Summary
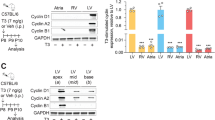
Regulation of Na,K-ATPase mRNAα isoform and mRNAβ expression by thyroid hormone (T3) in neonatal rat myocardium was examined. In euthyroid neonates between ages of 2 and 5 days, mRNAα1, mRNAα3, and mRNAβ1 abundances were nearly constant while mRNAα2 was undetectable. During the interval between postnatal days 5 and 15, mRNAα3 decreased to negligible levels and mRNAα2 became expressed and increased in abundance to account for ∼20% of the mRNAα pool by the 15th postnatal day. To examine the effect of T3 on this developmental program, neonates were injected with 75 μg T3/100 g body weight or diluent alone on the second and third postnatal days and myocardial Na,K-ATPase subunit-mRNA abundances were determined on the third and fourth postnatal days. Because T3 treatment increased the RNA/DNA ratios of myocardial tissue, the subunit-mRNA abundances were normalized per unit DNA. Following 24 and 48 hr of T3 treatment, the abundances of mRNAα1, mRNAα3, and mRNAβ1 increased, while mRNAα2 continued to remain undetectable during the 2-day interval between the second to fourth postnatal days. It is concluded that T3 augments the abundance of Na,K-ATPase subunit mRNAs that are already being expressed in the neonatal rat myocardium. The results further suggest that T3 does not act as a “molecular switch” in the developmental expression of the mRNAα isoforms in rat myocardium during the first four postnatal days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charlemagne, D., Mayoux, E., Poyard, M., Oliviero, P., Geering, K. 1987. Identification of two isoforms of the catalytic subunit of Na,K-ATPase in myocytes isolated from adult rat heart.J. Biol. Chem. 262:8941–8943
Chaudhury, S., Ismail-Beigi, F., Gick, G.G., Levenson, R., Edelman, I.S. 1987. Effect of thyroid hormone on the abundance of Na,K-adenosine triphosphatase α-subunit messenger ribonucleic acid.Mol. Endocrinol. 1:83–89
Chirgwin, J.M., Przbyla, A.E., MacDonald, R.J., Rutter, W.J. 1979. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease.Biochemistry 18:5294–5299
Curfman, G.D., Crowley, T.J., Smith, T.W. 1977. Thyroid induced alterations in myocardial sodium-and potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase, monovalent cation active transport, and cardiac glycoside binding.J. Clin. Invest. 59:586–590
Drugge, E.D., Rosen, M.R., Robinson, R.B. 1985. Neuronal regulation of the development of the α-adrenergic chronotropic response in the rat heart.Circ. Res. 57:415–423
Dubois, J.D., Dussault, J.H. 1977. Ontogenesis of thyroid function in the neonatal rat. Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) production rates.Endocrinology 101:435441
Dussault, J.H., Labrie, F. 1975. Development of hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in the neonatal rat.Endocrinology 97:1321–1324
Emanuel, J.R., Garetz, S., Stone, L., Levenson, R. 1987. Differential expression of Na,K-ATPase α and β subunit mRNA's in rat tissues and cell lines.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:9030–9034
Gick, G.G., Ismail-Beigi, F. 1990. Thyroid hormone induction of Na,K-ATPase and its mRNAs in a rat liver cell line.Am. J. Physiol. 258:C544-C551
Gick, G.G., Ismail-Beigi, F., Edelman, I.S. 1988. Thyroidal regulation of rat renal and hepatic Na,K-ATPase gene expression.J. Biol. Chem. 263:16610–16618
Gick, G.G., Melikian, J., Ismail-Beigi, F. 1990. Thyroidal enhancement of rat myocardial Na,K-ATPase: Preferential expression of α2 activity and mRNA abundance.J. Membrane Biol. 115:273–282
