Summary
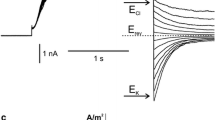
The outer membranes of plant cells contain channels which are highly selective for K+. In the giant-celled green algaChara corallina, K+ currents in the plasmalemma were measured during the action potential and when the cell was depolarized to the K+ equilibrium potential in high external K+ concentrations. Currents in both conditions were reduced by externally added tetraethylammonium (TEA+), Ba2+, Na+ and Cs+. In contrast to inhibition by TEA+, the latter three ions inhibited inward K+ current in a voltage-dependent manner, and reduced inward current more than outward. Ba2+ and Na+ also appeared to inhibit outward current in a strongly voltage-dependent manner. The blockade by Cs+ is studied in more detail in the following paper. TEA+ inhibited both inward and outward currents in a largely voltage-independent manner, with an apparentK D of about 0.7 to 1.1mm, increasing with increasing external K+. All inhibitors reduced current towards a similar linear leak, suggesting an insensitivity of the background leak inChara to these various K+ channel inhibitors. The selectivity of the channel to various monovalent cations varied depending on the method of measurement, suggesting that ion movement through the K+-selective channel may not be independent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, C.M. 1975. Ionic pores, gates, and gating currents.Q. Rev. Biophys. 7:179–210
Armstrong, C.M., Swenson, R.P., Jr., Taylor, S.R. 1982. Block of the squid axon K+ channels by internally and externally applied Ba2+ ions.J. Gen. Physiol. 80:663–682
Azimov, R.R., Geletyuk, V.I., Berestovsky, G.N. 1987. Single potential-dependent K+ channel of the cells of the algaNitellopsis obtusa.Biophysics 32:82–88
Barry, W.H. 1968. Coupling of excitation and cessation of cyclosis inNitella: Role of divalent cations.J. Cell Physiol. 72:153–159
Beilby, M.J. 1985. Potassium channels atChara plasmalemma.J. Exp. Bot. 36:228–239
Beilby, M.J. 1986a. Potassium channels and different states ofChara plasmalemma.J. Membrane Biol. 89:241–249
Beilby, M.J. 1986b. Factors controlling the K+ conductance inChara.J. Membrane Biol. 93:187–193
Beilby, M.J., Beilby, B.N. 1983. Potential dependence of the admittance ofChara plasmalemma.J. Membrane Biol. 74:229–245
Beilby, M.J., Coster, H.G.L. 1979. The action potential inChara corallina. II. Two activation-inactivation transients in voltage clamps of the plasmalemma.Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 6:323–335
Belton, P., Netton, C. van 1971. The effects of pharmacological agents on the electrical responses of cells ofNitella flexilis.Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 49:824–832
Eisenman, G. 1962. Cation selective glass electrodes and their mode of operation.Biophys. J. 2:259–323
Eisenman, G., Krasne, S.J. 1975. The ion selectivity of carrier molecules, membranes and enzymes.In: Biochemistry of Cell Walls and Membranes. MTP International Review of Science, Biochemistry Series 1, Vol. 2. C.F. Fox, editor, pp. 27–59. Butterworths, London
Eisenman, G., Latorre, R., Miller, C. 1986. Multi-ion conduction and selectivity in the high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel.Biophys. J. 50:1025–1034
Findlay, G.P., Tyerman, S.D., Paterson, G.J. 1988. Potassium channels in the plasmalemma ofChara inflata.In: Proceedings of the Seventh International Workshop on Plant Membrane Transport, Sydney, Australia, 1986. M.J. Beilby, J.R. Smith, and N.A. Walker, editors. University of Sydney Press, Sydney, Australia (in press)
Findlay, I., Dunne, M.J., Petersen, O.H. 1985. ATP-sensitive inward rectifier and voltage- and calcium-activated K+ channels in cultured pancreatic islet cells.J. Membrane Biol. 88: 165–172
French, R.J., Wells, J.B. 1977. Sodium ions as blocking agents and charge carriers in the potassium channel of the squid axon.J. Gen. Physiol. 70:707–724
Gitter, A.H., Beyenbach, K.W., Christine, C.W., Gross, P., Minuth, W.W., Fromter, E. 1987. High-conductance K+ channel in apical membranes of principle cells cultured from rabbit renal cortical collecting duct anlagen.Pfluegers Arch. 408:282–290
Gorman, A.L.F., Woolum, J.C., Cornwall, M.C. 1982. Selectivity of the Ca2+-activated and light-dependent K− channels for monovalent cations.Biophys. J. 38:319–322
Hermann, A., Gorman, A.L.F. 1981. Effects of tetraethylammonium on potassium currents in a molluscan neuron.J. Gen. Physiol. 78:87–110
Hess, P., Tsien, R.W. 1984. Mechanism of ion permeation through calcium channels.Nature (London) 309:453–456
Hille, B. 1984. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sinauer, Sunderland
