Summary
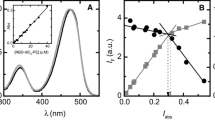
Voltage jump-current relaxation experiments have been performed with valinomycin-doped membranes of mixtures of 1,2-dipentadecylmethylidene-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine (PC) and charged-phosphatidic acid (PA). Both relaxation processes predicted by a simple carrier model could be resolved which allowed the calculation of the rate constants of the Rb+ transport. The dependence of the rate constants on the membrane composition indicates that (i) the lipids in the mixed membranes are homogeneously distributed and that (ii) no major difference exists between the composition of the membrane and that of the torus. The analysis of the stationary conductance data, however, shows that the valinomycin content of the mixed membranes depends strongly on their lipid composition. Addition of Ca++ ions to a 1∶1 mixture induces a phase separation into PA domains of very low conductivity and PC-enriched regions of high conductivity. Half saturation is reached atc ca=5×10−4 m. At 10−2 m Ca++ in the aqueous phase, the rate constants clearly indicate that all PA molecules are electrically “passivated” and only pure PC domains contribute to the membrane current. A detailed picture is thus derived of the coupling of a model transport system to the externally triggered membrane reorganization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht, O. 1979. Polymorphismus in reinen und gemischten Lipid-Monoschichten. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Ulm, Germany
Apell, H.-J., Bamberg, E., Läuger, P. 1979. Effects of surface charge on the conductance of the gramicidin channel.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 552:369–378
Benz, R., Cros, D. 1978. Influence of sterols on ion transport through lipid bilayer membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 506:265–280
Benz, R., Läuger, P. 1977. Transport kinetics of dipicrylamine through lipid bilayer membranes: Effects of membrane structure.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 468:245–258
Benz, R., Stark, G., Janko, K., Läuger, P. 1973. Valinomycin-mediated ion transport through neutral lipid membranes: Influence of hydrocarbon chain length and temperature.J. Membrane Biol. 14:339–364
Blume, A., Eibl, H. 1981. A calorimetric study of the thermotropic behaviour of 1,2-dipentadecylmethylidene phospholipids.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 640:609–618
Boheim, G., Hanke, W., Eibl, H. 1980. Lipid phase transition in planar bilayer membranes and its effect on carrier- and pore-mediated ion transport.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:3403–3407
Eibl, H., Nicksch, A. 1978. The synthesis of phospholipids by direct amination.Chem. Phys. Lipids 22:1–8
Galla, H.-J., Sackmann, E. 1975. Chemically induced phase separation in mixed vesicles containing phosphatidic acid. An optical study.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97:4114–4120
Ito, T., Ohnishi, S. 1974. Ca++-induced lateral phase separations in phosphatidic acid-phosphatidylcholine membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 352:29–37
Knoll, W. 1976. Kinetische Untersuchungen zum Rb+-Transport durch Valinomycin über künstliche Lipid-Membranen. Ph.D. Tesis, University of Konstanz, Germany
Knoll, W., Stark, G. 1975. An extended kinetic analysis of valinomycin-induced Rb-transport through monoglyceride membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 25:249–270
Krasne, S., Eisenman, G., Szabo, G. 1971. Freezing and melting of lipid bilayers and the mode of action of nonactin, valinomycin, and gramicidin.Science 174:412–415
Laclette, J.P., Montal, M. 1977. Interaction of calcium with negative lipids in planar bilayer membranes.Biophys. J. 19:199–202
Laprade, R., Ciani, S.M., Eisenman, G., Szabo, G. 1974. The kinetics of carrier-mediated ion permeation in lipid bilayers and its theoretical interpretation.In: Membranes — A Series of Advances. G. Eisenman, editor. Vol. 3, pp. 127–214. Marcel Dekker, New York
Läuger, P. 1972. Carrier-mediated ion transport.Science 178:24–30
Läuger, P., Neumcke, B. 1973. Theoretical analysis of ion conductance in lipid bilayer membranes.In: Membranes — A Series of Advances. G. Eisenman, editor. Vol. 2, pp. 1–59. Marcel Dekker, New York
Läuger, P., Stark, G. 1970. Kinetics of carrier-mediated ion transport across lipid bilayer membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 211:458–466
Lee, A.G. 1977. Lipid phase transitions and phase diagrams. II. Mixtures involving lipids.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 472:285–344
Lesslauer, W., Richter, J., Läuger, P. 1967. Some electrical properties of bimolecular phosphatidyl inositol membranes.Nature (London) 213:1224–1226
McLaughlin, S.G.A. 1977. Electrostatic potentials at membrane-solution interfaces.In: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport. F. Bronner and A. Kleinzeller, editors. Vol. 9, pp. 71–144.
Mueller, P., Rudin, D.O., Tien, H.T., Wescott, W.C. 1962. Reconstitution of excitable membrane structure in vitro and its transformation into an excitable system.Nature (London) 194:979–980
Neher, E., Eibl, H. 1977. The influence of phospholipid polar groups on gramicidin channels.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 464:37–44
Ohnishi, S., Ito, T. 1974. Calcium-induced phase separations in phosphatidylserine-phosphatidylcholine membranes.Biochim. 13:881–887
Overath, P., Schairer, H.U., Stoffel, W. 1970. Correlation of in vivo and in vitro phase transitions of membrane lipids inE. coli.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 67:606–612
Pohl, G.W., Knoll, W., Gisin, B.F., Stark, G. 1976. Optical and electrical studies on dansyllysine-valinomycin in thin lipid membranes.Biophys. Struct. Mechanism 2:119–137
Rose, B., Loewenstein, W.R. 1976. Permeability of a cell junction and the local cytoplasmic free ionized calcium concentration: A study with aequorin.J. Membrane Biol. 28:87–119
Sackmann, E. 1978. Dynamic molecular organization in vesicles and membranes.Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 82:891–909
Stark, G., Benz, R., Pohl, G.W., Janko, K. 1972. Valinomycin as a probe for the study of structural changes in black lipid membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 266:603–612
Stark, G., Ketterer, B., Benz, R., Läuger, P. 1971. The rate constants of valinomycin-mediated ion transport through thin lipid membranes.Biophys. J. 11:981–994
Szabo, G. 1974. Dual mechanism for the action of cholesterol on membrane permeability.Nature (London) 252:47–49
Träuble, H. 1971. Phasenumwandlungen in Lipiden, mögliche Schaltprozesse in biologischen Membranen.Naturwissenschaften 58:277–284
Träuble, H., Eibl, H. 1974. Electrostatic effects on lipid phase transition: Membrane structure and ionic environment.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71:214–219
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, G., Eibl, H. & Knoll, W. Carrier-mediated ion transport through black membranes of lipid mixtures and its coupling to Ca++-induced phase separation. J. Membrain Biol. 70, 147–155 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870224
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870224