Gustafson, T.A., Bahl, J.J., Markham, B.E., Roeske, W.R., Morkin, E. 1987. Hormonal regulation of myosin heavy chain and α-actin gene expression in cultured fetal rat heart myocytes.J. Biol. Chem. 262:13316–13322
Gustafson, T.A., Markham, B.E., Bahl, J.J., Morkin, E. 1987. Thyroid hormone regulates expression of a transfected α-myosin heavy chain fusion gene in fetal heart cells.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:3122–3126
Haber, R.S., Loeb, J.N. 1988. Selective induction of high ouabain-affinity isoform of Na+−K+-ATPase by thyroid hormone.Am. J. Physiol. 255:E912-E919
Hara, Y., Nikamato, A., Kojima, T., Matsumoto, A., Nakao, M. 1988. Expression of sodium pump activities in BALB/c 3T3 cells transfected with cDNA encoding the α3-subunits of rat brain Na+, K+-ATPase.FEBS Lett. 238:27–30
Hubert, J.J., Schenk, D.B., Skelly, H., Leffert, H.L. 1986. Rat hepatic (Na+,K+)-ATPase α-subunit isolation by immunoaffinity chromatography and structural analysis by peptide mapping.Biochemistry 25:4156–4163
Ismail-Beigi, F., Edelman, I.S. 1971. The mechanism of the calorigenic action of thyroid hormone.J. Gen. Physiol. 57:710–722
Ismail-Beigi, F., Edelman, I.S., Gick, G.G. 1988. Greater induction of Na,K-ATPase alpha-2versus alpha-1 mRNA abundance by thyroid hormone in rat skeletal muscle and ventricular myocardium.Clin. Res.,36:542 (Abstr.)
Izumo, S., Mahdavi, V. 1988. Thyroid hormone receptor α isoforms generated by alternative splicing differentially activate myosin HC gene transcription.Nature (London) 334:539–542
Izumo, S., Nadal-Ginard, B., Mahdavi, V. 1986. All members of the myosin heavy chain multi-gene family respond to thyroid hormone in a highly tissue specific manner.Science 231:597–600
Jorgensen, P.L. 1982. Mechanism of the Na+,K+ pump. Protein structure and conformations of the pure (Na++K+)-ATPase.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 694:27–68
Lin, M.H., Akera, T. 1978. Increased (Na++K+)-ATPase concentrations in various tissues of rats caused by thyroid hormone treatment.J. Biol. Chem. 253:723–726
Lo, C.-S., Edelman, I.S. 1976. The effect of triiodothyronine on the synthesis and degradation of renal cortical (Na++K+)-adenosine triphosphatase.J. Biol. Chem. 251:7834–7840
Lo, C.-S., Lo, T.N. 1980. Effect of triiodothyronine on the synthesis and degradation of the small subunit of renal cortical (Na++K+)-adenosine triphosphatase.J. Biol. Chem. 225:2131–2136
Lytton, J., Lin, J.C., Guidotti, G. 1985. Identification of two molecular forms of (Na+,K+)-ATPase in rat adipocytes.J. Biol. Chem. 260:1177–1184
Martin-Vasallo, P., Dackowski, W., Emanuel, J.R., Levenson, R. 1989. Identification of a putative isoform of the Na,K-ATPase β subunit. Primary structure and tissue-specific expression.J. Biol. Chem. 264:4613–4618
McDonough, A.A., Brown, T.A., Horowitz, B., Chiu, R., Schlotterbeck, J., Bowen, J., Schmitt, C.A. 1988. Thyroid hormone coordinately regulates Na+−K+-ATPase α- and β-subunit mRNA levels in the kidney.Am. J. Physiol. 254:C323-C329
Oppenheimer, H.H. 1983. The nuclear receptor-triiodothyronine complex: Relationship to thyroid hormone distribution, metabolism, and biological action.In: Molecular Basis of Thyroid Hormone Action. J.H. Oppenheimer and H.H. Samuels, editors. pp. 1–34. Academic, New York
Orlowski, J., Lingrel, J.B. 1988. Tissue-specific and developmental regulation of rat Na,K-ATPase catalytic α isoform and β subunit mRNAs.J. Biol. Chem. 263:10436–10442
