Abstract
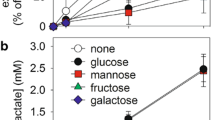
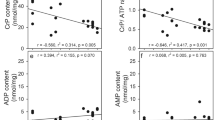
The present study was undertaken to investigate whether neural activity of hippocampal slices can be preserved after replacingd-glucose with glycolytic intermediate metabolites such as lactate, pyruvate and citrate or with other sugars such as fructose, mannose, maltose, glucosamine, sucrose and galactose. As an index of neural activity, population spikes (PS) were recorded in the granule cell layers after electrical stimulation to the perforant path of guinea pig hippocampal slices. In addition, we determined the levels of ATP and creatine phosphate (CrP) in each slice after the replacement ofd-glucose with these substrates, and correlated it with the neural activity. Substrates other thand-glucose could not maintain the PS for even 20 min although the slices perfused with medium containing lactate, pyruvate, galactose, fructose and maltose maintained similar levels of ATP and CrP as in slices incubated in thed-glucose-containing medium. These results indicate thatd-glucose is essential for the preservation of synaptic activity in addition to its main role as the substrate for energy production to maintain the levels of high energy phosphates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agardh, C. D., Chapman, A. G., Nilsson B., and Siesjo, B. K., J. Neurochem.36 (1981) 490.
Lewis, L. D., Ljunggren, B. R., Ratcheson, A., and Siesjo, B. K., J. Neurochem.23 (1974) 673.
Mcllwain, H., and Bachelard, H. S., in Biochemistry and the Central Nervous System, 5th edn, p. 660. Churchill Livingstone New York 1985.
Cox, D. W. G., and Bachelard, H. S., Brain Res.239 (1982) 527.
Cox, D. W. G., and Bachelard, H. S., Expl Brain Res.69 (1988) 368.
Schurr, A., West, C. A., and Rigor, B. M., Science240 (1988) 1327.
Fowler, J. C., J. Neurochem.60 (1993) 572.
Okada, Y., and Ozawa, S., Eur. J. Pharmac.68 (1980) 483.
Okada, Y., in: Mechanism of Cerebral Hypoxia and Stroke, p. 191. Ed. G. Somjen. Plenum, New York 1988.
Okada, Y., Brain Res.72 (1974) 346.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J., J. biol. Chem.193 (1951) 265.
Lipton, P., and Whittingham, T., J. Physiol. Lond.325 (1982) 51.
Okada, Y., Brain Medical, Jap.4 (1992–3) 39.
Cox, D. W. G., Funct. biol. Med.4 (1985) 106.
Cox, D. W. G., Drower, J., and Bacheblard, H. S., Expl Brain Res.57 (1985) 464.
Herman, S., Bachelard, H. S., Cox, D. W. G., and Drower, J., J. Physiol.352 (1984) 91.
Schurr, A., Reid, K. H., Tseng, M. T., Edmonds, H. L., Rigor, M. Jr, Comp. Biochem. Physiol.82A (1985) 701.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanatani, T., Mizuno, K. & Okada, Y. Effects of glycolytic metabolites on preservation of high energy phosphate level and synaptic transmission in the granule cells of guinea pig hippocampal slices. Experientia 51, 213–216 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01931098
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01931098