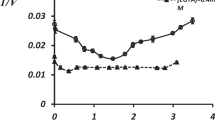
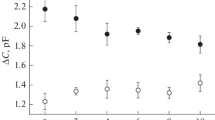
Summary
The effect of phospholipase A2 and of related agents on ouabain binding and Na,K-ATPase activity were studied in intact and detergent-treated membrane preparations of rat brain cortex and pig kidney medulla. It was found that phospholipase A2 (PLA2) may distinguish or dissociate ouabain binding complexes I (ATP+Mg+Na) and II (Pi+Mg), stimulating the former and inhibiting the latter. Procedures which break the permeability barriers of vesicular membrane preparations, such as repeated freezing-thawing, sonication or hypoosmotic shock failed to mimic the effect of PLA2, indicating that it was not acting primarily by opening the inside-out oriented vesicles. The detergent digitonin exhibited similar effects on ouabain binding in both ATP+Mg+Na and Pi+Mg media. Other detergents were ineffective.
The ability of PLA2 to distinguish between ouabain binding type I and II can be manifested even in SDS-treated, purified preparations of Na,K-ATPase. The number of ATP+Mg+Na-dependent sites is unchanged, while the Pi+Mg-dependent sites are decreased in number in a manner similar to that seen in original membranes. This inhibition is completely lost in the reconstituted Na,K-ATPase system, where the ATP- as well as Pi-oriented ouabain sites are inhibited by PLA2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeywardena, M.Y., Charnock, J.S. 1983. Modulation of cardiac glycoside inhibition of Na, K-ATPase by membranes: Difference between species.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 729:75–84
Abeywardena, M.Y., McMurichie, E.J., Russel, G.R., Charnock, J.S. 1984. Species variation in the ouabain sensitivity of cardiac Na, K-ATPase: A possible role for membrane lipids.Biochem. Pharmacol. 33:3649–3654
Albers, R.W., Koval, G.J., Siegel, G.J. 1968. Studies on the interaction of ouabain and other cardioactive steroids with sodium-potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase.Mol. Pharmacol. 4:324–336
Bodemann, H.H., Hoffman, J.F. 1976a. Side-dependent effects of internal versus external Na and K on ouabain binding to reconstituted human red blood cells ghosts.J. Gen. Physiol. 67:497–525
Bodemann, H.H., Hoffman, J.F. 1976b. Comparison of the side-dependent effects of Na and K on orthophosphate-, UTP- and ATP-promoted ouabain binding to reconstituted human red blood cell ghosts.J. Gen. Physiol. 67:527–545
Cantley, L.C. 1980. Structure and mechanism of the Na, K-ATPase.Curr. Topics Bioenerg. 11:201–237
Charnock, J.S., Simonson, L.P., Almeida, A.F. 1977. Variation in sensitivity of the cardiac glycoside receptor characteristics of Na, K-ATPase to lipolysis and temperature.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 465:77–92
Cressie, L.C., Keightley, O.D. 1981. Analysing data from hormone-receptor assays.Biometrics 37:235–249
De Robertis, E., DeIraldi, A.P., DeLorez, G.R., Salganicoff, A.L. 1962. Cholinergic and noncholinergic nerve endings in the rat brain.J. Neurochem. 9:23–35
Erdman, E., Schoner, W. 1973. Ouabain-receptor interactions in Na,K-ATPase preparations: III. On the stability of the ouabain receptor against physical treatment, hydrolases and SH reagents.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 330:316–324
Forbush, B. III. 1982. Characterisation of right-side-out membrane vesicles rich in Na,K-ATPase and isolated from dog kidney medulla.J. Biol. Chem. 257:12678–12684
Fortes, P.A.G. 1977. Anthroylouabain A: A specific fluorescent probe for the cardiac glycoside receptor on Na,K-ATPase.Biochemistry 16:531–540
Garrahan, P.J., Horestein, A., Rega, A.F. 1977. The interaction of ligands with the Na,K-ATPase during Na,K-ATPase activity.In: Na,K-ATPase: Structure and kinetics. J.C. Skou and J.G. Norby, editors. pp. 261–274. Academic, London
Goldmann, S.S., Albers, R.W. 1973. Sodium-potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase: IX. The role of phospholipids.J. Biol. Chem. 248:867–874
Goodman, S.L., Wheeler, K.P. 1978. Ouabain binding to phospholipid dependent adenosine triphosphatase.Biochem. J. 169:313–320
Jones, L.R., Maddock, S.W., Besh, H.R. 1980. Unmasking effect of alamethicin on beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase activities of cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles.J. Biol. Chem. 255:9971–9980
Jorgensen, P.L. 1975. Isolation and characterization of the components of the sodium pump.Q. Rev. Biophys. 7:239–274
Jorgensen, P.L. 1974. Purification and characterization of Na,K-ATPase: III. Purification from the outer medulla of mammalian kidney after selective removal of membrane components by SDS.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 356:36–52
