainzer Krankengut. In: Hofmann-v.Kap-herr S (ed) Anorektale Fehlbindungen. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart, pp 77–78
Christensen K, Madsen CM, Hauge M, Koch K (1990) An epidemiological study of congenital anorectal malformations: 15 Danish birth cohorts followed for 7 years. Pediatr Perinat Epid 4: 269–275
Czeizel A, Ludányi I (1985) An aetiological study of the Vacterl-association. Eur J Pediatr 144: 331–337
Forster IW (1978) Association of anorectal and other congenital abnormalities. J R Coll Surg Edinb 23: 92–95
Freeman NV (1966) Congenital atresia and stenosis of the colon. Br J Surg 53: 595–599
Greenwood RD, Rosenthal A, Nadas AS (1975) Cardiovascular malformations associated with imperforate anus. J Pediatr 86: 576–579
Hoekstra JW (1991) Urogenital tract anomalies in children with congenital anorectal malformations. PhD thesis. Rotterdam
Höllwarth M, Menardi G (1983) Begleitmißbildungen bei anorektalen anomalien. In: Hofmann-v.Kap-herr S (ed) Anorektale Fehlbindungen. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart, pp 63–67
International clearinghouse for birth defects monitoring systems (1991) Congenital malformations worldwide. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Khoury MJ, Cordero JF, Greenberg F, James JMS, Erickson JD (1983) A population study of the VACTERL association: evidence for its etiologic heterogeneity. Pediatr 71: 815–820
Kiesewetter WB, Chang JHT (1977) Imperforate anus: a five to thirty year follow-up perspective. Progr Pediatr Surg 10: 111–120
Lund DP, Hendren WH (1993) Cloacal extrophy: experience with 20 cases. J Pediatr Surg 28: 1360–1369
Magnus RV (1968) Rectal atresia as distinguished from rectal agenesis. J Pediatr Surg 3: 593–598
Otte JB. L'imperforation anale (1983) Quelques données épidémiologiques belges. Acta Chir Belg. 83: 158–12
Ottolenghi A, Sulpasso M, Bianchi S, Bettili G, Salloum A, Liber H (1994) Ectopic anus in childhood. Eur J Pediatr Surg 4: 145–150
Peña A (1988) Surgical managemen of anorectal malformations: a unified concept. Pediatr Surg Int 3: 82–93
Rich MA, Brock WA, Peña A (1988) Spectrum of genitourinary malformations in patients with imperforate anus. Pediatr Surg Int 3: 110–113
Rintala R, Lindahl H, Louhimo I (1986) Vater association and anorectal malformations. Z Kinderchir 41: 22–26
Rochels R (1983) Anorektale fehlbildungenssyndrome mit okulärer Beteiligung. In: Hofmann-v.Kap-herr S (ed) Anorektale Fehlbindungen. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart, pp 69–72
Smith ED (1988) Incidence, frequency of types, and etiology of anorectal malformations. In: Stephens FD, Smith ED (eds) Anorectal malformations in children: update 1988. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 231–247
Smith ED, Saeki M (1988) Associated anomalies. In: Stephens FD, Smith ED (eds) Anorectal malformations in children: update 1988. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 501–549
Smith ED, Stephens FD (1988) Duplication and vesicointestinal fissure. In: Stephens FD, Smith ED (eds) Anorectal malformations in children: update 1988. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 551–580
Spouge D, Baird PA (1986) Imperforate anus in 100,000 consecutive live-born infants. Am J Med Genet [Suppl] 2: 151–161
Spranger J, Benirschke, K, Hall JG, et al (1982) Errors of morphogenesis: concepts and terms. J Pediatr 100: 160–165
Stephens FD, Smith ED (1986) Classification, identification, and assessment of surgical treatment of anorectal anomalies. Pediatr Surg Int 1: 200–205
Teixeira OHP, Malhotra K, Sellers J, Mercer S (1983) Cardiovascular anomalies with imperforate anus. Arch Dis Child 58: 747–749
Tulloh RMR, Tansey SP, Parashar K, Giovanni de JV, Wright JGC, Silove ED (1994) Echocardiographic screening in neonates undergoing surgery for selected gastrointestinal malformations. Arch Dis Child 70: F206-F208
Weaver DD, Mapstone CL, Yu P (1986) The VATER association. Analysis of 46 patients. Am J Dis Child 140: 225–229
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassink, E.A.M., Rieu, P.N.M.A., Hamel, B.C.J. et al. Additional congenital defects in anorectal malformations. Eur J Pediatr 155, 477–482 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01955185
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01955185