Summary
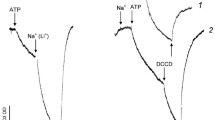
Dunaliella acidophila is an unicellular green alga which grows optimally at pH 0–1 while maintaining neutral internal pH. A plasma membrane preparation of this algae has been purified on sucrose density gradients. The preparation exhibits vanadatesensitive ATPase activity of 2 μmol Pi/mg protein/min, an activity 15 to 30-fold higher than that in the related neutrophilic speciesD. salina. The following properties suggest that the ATPase is an electrogenic plasma membrane H+ pump. (i) ATP induces proton uptake and generates a positive-inside membrane potential as demonstrated with optical probes. (ii) ATP hydrolysis and proton uptake are inhibited by vanadate, diethylstilbestrol, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and erythrosine but not by molybdate, azide or nitrate. (iii) ATP hydrolysis and proton uptake are stimulated by fussicoccin in a pH-dependent manner as found for plants plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Unusual properties of this enzyme are: (i) theK m for ATP is around 60 μM, considerably lower than in other plasma membrane H+-ATPases, and (ii) the ATPase activity and proton uptake are stimulated three to fourfold by K+ and to a smaller extent by other monovalent cations. These results suggest thatD. acidophila possesses a vanadate-sensitive H+-ATPase with unusual features enabling it to maintain the large transmembrane pH gradient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertano, P., Pinto, G., Santisi, S., Taddei, R. 1982.Spermatosopsis acidophila Kalina, a little known alga from highly acidic environment.G. Botanico Italiano 115:65–76
Ames, B.N. 1966. Assay of inorganic phosphate total phosphate and phosphatases.In: Methods in Enzymology. S.P. Colowick, and N.O. Kaplan, editors. Vol. 8, pp. 115–118. Academic, New York
Blatt, M., Clint, G.M. 1989. Mechanism of fusicoccin action: Kinetic modification and inactivation of K+ channeles in guard cells.Planta 178:509–529
Bowman, B.J., Blasco, F., Slayman, C.W. 1981. Purification and characterization of the plasma membrane ATPase ofNeurospora crassa.J. Biol. Chem. 256:12343–12349
Briskin, D.P. 1986. Plasma membrane H+ transporting ATPase: Role in K+ ion transport.Physiol. Plant. 68:159–163
Briskin, D.P. 1988. Chemical equivalence of phosphoenzyme reaction states in the catalytic mechanism of the red beet (Beta vulgaris L.) plasma membrane ATPase.Plant Physiol. 88:77–83
Dufour, J.P., Goffeau, A. 1980. Molecular and kinetic properties of the purified plasma membrane ATPase of the yeastSchizosaccharomyces pombe.Eur. J. Biochem. 105:145–154
Feyerbend, M., Weiler, E.W. 1988. Characterization and localization of fusicoccin-binding sites in leaf tissues ofVicia faba L. probed with a novel radio ligand.Planta 174:115–122
Gilmour, D.J., Kaadem, R., Gimmler, H. 1985. Vanadate inhibition of ATPases ofDunaliella parva in vitro and in vivo.J. Plant. Physiol. 118:111–126
Gimmler, H., Bental, M., Degani, H., Avron, M., Pick, U. 1989a. H+ export capacity ofDunaliella acidophila and the permeability of the plasma membrane for H+ and weak acids.In: Current Research in Photosynthesis. M. Baltcheffsky, editor. Vol. IV, pp. 773–776 Kluwer Academic, The Netherlalands
Gimmler, H., Weis, U., Weiss, C., Kugel, H., Treffny, B. 1989b.Dunalliella acidophila (Kalina) masyuk-an alga with a positive membrane potential.New Phytol. 113d:175–184
Gläser, H.U., Höfer, M. 1987. Ion-dependent generation of the electrochemical proton gradient ΔμH+ in reconstituted plasma membrane vesicles from the yeastMetschnikovia reukaufii.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 905:287–294
Gläser, H.U., Sekler, I., Pick, U. 1990. Indications for a K+/H+ cotransport system in plasma membranes from two acidophilic organisms.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1019:293–299
Goffeau, A., Slayman, C.W. 1981. The proton translocating ATPase of the fungal plasma membrane.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 639:197–223
Harper, J.E., Surowy, T.R., Sussman, M.R. 1989. Molecular cloning and sequence of cDNA encoding the plasma membrane H+-ATPase from the plantArabidopsis thaliana.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:1234–1238
Markwell, M.A., Haas, S.M., Bieber, L.L., Tolbert, W.E. 1978. A modification of the Lowery procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples.Anal. Biochem. 87:206–210
Pardo, J.M., Serrano, R. 1989. Structure of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase gene from the plantArabidopsis thaliana.J. Biol. Chem. 264:8557–8562
Rasi-Caldogno, F., Demichelis, M.I., Pugliarello, M.C., Marre, E. 1986. H+ pumping driven by the plasma membrane ATPase in membrane vesicles from radish: Stimulation by fusicoccin.Plant Physiol. 82:121–129
Serrano, R. 1988. Structure and function of proton translocating ATPase in plasma membrane of plants and fungi.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 947:1–28
Serrano, R. 1989. Structure and function of plasma membrane ATPase.Annu. Rev. Plant Mol. Biol. 40:61–94
Stout, R.G., Cleland, R.E. 1980. Partial characterization of fusicoccin binding to receptor sites on oat root membrane.Plant Physiol. 66:353–359
Sussman, M.R., Surowy, T.K. 1987. Physiology and molecular biology of membrane ATPases.Oxford Surv. Plant Mol. Cell Biol. 4:47–70
Weiss, M., Sekler, I., Pick, U. 1989. Characterization of a soluble and membrane bound forms of a vanadate sensitive ATPase from plasma membranes of the halotolerant algaDunaliella salina.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 974:254–260
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekler, I., Gläser, HU. & Pick, U. Characterization of a plasma membrane H+-ATPase from the extremely acidophilic algaDunaliella acidophila . J. Membrain Biol. 121, 51–57 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870650
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870650