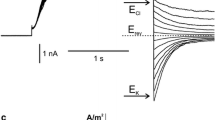
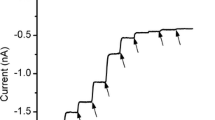
Summary
The outer membranes of plant cells contain channels which are highly selective for K+. However, many of their properties and their similarities to K+ channels found in animal cells had not previously been established. The channels open when the cells are depolarized in solutions with a high K+/Ca2+ ratio. In this work, the pharmacology of a previously identified plant K+ channel was examined. This survey showed that the channels have many properties which are similar to those of high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels (highG K+(Ca2+)). K+ currents inChara were reduced by TEA+, Na+, Cs+, Ba2+, decamethonium and quinine, all inhibitors of, among other things, highG K+(Ca2+) channels. Tetracaine also inhibited K+ currentsChara, but its effect on most types of K+ channels in animal tissues is unknown. The currents were not inhibited by 4-aminopyridine (4AP), caffeine, tolbutamide, dendrotoxin, apamin or tubocurarine, which do not inhibit highG K+(Ca2+) channels, but affect other classes of K+ channels. The channels were “locked open” by 4AP, in a remarkably similar manner to that reported for K+(Ca2+) channels of a molluscan neuron. No evidence for the role of the inositol cycle in channel behavior was found, but its role in K+ channel control in animal cells is obscure. Potassium conductance was slightly decreased upon reduction of cytoplasmic ATP levels by cyanide + salicylhydroxamic acid (SHAM), consistent with channel control by phosphorylation. The anomalously strong voltage dependence of blockade by some ions (e.g. Cs+) is consistent with the channels being multiion pores. However, the channels also demonstrate some differences from the highG K+(Ca2+) channels found in animal tissues. The venom of the scorption,Leiurus quinquestriatus (LQV), and a protein component, charybdotoxin (CTX), an apparently specific inhibitor of highG K+(Ca2+) channels in various animal tissues, had no effect on the K+ channels in theChara plasmalemma. Als,, pinacidil, an antihypertensive drug which may increase highG K+(Ca2+) channel activity had no effect on the channels inChara. Although the described properties of theChara K+ channels are most similar to those of high conductance K+(Ca2+) in animal cells, the effects of CTX and pinacidil are notably different; the channels are clearly of a different structure to those found in animal cells, but are possibly related.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R.D. 1969. Mechanism of the seismonastic reaction inMimosa pudica.Plant Physiol. 44:1101–1107
Almers, W. 1976. Differential effects of tetracaine on delayed potassium currents and contraction of frog skeletal muscle.J. Physiol. (London) 262:613–637
Applewhite, P.B. 1972. Drugs affecting sensitivity to stimuli in the plantMimosa and the protozoanSpirostomum.Physiol. Behaviour 9:869–871
Arkhammar, P., Nilsson, T., Rorsman, P., Berggren, P.O. 1987. Inhibition of ATP-regulated K+ channels precedes depolarization-induced increase in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration in pancreatic β-cells.J. Biol. Chem. 262:5448–5454
Armstrong, C.M., Lopez-Barneo, J. 1987. External calcium ions are required for potassium channel gating in squid neurons.Science 236:712–714
Armstrong, C.M., Matteson, D.R. 1986. The role of calcium ions in the closing of K channels.J. Gen. Physiol. 87:817–832
Azimov, R.R., Geletyuk, V.I., Berestovsky, G.N. 1987. Single potential-dependent K−-channel in the cells of algaeNitellopsis obtusa.Biophysics 32:82–88
Beilby, M.J. 1985. Potassium channels atChara plasmalemma.J. Exp. Bot. 36:228–239
Beilby, M.J. 1986a. Factors controlling the K+ conductance inChara.J. Membrane Biol. 93:187–193
Beilby, M.J.,1986b. Potassium channels and different states ofChara plasmalemma.J. Membrane Biol. 89:241–249