Orlowski, J., Lingrel, J.B. 1990. Thyroid and glucocorticoid hormone regulate the expression of multiple Na,K-ATPase gene in cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocyte.J. Biol. Chem. 265:3462–3470
Pappano, A.J. 1977. Ontogenetic development of autonomic neuroeffector transmission and transmitter reactivity in embryonic and fetal hearts.Pharmacol. Rev. 29:3–33
Philipson, K.D., Edelman, I.S. 1977. Thyroid hormone control of Na++K+-ATPase and K+-dependent phosphatase.Am. J. Physiol. 232:C196-C201
Russell, S.D., Cambon, N., Nadal-Ginard, B., Whalen, R.G. 1988. Thyroid hormone induces a nerve-independent precocious expression of fast myosin heavy chain mRNA in rat hindlimb skeletal muscle.J. Biol. Chem. 263:6370–6374
Schneider, J.W., Mercer, R.W., Gilmore-Herbert, M., Utset, M.F., Lai, C., Greene, A., Benz, E.D., Jr. 1988. Tissue specificity, localization in brain, and cell-free translation of mRNA encoding the A3 isoform of Na+,K+-ATPase.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:284–288
Shull, G.E., Greeb, J., Lingrel, J.B. 1986. Molecular cloning of three distinct forms of the Na+,K+-ATPase α-subunit form from brain.Biochemistry 25:8125–8132
Shull, G.E., Lane, L.K., Lingrel, J.B. 1986. Amino-acid sequence of the β subunit of the (Na++K+)ATPase deduced from a cDNA.Nature (London) 321:429–431
Shull, M.M., Pugh, D.G., Lingrel, J. 1989. Characterization of the human Na,K-ATPase α2 gene and identification of intragenic restriction fragment length polymorphism.J. Biol. Chem. 264:17535–17543
Shyjan, A.W., Gottardi, C., Levenson, R. 1990. The Na,K-ATPase β2 subunit is expressed in rat brain and copurifies with Na,K-ATPase activity.J. Biol. Chem. 265:5166–5169
Snedecor, G.W., Cochran, W.G. 1976. Statistical Methods. Iowa University Press. Ames (IA)
Sweadner, K.J. 1979. Two molecular forms of (Na++K+)-stimulated ATPase in brain.J. Biol. Chem. 254:6060–6067
Sweadner, K.J., Farshi, S.K. 1987. Rat cardiac ventricle has two Na+,K+-ATPases with different affinities for ouabain: Developmental changes in immunologically different catalytic subunits.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:8404–8407
Thomas, P.S. 1980. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:5201–5205
Urayama, O., Shutt, H., Sweadner, K.J. 1989. Identification of three isozyme proteins of the catalytic subunit of the Na,K-ATPase in rat brain.J. Biol. Chem. 264:8271–8280
Urayama, O., Sweadner, K.J. 1988. Ouabain sensitivity of alpha 3 isozyme of rat Na,K-ATPase.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 156:796–800
Young, R.A., Meyers, B., Alex, S., Fang, S., Braverman, L.E. 1988. Thyroxine binding to serum thyronine-binding globulin in thyroidectomized adult and normal neonatal rats.Endocrinology 122:2318–2323
Young, R.M., Lingrel, J.B. 1987. Tissue distribution of mRNAs encoding the alpha isoforms and beta subunit of rat Na+,K+ ATPase.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 145:52–58
Yuh, Y.-S., Thompson, E.B. 1989. Glucocorticoid effect on oncogene/growth gene expression in human T lymphoblastic leukemic cell line CCRF-CEM. Specific c-myc mRNA suppression by dexamethasone.J. Biol. Chem. 264:10904–10910
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melikian, J., Ismail-Beigi, F. Thyroid hormone regulation of Na,K-ATPase subunit-mRNA expression in neonatal rat myocardium. J. Membrain Biol. 119, 171–177 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871416
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871416