Summary
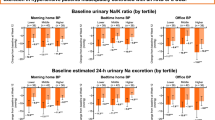
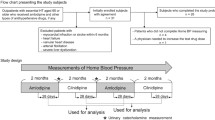
Thirteen patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension and whose average supine blood pressure with no treatment was 165/104 mmHg were studied as inpatients for 3 consecutive one-week periods on different sodium intakes. On the last day of each dietary period, they received a single, 20-mg nitrendipine tablet and blood pressure was monitored every 10 minutes for 2 hours after drug administration.
Nitrendipine significantly lowered blood pressure independently of the level of sodium intake, and the maximum blood-pressure lowering effect was achieved approximately 1 hour after the dose. The blood-pressure lowering effect of nitrendipine was greater on high sodium intake as compared to low sodium intake (p<0.02), and it was also greater with higher initial blood pressures. However, the sodium-related effect on blood pressure was, at least in part, independent of the pretreatment blood pressure.
These results suggest that calcium antagonists, such as nitrendipine, are effective in reducing blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension and could be drugs of choice in those who are unable to restrict their salt intake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki K, Kando S, Mochizuki A. Antihypertensive effects of cardiovascular calcium-antagonists in hypertensive patients in the absence of beta-adrenergic blockade.Am Heart J 1978; 96:218–226.
Buhler FR, Hulthen UL, Bolli P. Calcium channel inhibitors for identification of mechanisms and treatment of hypertension.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1982; 4:S267–S268.
Andren L, Hansson L, Oro L, Ryman T. Experience with nitrendipine a new calcium antagonist in hypertension.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1982; 4:S387–S391.
Ferrara LA, Fasano ML, de Simone G, Soro S, Gagliardi R. Antihypertensive and cardiovascular effects of nitrendipine: A controlled study vs. placebo.Clin Pharmacol Ther 1985; 38:435–438.
Guazzi MD, Fiorentini C, Olivari MT, Bartorelli A, Necchi G, Palese A. Short and long-term efficacy of calcium antagonistic agent (nifedipine) combined with methyldopa in the treatment of severe hypertension.Circulation 1980; 61: 913–919.
Franz IW, Wiewel D. Antihypertensive effects on blood pressure at rest and during exercise of calcium antagonist, β-receptor blockers and their combination in hypertensive patients.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1984; 6(Suppl 7):S1037–S1042.
Pasanisi F, Elliot HL, Meredith PA et al. Cobined alpha adrenoceptor antagonism and calcium channel blockade in normal subject.Clin Pharmacol Ther 1984; 36:716–723.
MacGregor GA, Cappuccio FP, Markandu ND. Sodium intake, high blood pressure and calcium channel blockers.Am J Med 1987; 82(Suppl 3B):16–22.
Leonetti G, Rupoli L, Gradnik R, Zanchetti A. Effects of a low-sodium diet on hypertensive and natriuretic responses to acute administration of nifedipine.J Hypertension 5(Suppl 4):S57–S60.
Cappuccio FP, Markandu ND, MacGregor GA. Calcium antagonists and sodium balance: Effects of changes in sodium intake and of the addition of thiazide diuretic on the blood pressure lowering effect of nifedipine.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1987; 10(Suppl 10):S57–S60.
Rosenthal J. Antihypertensive effects of nifedipine, mefruside and a combination of both substances in patients with essential hypertension. In:Fifth International Adalat Symposium. New Therapy of Ischemic Heart Disease and Hypertension. Amsterdam. Excerpta Medica 1983:175–179.
Cappuccio FP, Markandu ND, Tucker FA, Shore AC, MacGregor GA. A double-blind study on the effect of thiazide diuretic in hypertensive patients already on nifedipine and beta-blocker.J Hypertension 1987; 5:733–738.
Cappuccio FP, Markandu ND, Tucker F, Sagnella GA, MacGregor GA. Does a diuretic cause a further fall in blood pressure in hypertensive patients already on nifedipine?J Clin Hypertens 1986; 4:346–353.