Beilby, M.J., Beilby, B.N. 1983. Potential dependence of the admittance ofChara plasmalemma.J. Membrane Biol. 74:229–245
Belles, B., Hescheler, J., Trube, G. 1987. Changes of membrane currents in cardiac cells induced by long whole-cell recordings and tolbutamide.Pfluegers Arch. 409:582–588
Benoit, E., Dubois, J.M. 1986. Toxin I from the snakeDendroaspsis polylepis polylepis: A highly specific blocker of one type of potassium channel in myelinated nerve fibre.Brain Res. 377:374–377
Berridge, M.J. 1984. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers.Biochem. J. 220:345–360
Bertl, A., Gradmann, D. 1987. Current-voltage relationships of potassium channels in the plasmalemma ofAcetabularia.J. Membrane Biol. 99:41–49
Blatt, M.R. 1987. Electrical characteristics of stomatal guard cells: The contribution of ATP-dependent, “electrogenic” transport revealed by current-voltage and difference-current voltage analysis.J. Membrane Biol. 98:257–274
Blatt, M.R., Slayman, C.L. 1983. KCl leakage from microelectrodes and its impact on the membrane parameters of a nonexcitable cell.J. Membrane Biol. 72:223–234
Blum, R.M., Hoffman, J.F. 1971. The membrane locus of Castimulated K transport in energy depleted human red blood cells.J. Membrane Biol. 6:315–328
Bourque, C.W., Brown, D.A. 1987. Apamin andD-tubocurarine block the afterhyperpolarization of rat supraoptic neurosecretory neurons.Neurosci. Lett. 82:185–190
Brownlee, C., Wood, J.W. 1986. A gradient of cytoplasmic free calcium in growing rhizoid cells ofFucus serrulatus.Nature (London) 320:624–626
Carbone, E., Prestipino, G., Spadavecchia, L., Franciolini, F., Possani, L.D. 1987. Blocking of the squid axon K+ channel by noxiustoxin: A toxin from the venom of the scorpionCentruroides noxius.Pfluegers Arch. 408:423–431
Carbone, E., Wanke, E., Prestipino, G., Possani, L.D., Maelicke, A. 1982. Selective blockage of voltage-dependent K+ channels by a novel scorpion toxin.Nature (London) 296:90–91
Castle, N.A., Haylett, D.G. 1987. Effect of channel blockers on potassium efflux from metabolically exhausted frog skeletal muscle.J. Physiol. (London) 383:31–43
Cecchi, X., Wolff, D., Alvarez, O., Latorre, R. 1987. Mechanisms of Cs+ blockade in a Ca2+-activated K+ channel from smooth muscle.Biophys. J. 52:707–716
Cook, D.L., Hales, C.N. 1984. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic β-cells.Nature (London) 311:271–273
Cook, N.S., Haylett, D.G. 1985. Effects of apamin, quinine and neuromuscular blockers on calcium-activated potassium channels in guinea-pig hepatocytes.J. Physiol. (London) 358:373–394
Darbon, H., Zlotkin, E., Kopeyan, C., Van Rietschoten, J., Rochat, H. 1982. Covalent structure of the insect toxin ofAndroctonus australis Hector.Toxicon 20:64
Dun, N.J., Jiang, Z.G., Mo, N. 1986. Tubocurarine suppresses slow calcium-dependent after-hyperpolarisation in guinea-pig inferior mesenteric ganglion cells.J. Physiol. (London) 375:499–514
Eckert, R., Brehm, P. 1979. Ionic mechanisms of excitation inParamecium.Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng 8:353–383
Ettlinger, C., Lehle, L. 1988. Auxin induces rapid changes in phophatidylinositol metabolites.Nature (London) 331:176–178
Findlay, G.P., Hope, A.B. 1964. Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis VII. The separate electrical characteristics of the plasmalemma and tonoplast.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 17:62–77
Findlay, I., Dunne, M.J., Ullrich, S., Wollheim, C.B., Petersen, O.H. 1985. Quinine inhibits Ca2+-independent K+ channels whereas tetraethylammonium inhibits Ca2+-activated K+ channels in insulin-secreting cells.FEBS Lett. 185:4–8
Fishman, M.C., Spector, I. 1981. Potassium current suppression by quinidine reveals additional calcium currents in neuroblastoma cells.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78:5245–5249
Frankenhaeuser, B., Hodgkin, A.L. 1957. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons.J. Physiol. (London) 137:218–244
