Summary
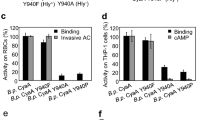
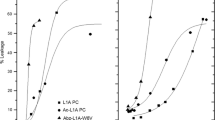
Staphylococcus aureus α-toxin causes cell damage by forming an amphiphilic hexamer that inserts into the cell membrane and generates a hydrophilic pore. To investigate the role of the three histidine residues of this toxin we modified them with diethylpyrocarbonate, obtaining N-carbethoxy-histidine whose appearance may be followed spectrophotometrically. Despite the statistical nature of random chemical modification, it was possible to establish that modification of any one of the three histidines was enough to impair α-toxin activity on red blood cells and platelets. Two out of three histidines were essential for the interaction of the toxin with model membranes such as lipid vesicles and planar bilayers. Loss of lytic activity in both natural and model membranes was due both to defective binding and to defective oligomerization. When α-toxin hexamers inserted into lipid vesicles were assayed for chemical modifiability two histidines per monomer were found to be protected from diethylpyrocarbonate modification, whereas only one was protected after delipidation of the oligomer with a detergent. A possible model for the role of each histidine in the monomer is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbuthnott, J.P., Freer, J.H., Bernheimer, A.W. 1967. Physical states of Staphylococcal α-toxin.J. Bacteriol. 94: 1170–1177
Belmonte, G., Cescatti, L., Ferrari, B., Nicolussi, T., Ropele, M., Menestrina, G. 1987. Pore formation byStaphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin in lipid bilayers: Dependence upon temperature and toxin concentration.Eur. Biophys. J. 14:349–358
Bhakdi, S., Mackman, N., Nicaud, J.-M., Holland, I.B. 1986Escherichia coli hemolysin may damage target cell membranes by generating transmembrane pores.Infect. Immun. 52:63–69
Bhakdi, S., Muhly, M., Mannhardt, U., Hugo, F., Klappatek, K., Mueller-Eckhardt, C., Roka, L. 1988. Staphylococcal α-toxin promotes blood coagulation via attack on human platelets.J. Exp. Med. 168:527–542
Bhakdi, S., Tranum-Jensen, J. 1987. Damage to mammalian cells by proteins that form transmembrane pores.Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 107:147–223
Blomqvist, L., Thelestam, M. 1986. Early events in the action of Staphylococcal alpha-toxin on the plasma membrane of adrenocortical Y1 tumor cells.Infect. Immun. 53:636–640
Cassidy, P., Harshman, S. 1976. Studies on the binding of Staphylococcal125I-labeled α-toxin to rabbit erythrocytesBiochemistry 15:2348–2355
Cescatti, L., Pederzolli, C., Menestrina, G. 1991. Modification of lysine residues ofStaphylococcus aureus α-toxin: Effects on its channel-forming properties.119:53–64
Forti, S., Menestrina, G. 1989. Staphylococcal α-toxin increases the permeability of lipid vesicles by a cholesterol and pH dependent assembly of oligomeric channels.Eur. J. Biochem. 181:767–773
Freer, J.H. 1982. Cytolytic toxins and surface activity.Toxicon 20:217–221
Freer, J.H., Arbuthnott, J.P. 1983. Toxins ofStaphylococcus aureus.Pharmac. Ther. 19:55–106
Freer, J.H., Arbuthnott, J.P., Bilcliffe, B. 1973. Effects of Staphylococcal α-toxin on the structure of erythrocytes membranes.J. Gen. Microbiol. 75:321–332
Füssle, R., Bhakdi, S., Sziegoleit, A., Tranum-Jensen, J., Kranz, T., Wellensiek, H.J. 1981. On the mechanism of membrane damage byStaphylococcus aureus α-toxin.J. Cell. Biol. 91:83–94
Gray, G.S., Kehoe, M. 1984. Primary sequence of the α-toxin gene fromStaphylococcus aureus Wood 46.Infect. Immun. 46:615–618
Horiike, K, McCormick, D.B. 1979. Correlation between biological activity and the number of functional groups chemically modified.J. Theor. Biol. 79:403–414
Ikigai, H., Nakae, T. 1984. The rate assay of alpha-toxin assembly in membrane.FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 24:319–322
Ikigai, H., Nakae, T. 1985. Conformational alterations in alpha-toxin fromStaphylococcus aureus, concomitant with the transformation of the water-soluble monomer to the membrane oligomer.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 130:175–181
Kim, Y.S., Park, C. 1988. Inactivation ofAcinetobacter clacoaceticus acetate kinase by diethylpyrocarbonate.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 956:103–109
Kinsman, O., Johnson, P., Haraldsson, I., Lindberg, M., Arbuthnott, J.P., Wadstrom, T. 1981. Decreased virulence of α-haemolytic negative and coagulase negative mutants ofStaphylococcus aureus in experimental infections in mice.In: Staphylococci and Staphylococcal Infections. J. Jeljaszewicz, editor.Zentralbl. Backteriol Suppl. 10, pp. 651–659. Gustav-Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature (London) 227:680–685
McCartney, A.C., Arbuthnott, J.P. 1978. Mode of action of membrane damaging toxins produced by staphylococci.In: Bacterial Toxins and Cell Membranes. J. Jeljaszewicz and T. Wadström, editors. pp. 89–127. Academic, London
Menestrina, G. 1986. Ionic channels formed byStaphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin: Voltage-dependent inhibition by divalent and trivalent cations.J. Membrane Biol. 90:177–190
Menestrina, G. 1988.Escherichia coli hemolysin permeablizes small unilamellar vesicles loaded with calcein by a single hit mechanism.FEBS Lett. 232:217–220
Meyer, S.E., Cromartie, T.H. 1980. Role of essential histidine residues inl-α-hydroxy acid oxidase from rat kidney.Biochemistry 19:1874–1881
Miles, E.W. 1977. Modification of histidyl residues in proteins by diethylpyrocarbonate.Methods. Enzymol. 47:431–442
Radomski, M., Moncada, S. 1983. An improved method for washing of human platelets with prostacyclin.Thromb. Res. 30:383–389
Reichwein, J., Hugo, F., Roth, M., Sinner, A., Bhakdi, S. 1987. Quantitative analysis of the binding and oligomerization of Staphylococcal alpha-toxin in target erythrocyte membranes.Infect. Immun. 55:2940–2944
Thelestam, M., Blomqvist, L. 1988. Staphylococcal α-toxin — recent advances.Toxicon 26:51–65
Tobkes, N., Wallace B.A., Bayley, H. 1985. Secondary structure and assembly mechanism of an oligomeric channel protein.Biochemistry 24:1915–1920
Tsou, C.-L. 1962. Relation between modification of functional groups of proteins and their biological activity: I. A graphical method for the determination of the number and type of essential groups.Sci. Sin. 11:1535–1558
Watanabe, M., Tomita, T., Yasuda, T. 1987. Membranedamaging action of staphylococcal α-toxin on phospholipid cholesterol liposomes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 898:257–265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pederzolli, C., Cescatti, L. & Menestrina, G. Chemical modification ofStaphylococcus aureus α-toxin by diethylpyrocarbonate: Role of histidines in its membrane-damaging properties. J. Membrain Biol. 119, 41–52 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868539
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868539