Hille, B., Schwarz, W. 1978. Potassium channels as multi-ion single-file pores.J. Gen. Physiol. 72:409–442
Keifer, D.W., Lucas, W.J. 1982. Potassium channels inChara corallina. Control and interaction with the electrogenic H+ pump.Plant Physiol. 69:781–788
Kikuyama, M. 1986. Tonoplast action potential ofCharaceae.Plant Cell Physiol. 27:1461–1468
Kitasato, H. 1973. K permeability ofNitella clavata in the depolarised state.J. Gen. Physiol. 62:535–549
Koppenhöfer, E. 1972. Die Wirkung von Kupfer, TTX, Cocain und TEA auf das Ruhe- und Aktionspotential vonNitella.Pfluegers Arch. 336:299–309
Latorre, R. 1986. The large calcium-activated potassium channel.In: Ion Channel Reconstitution. C. Miller, editor. pp. 431–467. Plenum, New York
Lunevsky, V.Z., Zherelova, O.M., Vostrikov, I.Y., Berestovsky, G.N. 1983. Excitation ofCharaceae cell membranes as a result of activation of calcium and chloride channels.J. Membrane Biol. 72:43–58
Miller, C. 1982.Bis-quaternary ammonium blockers as structural probes of the sarcoplasmic reticulum K+ channel.J. Gen. Physiol. 79:869–891
Miller, C., Latorre, R., Reisin, I. 1987. Coupling of voltage-dependent gating and Ba++ block in the high-conductance, Ca++-activated K+ channel.J. Gen. Physiol. 90:427–449
Netton, C. van, Belton, P. 1978.45Ca displacement related to pharmacologically induced prolonged action potentials inNitella flexilis.Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 56:294–298
Plaks, A.V., Sokolik, A.I., Yurin, V.M. 1987. Transport properties of the plasmalemma inNitella cells deprived of the tonoplast.Soviet Plant Physiol. 34:271–276
Schauf, C.L., Wilson, K.J. 1987a. Effects of abscisic acid on K+ channels inVicia faba guard cell protoplasts.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 145:284–290
Schauf, C.L., Wilson, K.J. 1987b. Properties of single K+ and Cl− channels inAsclepias tuberosa protoplasts.Plant Physiol. 85:413–418
Schroeder, J.I., Raschke, K., Neher, E. 1987. Voltage dependence of K+ channels in guard cell protoplastsProc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:4108–4112
Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1983. Activation of K+-channel in membrane excitation ofNitella axilliformis.Plant Cell Physiol. 24:1511–1524
Smith, J.R., Kerr, R.J. 1987. Potassium transport across the membranes ofChara. IV. Interactions with other ions.J. Exp. Bot. 38:788–799
Sokolik, A.I., Yurin, V.M. 1981. Transport properties of potassium channels of the plasmalemma ofNitella cells at rest.Soviet Plant Physiol. 28:206–212
Sokolik, A.I., Yurin, V.M. 1986. Potassium channels in plasmalemma ofNitella cells at rest.J. Membrane Biol. 89:9–22
Stanfield, P.R. 1983. Tetraethylammonium ions and the potassium permeability of excitable cells.Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 97:1–67
Tester, M. 1988a. Pharmacology of K+ channels in the plasmalemma of the green alga,Chara corallina.J. Membrane Biol. 103:159–169
Tester, M. 1988b. Potassium channels in the plasmalemma ofChara corallina are multi-ion pores: Voltage-dependent blockade by Cs+ and anomalous permeabilities.J. Membrane Biol. 105:87–94
Thaler, M., Steigner, W., Kohler, K., Simonis, W., Urbach, W. 1987. Releases of repetitive transient potentials and opening of potassium channels by barium inEremosphaera viridis.FEBS Lett. 219:351–354
Tsien, R.W. 1983. Calcium channels in excitable cell membranes.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 45:341–358
Tsien, R.W., Hess, P., McCleskey, E.W., Rosenberg, R.L. 1987. Calcium channels: Mechanisms of selectivity, permeation and block.Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 16:265–290
Vergara, C., Latorre, R. 1983. Kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rabbit muscle incorporated into planar lipid bilayers: Evidence for a Ca2+ and Ba2+ blockade.J. Gen. Physiol. 83:543–568
Vergara, C., Moczydlowski, E., Latorre, R. 1984. Conduction, blockade and gating in a Ca2+-activated K+ channel incorporation into planar lipid bilayers.Biophys. J. 45:73–76
Villarroel, A., Alvarez, O., Latorre, R. 1986. Blockade of a Ca-activated K channel by quaternary ammonium ions.Biophys. J. 49:576a (abstr.)
Woodhull, A.M. 1973. Ionic blockade of sodium channels in nerve.J. Gen. Physiol. 61:687–708
Yellen, G. 1984. Ionic permeation and blockade in Ca2+-activated K+ channels from bovine chromaffin cells.J. Gen. Physiol. 84:157–186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tester, M. Blockade of potassium channels in the plasmalemma ofChara corallina by tetraethylammonium, Ba2+, Na+ and Cs+ . J. Membrain Biol. 105, 77–85 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871108
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871108