Gillespie, J.I. 1977. Voltage-dependent blockage of the delayed potassium current in skeletal muscle by 4-aminopyridine.J. Physiol. (London) 273:64P-65P
Guggino, S.E., Guggino, W.B., Green, N., Sacktor, B. 1987. Blocking agents of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cultured medullary thick ascending limb cells.Am. J. Physiol. 252:C128-C137
Halliwell, J.V., Othman, I.B., Pelchen-Matthews, A., Dolly, J.O. 1986. Central action of dendrotoxin: Selective reduction of a transient K conductance in hippocampus and binding to localized acceptors.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:493–497
Harvey, A.L., Karlsson, E. 1980. Dendrotoxin from the venom of the green mamba,Dendroaspis angusticeps.Naunyn Schmeideberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 312:1–6
Heim, S., Wagner, K.G. 1986. Evidence of phosphorylated phosphatidylinositols in the growth cycle of suspension cultured plant cells.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 134:1175–1181
Hermann, A., Erxleben, C. 1987. Charybdotoxin selectively blocks small Ca-activated K channels inAplysia neurons.J. Gen. Physiol. 90:27–47
Hermann, A., Gorman, A.L.F. 1980. Dual action of caffeine on K+ conductance.Pfluegers Arch. 384:R-12
Hermann, A., Gorman, A.L.F. 1981. Effects of 4-aminopyridine on potassium currents in a molluscan neuron.J. Gen. Physiol. 78:63–86
Hille, B. 1984. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sinauer. Sunderland
Hokin, L.E. 1985. Receptors and phosphoinositide-generated second messengers.Annu. Rev. Biochem. 54:205–235
Hugues, M., Romey, G., Duval, D., Vincent, J.P., Lazdunski, M. 1982. Apamin as a selective blocker of the calcium-dependent potassium channel in neuroblastoma cells: Voltageclamp and biochemical characterization of the toxin receptor.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:1308–1312
Irvine, R.F., Letcher, A.J., Dawson, R.M.C. 1980. Phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase in higher plants.Biochem. J. 192:279–283
Kakei, M., Noma, A., Shibasaki, T. 1985. Properties of adenosinetriphosphate-regulated potassium channels in guinea-pig ventricular cells.J. Physiol. (London) 363:441–462
Keifer, D.W., Lucas, W.J. 1982. Potassium channels inChara corallina. Control and interaction with the electrogenic H+ pump.Plant Physiol. 69:781–788
Kitasato, H. 1973. K permeability ofNitella clavata in the depolarized state.J. Gen. Physiol. 62:535–549
Kiyosawa, K. 1975. Permeabilities of theChara cell wall to saccharides, albumin and Ficoll.Bot. Mag. 88:47–57
Kloerke, D.A., Petersen, J., Jorgensen, P.L. 1987. Purification of Ca2+-activated K+ channel protein on calmodulin affinity columns after detergent solubilization of luminal membranes from outer renal medulla.FEBS Lett. 216:211–216
Kumon, K., Suda, S. 1984. Ionic fluxes from pulvinar cells during the rapid movement ofMimosa pudica L.Plant Cell Physiol. 25:975–979
Lackington, I., Orrega, F. 1981. Inhibition of calcium-activated potassium conductance of human erythrocytes by calmodulin inhibitory drugs.FEBS Lett. 133:103–106
Lancaster, B., Nicoll, R.A. 1987. Properties of two calciumactivated hyperpolarizations in rat hippocampal neurones.J. Physiol. (London) 389:187–203
Latorre, R. 1986. The large calcium-activated potassium channel.In: Ion Channel Reconstitution. C. Miller, editor. pp. 431–467. Plenum, New York
Latorre, R., Miller, C. 1983. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels.J. Membrane Biol. 71:11–30
Lebrun, P., Atwater, I., Claret, M., Malaisse, W.J., Herchuelz, A. 1983. Resistance to apamin of the Ca2+-activated K+ permeability in pancreatic β-cells.FEBS Lett. 161:41–44
Leneveu, E., Simonneau, M. 1986. Scorpion venom inhibits selectively Ca2+-activated K+ channelsin situ.FEBS Lett. 209:165–168
Lucero, M.T., Pappone, P.A. 1987.Pandinus imperator scorpion venom blocks K channels in GH3 cells.Biophys. J. 51:54a (abstr.)
