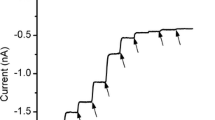
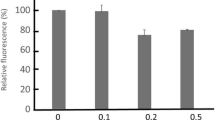
Summary
Previous studies have shown that human erythrocytes when subjected to a high voltage pulsation, in the microsecond time range, lysed in an isotonic medium. The hemolysis was the result of the colloid osmotic swelling, which, in turn, was caused by the voltage perforation of the red cell membranes. In this work we demonstrate that in a low ionic medium at least 35% of the pores was related to the opening of Na+/K+ ATPase channels. The membrane conductance generated by the externally applied electric field could be partially blocked by a specific inhibitor, ouabain, or by a specific cross-linking reagent, Cu++-phenanthroline, of the ATPase. The effect of ouabain was saturable and had a mid-point of saturation at 0.15 μm. This value agrees with the physiological inhibition constant of the drug. K+ ion in the external medium suppressed the effect of ouabain, as has also been demonstrated in physiological studies. Experiment presented in this communication also suggests that the Na+/K+ ATPase was not perforable in a high ionic medium, and that a large fraction of the voltage-induced pores occurred at as yet unidentified sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benz, R., Beckers, F., Zimmermann, U. 1979. Reversible electrical breakdown of lipid bilayer membranes: A charge-pulse relaxation study.J. Membrane Biol. 48:181
Donlon, J.A., Rothstein, A. 1969. The cation permeability of erythrocytes in low ionic strength media of various tonicities.J. Membrane Biol. 1:37
Edidin, M. 1974. Rotational and translational diffusion in membranes.Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 3:179
Fairbanks, G., Steck, T.L., Wallach, D.F.H. 1971. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane.Biochemistry 10:2606
Forbush, B., Hoffman, J.F. 1979. Evidence that ouabain binds to the same large polypeptide chain of dimeric Na,K ATPase that is phosphorylated from Pi.Biochemistry 18:2308
Giotta, G.J. 1976. Quaternary structure of (Na++K+) dependent adenosine triphosphatase.J. Biol. Chem. 251:1247
Harris, J.W., Kellermeyer, R.W. 1972. The Red Cell. p. 474. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Hoffman, J.F., Kaplan, J.H., Callahan, T.J. 1979. The Na∶K pump in red cells is electrogenic.Fed. Proc. 38:2440
Kinosita, K., Jr., Tsong, T.Y. 1977a. Hemolysis of human erythrocytes by a transient electric field.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 74:1923
Kinosita, K., Jr., Tsong, T.Y. 1977b. Voltage-induced pore formation and hemolysis of human erythrocytes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 471:227
Kinosita, K., Jr., Tsong, T.Y. 1977c. Formation and resealing of pores of controlled sizes in human erythrocyte membrane.Nature (London) 268:438
Kinosita, K., Jr., Tsong, T.Y. 1978. Survival of sucrose-loaded erythrocytes in the circulation.Nature (London) 272:258
Kinosita, K., Jr., Tsong, T.Y. 1979. Voltage-induced conductance in human erythrocyte membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 554:479
Kobashi, K. 1968. Catalytic oxydation of sulfhydryl groups byo-phenoanthroline copper complex.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 158:239
Kyte, J. 1975. Structural studies of sodium and potassium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase.J. Biol. Chem. 250:7443
Rao, A. 1979. Disposition of the band 3 polypeptide in the human erythrocyte membrane.J. Biol. Chem. 254:3503
Riemann, F., Zimmerman, U., Pilwat, G. 1975. Release and uptake of haemoglobine and ions in red blood cells induced by dielectric breakdown.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 394:449
Rothstein, A., Knauf, P.A., Cabantchick, Z.I., Balshin, M. 1974. The location and chemical nature of drug ‘targets’ within the human erythrocyte membrane.In: Drug and Transport Process. B.A. Callingham, editor. p. 53. University Park Press, Baltimore
Sale, A.J.H., Hamilton, W.A. 1968. Effects of high electric fields on microorganisms. III. Lysis of erythrocytes and protoplasts.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 163:37
Steck, T.L. 1972. Cross-linking of the major proteins of the isolated erythrocyte membrane.J. Mol. Biol. 66:295
Tsong, T.Y., Kingsley, E. 1975. Hemolysis of human erythrocyte induced by a rapid temperature jump.J. Biol. Chem. 250:786
Tsong, T.Y., Tsong, T.T., Kingsley, E., Siliciano, R. 1976. Relaxation phenomena in human erythrocyte suspensions.Biophys. J. 16:1091
Wang, K., Richards, F.M. 1974. An approach to nearest neighbor analysis of membrane proteins. Application of the human erythrocyte membrane of a method employing cleavable cross-linkages.J. Mol. Biol. 249:8005
Weber, K., Osborn, M. 1975. Proteins and sodium dodecyl sulfate: Molecular weight determination on polyacrylamide gels and related procedures.In: The Proteins. H. Neurath and R.L. Hill, editors. p. 180. Academic Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teissie, J., Tsong, T.Y. Evidence of voltage-induced channel opening in Na/K ATPase of human erythrocyte membrane. J. Membrain Biol. 55, 133–140 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871155
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871155