Summary
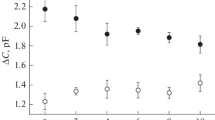
The (Na++K+)-ATPase from eel electroplax membranes is resolved into two polypeptides by means of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) preparative gel electrophoresis. From the literature, the larger polypeptide has been known to have a molecular weight in the range of 85,000 to 135,000, while the molecular weight of the smaller polypeptide is known to be between 40,000 and 60,000. When the two polypeptides are combined with a large/small molar ratio of 1∶2, a very Na+-dependent voltage-in-dependent ionophoric activity is observed. The Na+-specificity is manifested as a near absolute requirement for Na+ in order for the two polypeptides to cause an increase in conductance. Further work with tryptic digests of the two polypeptides suggests that the Na+-dependent ionophoric activity is associated with the smaller polypeptide of (Na++K+)-ATPase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers, R. W., Fahn, S., Koval, G. J. 1963. The role of sodium ions in the activation ofElectrophorus electric organ adenosine triphosphatase.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 50:474
Albers, R. W., Shamoo, A. E., Koval, G. J., Myers, M. 1973. A soluble (Na++K+)-ATPase and an associated Na+-ionophore fromElectrophorus electric organ.Ninth Int. Congr. Biochem., Stockholm, Sweden, July 1–7
Blumenthal, R., Shamoo, A. E. 1974. Ionophoric material derived from eel membrane preparations. II. Electrical characteristics.J. Membrane Biol. 19:141
Collins, R. C., Albers, R. W. 1972. The phosphoryl acceptor protein of Na−K-ATPase from various tissues.J. Neurochem. 19:1209
Diamond, J. M., Wright, E. M. 1969. Biological membranes: The physical basis of ion and nonelectrolyte selectivity.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 31:581
Eisenman, G. 1962. Cation selective glass electrodes and their mode of operation.Biophys. J. 2(2):259
Eisenman, G. 1965. The electrochemistry of cation-sensitive glass electrodes.Advanc. Analyt. Chem. Inst. 4:213
Eisenman, G., Krasne, S. 1973. The selectivity of carrier antibiotics for substituted ammonium ions.Biophys. J. 13:244a
Hille, B. 1971. The permeability of the sodium channel to organic cations in myelinated nerve.J. Gen. Physiol. 58:599
Hokin, L. E., Dahl, J. L., Deupree, J. D., Dixon, J. F., Perdue, J. F. 1973. Studies on the characterization of the sodium-potassium transport adenosine triphosphatase. X. Purification of the enzyme from the rectal gland ofSqualus acanthias.J. Biol. Chem. 248:2593
Jain, M. K., Mehl, L. E., Cordes, E. H. 1973. Incorporation of eel electroplax acetylcholinesterase into black lipid membranes. A possible model for the cholinergic receptor.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 51:192
Kyte, J. 1971a. Purification of the sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase from canine renal medulla.J. Biol. Chem. 246:4157
Kyte, J. 1971b. Phosphorylation of a purified (Na++K+)-adenosine triphosphatase.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 43:1259
Kyte, J. 1972. Properties of the two polypeptides of sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase.J. Biol. Chem. 247:7642
Laemmli, U. K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature 227:680
Sachs, G., Spenney, J. G., Saccomani, G., Goodall, M. C. 1974. Characterization of gastric mucosal membranes. VI. The presence of channel-forming substances.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 332:233
Shamoo, A. E., Albers, R. W. 1973a. Na+-selective ionophoric material derived from electric organ and kidney membranes.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 70:1191
Shamoo, A. E., Albers, R. W. 1973b. Isolation of a Na-specific ionophore from kidney and electric organ membranes.Biophys. Soc. J. 13:16a
Shamoo, A. E., Myers, M., Albers, R. W. 1973. Partial purification of peptidic Na+-ionophore from a (Na++K+)-ATPase preparation.Fed. Proc. 32:258 (abs.)
Shamoo, A. E., Myers, M., Blumenthal, R., Albers, R. W. 1974. Ionophoric material derived from eel membrane preparation. I. Chemical characteristics.J. Membrane Biol. 19:129
Siegel, G. J., Albers, R. W. 1970. Nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolases.In: Handbook of Neurochemistry. A. Lajtha, editor. Vol. 4, p. 13. Plenum Press, New York
Uesugi, S., Kahlenberg, A., Medzihradsky, F., Hokin, L. 1969. Studies on the characterization of the sodium-potassium transport adenosine-triphosphatase. IV. Properties of a Lubrol solubilized beef brain microsomal enzyme.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 130:156
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was initiated while the authors were at the Laboratory of Biophysics at the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shamoo, A.E., Myers, M. Na+-dependent ionophore as part of the small polypeptide of the (Na++K+)-ATPase from eel electroplax membrane. J. Membrain Biol. 19, 163–178 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869976
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869976