Lunevsky, V.Z., Zherelova, O.M., Vostrikov, I.Y., Berestovsky, G.N. 1983. Excitation ofCharaceae cell membranes as a result of activation of calcium and chloride channels.J. Membrane Biol. 72:43–58
MacKinnon, R., Miller, C. 1987. Charybdotoxin knock off by potassium in a calcium activated potassium channel.Biophys. J. 51:53a (abstr.)
MacRobbie, E.A.C. 1962. Ionic relations ofNitella translucens.J. Gen. Physiol. 45:861–878
Matthews, E.K. 1986. Calcium and membrane permeability.Br. Med. Bull. 42:391–397
Miller, C., Moczydlowski, E., Latorre, R., Phillips, M. 1985. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal tissue.Nature (London) 313:316–318
Moczydlowski, E., Latorre, R. 1983. Gating kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rat muscle incorporated into planar lipid bilayers.J. Gen. Physiol. 82:511–542
Moran, N., Ehrenstein, G., Iwasa, K., Bure, C., Mischke, C. 1986. Ionic channels in plant protoplasts.In: Ionic Channels in Cells and Model Systems. R. Latorre, editor. pp. 195–205. Plenum, New York
Morris, A.P., Gallacher, D.V., Irvine, R.F., Petersen, O.H. 1987. Synergism of inositol trisphosphate and tetrakisphosphate in activating Ca2+-dependent K+ channels.Nature (London) 330:653–655
Morse, M.J., Crain, R.C., Satter, R.L. 1987. Light-stimulated inositol-phospholipid turnover inSamanea saman leaf pulvini.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:7075–7078
Noma, A. 1983. ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle.Nature (London) 305:147–148
Okada, Y., Yada, T., Ohno-Shosaku, T., Oiki, S. 1987. Evidence for the involvement of calmodulin in the operation of Ca-activated K channels in mouse fibroblasts.J. Membrane Biol. 96:121–128
Okazaki, Y., Tazawa, M. 1987. Dependence of plasmalemma conductance and potential on intracellular free Ca2+ in tonoplast-removed cells of a brackish water CharaceaeLamprothamnium.Plant Cell Physiol. 28:703–708
Okazaki, Y., Yoshimoto, Y., Hiramoto, Y., Tazawa, M. 1987. Turgor regulation and cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in the algaLamprothamnium.Protoplasma 140:67–71
Pennefather, P., Lancaster, B., Adams, P.R., Nicoll, R.A. 1985. Two distinct Ca-dependent K currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:3040–3044
Penner, R., Peterson, M., Pierau, F.K., Dreyer, F. 1986. Dendrotoxin: A selective blocker of a non-inactivating potassium current in guinea-pig dorsal root ganglion neurones.Pfluegers Arch. 407:365–369
Plaks, A.V., Sokolik, A.I., Yurin, V.M. 1987. Transport properties of the plasmalemma inNitella cells deprived of the tonoplast.Soviet Plant Physiol. 34:271–276
Raven, J.A. 1968. The linkage of light-stimulated Cl influx to K and Na influxes inHydrodictyon africanum.J. Exp. Bot. 19:233–253
Rorsman, P., Trube, G. 1986. Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic β-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP.Pfluegers Arch. 405:305–309
Satter, R., Lee, Y., Morse, M.J., Crain, R.C., Cote, G., Moran, N. 1988. Light-and clock-controlled leaflet movements inSamanea saman: A physiological, biophysical and biochemical analysis.Bot. Acta (in press)
Schauf, C.L. 1987. Dendrotoxin blocks potassium channels and slows inactivation in myxicola giant axons.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 241:793–796