Poulter N, Thompson AV, Sever PS. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial to investigate the additive hypotensive effect of a diuretic (mefruside) to that produced by nifedipine.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1987; 10(Suppl 10): S53-S55.
MacGregor GA, Pevahouse JB, Cappuccio FP, Markandu ND. Nifedipine, sodium intake, diuretics and sodium balance.Am J Nephrol 1987; 7(Suppl 7):44–48.
Pevahouse JB, Markandu ND, Cappuccio FP et al. Long term nifedipine therapy, plasma atrial natriuretic peptide and sodium balance in hypertensive patients.J Hypertens 1987; 5:767.
Leonetti G, Cuspidi C, Sampieri L, Terzoli L, Zanchetti A. Comparison of cardiovascular, renal humoral effects of acute administration of two calcium channel blockers in normotensive and hypertensive subjects.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1982; 4(Suppl 3):S319–S324.
Zanchetti A, Stella A, and Golin R. Adrenergic sodium handling and the natriuretic action of calcium antagonists.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1985; 7(Suppl 6):S194–S198.
Ene MD, Williamson PS, Roberts CJC, Waddel G. The natriuresis following oral administration of the calcium antagonists nifedipine and nitrendipine.Br J Clin Pharm 1985; 19:423–427.
Krussel LR, Christensen CK, Lederballe Pedersen O. Acute natriuretic effect of nifedipine in hypertensive patients and normotensive controls. A proximal tubular effect?Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1987; 32:121–126.
Zanchetti A, Leonetti G. Natriuretic effect of calcium antagonists.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1985; 7(Suppl 4):S33-S37.
Luft FC, Aronof GR, Sloan RS, Fineberg NS, Weinberger MH. Calcium channel blockade with nitrendipine effects on sodium homeostasis, the renin-angiotensin system and sympathetic nervous system in humans.Hypertension 1985; 7:438–442.
MacGregor GA, Pevahouse JB, Cappuccio FP, Markandu ND. Nifedipine, diuretics and sodium balance.J Hypertens 1987; 5(Suppl 4):S127–S131.
Leonetti G, Terzoli L, Rupoli L, Gradnik R, Zanchetti A. Renal effects of felodipine in hypertension.Drugs 1987; 34(Suppl 3):59–66.
Roger EK.Experimental Design Procedures for the Behavioral Sciences Belmont, California: Brooks/Cole, 1968.
Winer BJ.Statistical Principles in Experimental Design. London: McGraw-Hill, 1971.
SPSS IncSPSSX User's Guide. New York: McGraw-hill, 1983.
MacGregor GA, Sagnella GA, Macray KD. Misleading paper about misleading statistics.Lancet 1985; II:926–927.
Gibaldi M, Perrier D.Pharmacokinetics New York: Marcel Dekker, 1982.
Robinson BF, Bayley S, Dobbs JJ. Responses of forearm resistance vessels to verapamil and sodium nitroprusside in normal and hypertensive man: Evidence for a functional abnormality of vascular smooth muscle in primary hypertension.Clin Sci 1982;63:33–42.
Kiowsky W, Erne P, Bertel D, Bolli P, Bühler F. Acute and chronic sympathetic reflex activation and antihypertensive response to nifedipine.J Am Coll Cardiol 1986; 7:344–348.
Guazzi M. Treatment of hypertension with nifedipine, a calcium antagonist agent.Circulation 1979; 59:1056–1062.
Guazzi MD, Polese A, Fiorentini C. Treatment of hypertension with calcium antagonists.Hypertension 1983; 5:II85-II92.
MacGregor GA, Markandu ND, Singer DRJ, Cappuccio FP, Shore AC, Sagnella GA. Moderate sodium restriction with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor in essential hypertension: A double-blind study.Br Med J 1987; 294: 531–534.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galletti, F., Strazzullo, P., Cappuccio, F.P. et al. Calcium-channel blockers and sodium intake: A controlled study in patients with essential hypertension. Cardiovasc Drug Ther 3, 135–140 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01883856
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01883856