Jorgensen, P.L., Skou, J.C. 1971. Purification and characterization of Na,K-ATPase: I. Influence of detergents on the activity of Na,K-ATPase in preparations from the outer medulla of rabbit kidney.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 233:366–380
Karlish, S.J.D., Pick, U. 1981. Sidedness of the effects of sodium and potassium ions on the conformational state of the sodium-potassium pump.J. Physiol. (London) 312:505–529
Kimmelberg, H.K., Papahadjopoulos, D., 1974. Effects of phospholipid acyl chain fluidity, phase transitions and cholesterol on Na,K-stimulated triphosphatase.J. Biol. Chem. 249:1071–1080
Lane, L.K., Anner, B.M., Wallick, E.T., Ray, M.V., Schwartz, A. 1978. Effect of phospholipase treatment on the partial reactions of and ouabain binding to a purified sodium and potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase.Biochem. Pharmacol. 27:225–231
Lee, J.A., Fortes, P.A.G. 1985. Anthroylouabain binding to different forms of Na,K-ATPase.In: The Sodium Pump. I. M. Glynn and J. C. Ellory, editors. pp. 277–282. Company of Biologists, Cambridge, England
Lindenmayer, G.E., Schwartz, A. 1973. Nature of the transport adenosine triphosphatase digitalis complex: IV. Evidence that sodium-potassium competition modulates the rate of ouabain interaction with Na,K-adenosine-triphosphatase during enzyme catalysis.J. Biol. Chem. 248:1291–1300
Lin-Shiau, S.Y., Chen, C.C. 1982. Effects of beta-bungarotoxin and phospholipase A2 from Naja Naja snake venom on ATPase activities of synaptic membranes from rat cerebral cortex.Toxicon 20:409–418
Matsuda, T., Iwata, H. 1986. Phospholipid composition of cardiac Na,K-ATPase from various species.Experientia 42:405–407
Moczydlowski, E.G., Fortes, P.A.G. 1980. Kinetics of cardiac glycoside binding to Na,K-adenosine triphosphatase studied with a fluorescence derivative of ouabain.Biochemistry 19:969–977
Pullman, M.E., Penefsky, H.S., Datta, A., Racker, E. 1960. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation: I. Purification and properties of soluble dinitrophenol stimulated adenosine triphosphatase.J. Biol. Chem. 235:3322–3329
Roelofsen, B. 1981. The (non) specificity in the lipid-requirement of calcium and sodium plus potassium-transporting adenosine triphosphatases.Life Sci. 29:2235–2247
Roelofsen, B., Van Deenen, L.L.M., 1973. Lipid requirement of membrane bound ATPase: Studies on human erythrocyte ghosts.Eur. J. Biochem. 40:245–257
Scatchard, G. 1949. The attraction of proteins for small molecules and ions.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 51:660–672
Schmalzing, G., Kutschera, P. 1982. Modulation of ATPase activities of human erythrocyte membranes by free fatty acids or phospholipase A2.J. Membrane Biol. 69:65–76
Schull, G.E., Schwartz, A., Lindgrel, J.B., 1985. Amino acid sequence of the catalytical subunit of the Na,K-ATPase deduced from the complementary DNA.Nature (London) 316:691–695
Stahl, W.L. 1986. The Na,K-ATPase of the nervous tissue.Neurochem. Int. 8:449–476
Svoboda, P., Mosinger, B. 1981. Catecholamines and the rat brain microsomal Na,K-ATPase: I. Protection against lipoperoxidative damage.Biochem. Pharmacol. 30:427–432
Sweadner, K.J. 1978. Purification from rat brain of an intrisic membrane protein fraction enriched in Na,K-ATPase.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 508:486–499
Sweadner, K.J. 1979. Two molecular forms of Na,K-stimulated ATPase in brain. Separation and difference in affinity for strophantidin.J. Biol. Chem. 254:6060–6067
Sweadner, K.J. 1985. Enzymatic properties of separated isoenzymes of the Na,K-ATPase: Substrate affinities, kinetic cooperativity and ion transport stoichimetry.J. Biol. Chem. 260:11508–11513
Taniguchi, K., Iida, S. 1973. The role of phospholipids in the binding of ouabain to sodium and potassium dependent adenosine triphosphatase.Mol. Pharmacol. 9:350–359
Taussky, H.H., Shorr, E. 1953. A microcolorimetric method for the determination of inorganic phosphorus.J. Biol. Chem. 202:675–685
Walter, H. 1975. Tightness and orientation of vesicles from guinea-pig kidney estimated from reaction of adenosine triphosphatase dependent on sodium and potassium ions.Eur. J. Biochem. 58:595–601
Walter, H. 1979. Permeability of plasma membrane vesicles to ouabain and Mg2+ as a factor determining the rate of binding of ouabain to Na,K-ATPase.Z. Naturforsch. 34:1224–1231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Svoboda, P., Amler, E. & Teisinger, J. Different sensitivity of ATP + Mg + Na (I) and Pi + Mg (II) dependent types of ouabain binding to phospholipase A2 . J. Membrain Biol. 104, 211–221 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872323
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872323