Schauf, C.L., Wilson, K.J. 1987a. Effects of abscisic acid on K+ channels inVicia faba guard cell protoplasts.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 145:284–290
Schauf, C.L., Wilson, K.J. 1987b. Properties of single K+ and Cl− channels inAsclepias tuberosa protoplasts.Plant Physiol. 85:413–418
Schroeder, J.I., Hedrich, R., Fernandez, J.M. 1984. Potassiumselective single channels in guard cell protoplasts ofVicia faba.Nature (London) 312:361–362
Schroeder, J.I., Raschke, K., Neher, E. 1987. Voltage dependence of K+ channels in guard cell protoplasts.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:4108–4112
Schwarz, W., Passow, H. 1983. Ca2+-activated K+ channels in erythrocytes and excitable cells.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 45:359–374
Smart, T.G. 1987. Single calcium-activated potassium channels recorded from cultured rat sympathetic neurones.J. Physiol. (London) 389:337–360
Smith, J.R. 1984. The electrical properties of plant cell membranes. II. Distortion of non-linear current-voltage characteristics induced by the cable properties ofChara.Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 11:211–224
Smith, C., Phillips, M., Miller, C. 1986. Purification of charybdotoxin, a specific inhibitor of the high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel.J. Biol. Chem. 261:14607–14613
Sokolik, A.I., Yurin, V.M. 1986. Potassium channels in plasmalemma ofNitella cells at rest.J. Membrane Biol. 89:9–22
Stansfield, C.E., Marsh, S.J., Halliwell, J.V., Brown, D.A. 1986. 4-aminopyridine and dendrotoxin induce repetitive firing in rat visceral sensory neurones by blocking a slowly inactivating outward current.Neurosci. Lett. 64:299–304
Tester, M., Beilby, M.J., Shimmen, T. 1987. Electrical characteristics of the tonoplast ofChara corallina: A study using permeabilised cells.Plant Cell Physiol. 28:1555–1568
Thompson, S.H. 1977. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones.J. Physiol. (London) 265:465–488
Trube, G., Rorsman, P., Ohno-Shosaku, T. 1986. Opposite effects of tolbutamide and diazoxide on the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic β-cells.Pfluegers Arch. 407:493–499
Villarroel, A., Alvarez, O., Latorre, R. 1986. Blockade of a Caactivated K channel by quaternary ammonium ions.Biophys. J. 49:576a (abstr.)
Weller, U., Bernhardt, U., Siemen, D., Dreyer, F., Vogel, W., Habermann, E. 1985. Electrophysiological and neurobiochemical evidence for the blockade of a potassium channel by dendrotoxin.Naunyn-Schmeideberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 330:77–83
Weston, A.H., Abbott, A. 1987. New class of antihypertensive acts by opening K+ channels.Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 8: 283–284
Williamson, R.E., Ashley, C.C. 1982. Free Ca2+ and cytoplasmic streaming in the algaChara.Nature (London) 296:647–651
Yellen, G. 1987. Permeation in potassium channels: Implications for channel structure.Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 16:227–246
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tester, M. Pharmacology of K+ channels in the plasmalemma of the green algaChara corallina . J. Membrain Biol. 103, 159–169 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870946
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870946