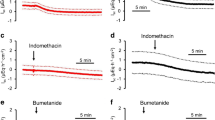
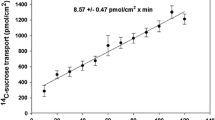
Summary
The transepithelial resistance, the cell membrane resistance and the ratio of resistances of the serosal (baso-lateral) to the mucosal (brush border) cell membrane were measured in rat duodenum, jejunum and ileum by means of microelectrode techniques. These measured values were not affected in the presence of actively transported solutes in the mucosal bathing fluid.
Contribution of an electrical conductance through the extracellular shunt pathway to the total transepithelial conductance was quantitatively estimated using an electrically equivalent circuit analysis. These values estimated in respective tissues of small intestine were approx. 95% of the total transepithelial conductance, remaining unaffected by an active solute transport.
From these data, the changes in emf's of the mucosal and serosal membrane induced byd-glucose or glycine were separately evaluated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asano, T. 1964. Metabolic disturbances and short-circuit current across intestinal wall of rat.Am. J. Physiol. 207:415
Barry, R.J.C., Smyth, D.H., Wright, E.M. 1965. Short-circuit current and solute transfer by rat jejunum.J. Physiol. (London) 181:410
Blum, A.L., Hirschowitz, B.I., Helander, H.F., Sachs, G. 1971. Electrical properties of isolated cells of necturus gastric mucosa.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 241:261
Clarkson, T.W. 1967. The transport of salt and water across isolated rat ileum.J. Gen. Physiol. 50:695
Claude, P., Goodenough, D.A. 1973. Fracture faces of zonulae occludentes from “tight” and “leaky” epithelia.J. Cell Biol. 58:390
Dobsen, J.G., Jr., Kidder, G.W., III 1968. Edge damage effect inin vitro frog skin preparations.Am. J. Physiol. 214:719
Field, M., Fromm, D., McColl, I. 1971. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. I. Na and Cl fluxes and short-circuit current.Am. J. Physiol. 220:1388
Frizzell, R.A., Schultz, S.G. 1972. Ionic conductances of extracellular shunt pathway in rabbit ileum. Influence of shunt on transmural sodium transport and electrical potential differences.J. Gen. Physiol. 59:318
Frömter, E. 1972. The route of passive ion movement through the epithelium ofNecturus gallbladder.J. Membrane Biol. 8:259
Frömter, E., Diamond, J. 1972. Route of passive ion permeation in epithelia.Nature New Biol. 235:9
Helman, S.I., Miller, D.A. 1971.In vitro techniques for voiding edge damage in studies of frog skin.Science 173:146
Helman, S.I., Miller, D.A. 1974. Edge damage effect on measurements of urea and sodium flux in frog skin.Am. J. Physiol. 226:1198
Loewenstein, W.R. 1966. Permeability of membrane junctions.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 137: (2):441
Loewenstein, W.R., Kanno, Y. 1964. Studies on an epithelial (gland) cell junction.J. Cell Biol. 22:565
Loewenstein, W.R., Socolar, S.J., Higashino, S., Kanno, Y., Davidson, N. 1965. Intercellular communication: Renal, urinary bladder, sensory, and salivary gland cells.Science 149:295
Munck, B.G. 1972. Effects of sugar and amino acid transport on transepithelial fluxes of sodium and chloride of short circuited rat jejunum.J. Physiol. 223:699
Munck, B.G., Schultz, S.G. 1974. Properties of the passive conductance pathway acrossin vitro rat jejunum.J. Membrane Biol. 16:163
Okada, Y., Inouye, A. 1976a. Studies on the origin of the tip potential of glass microelectrode.Biophys. Struct. Mech. 2:31
Okada, Y., Inouye, A. 1976b. pH-Sensitive glass microelectrodes and intracellular pH measurements.Biophys. Struct. Mech. 2:21
Okada, Y., Inouye, A. 1976c. Electrical properties and ion permeabilities in intestinal epithelia.Seibutsu Butsuri (in press) (in Japanese)
Okada, Y., Irimajiri, A., Inouye, A. 1976. Permeability properties and intracellular ion concentrations of epithelial cells in rat duodenum.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 436:15
Okada, Y., Sato, T., Inouye, A. 1975. Effects of potassium ions and sodium ions on membrane potential of epithelial cells in rat duodenum.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 413:104
Okada, Y., Tsuchiya, W., Irimajiri, A., Inouye, A. 1977. Electrical properties and active solute transport in rat small intestine. I. Potential profile changes associated with sugar and amino acid transports.J. Membrane Biol. 31:205
Reuss, L., Finn, A.L. 1974. Passive electrical properties of toad urinary bladder epithelium. Intercellular electrical coupling and transepithelial cellular and shunt conductances.J. Gen. Physiol. 64:1
Rose, R.C., Schultz, S.G. 1971. Studies on the electrical potential profile across rabbit ileum. Effects of sugars and amino acids on transmural and transmucosal electrical potential differences.J. Gen. Physiol. 57:639
Schultz, S.G., Frizzell, R.A., Nellans, H.N. 1974. Ion transport by mammalian small intestine.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 36:51
Schultz, S.G., Zalusky, R. 1964. Ion transport in isolated rabbit ileum.J. Gen. Physiol. 47:567
Silverblatt, F.J., Bulger, R.E. 1970. Gap junctions occur in vertebrate renal proximal tubule cells.J. Cell Biol. 47:513
Spenney, J.G., Shoemaker, R.L., Sachs, G. 1974. Microelectrode studies of fundic gastric mucosa: Cellular coupling and shunt conductance.J. Membrane Biol. 19:105
Ussing, H.H., Erlij, D., Lassen, U. 1974. Transport pathways in biological membranes.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 36:17
Ussing, H.H., Windhager, E.E. 1964. Nature of shunt path and active sodium transport path through frog skin epithelium.Acta Physiol. Scand. 61:484
Walser, M. 1970. Role of edge damage in sodium permeability of toad bladder and a means of avoiding it.Am. J. Physiol. 219:252
White, J.F., Armstrong, W.McD. 1971. Effect of transported solutes on membrane potentials in bullfrog small intestine.Am. J. Physiol. 221:194
Whittembury, G., Rawlins, F.A., Boulpaep, E.L. 1973. Paracellular pathway in kidney tubules: Electrophysiological and morphological evidence.In: Transport mechanism in epithelia, H.H. Ussing and N.A. Thorn, editors. P. 557. Munksgaard, Copenhagen
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okada, Y., Irimajiri, A. & Inouye, A. Electrical properties and active solute transport in rat small intestine. J. Membrain Biol. 31, 221–232 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869406
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869406