Summary
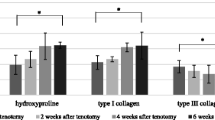
Changes in the collagen types and cross-linking of granulation and scar tissue in the injured site of partially ruptured gastrocnemius muscle were studied after a reproducible contusion injury to the left calf of a rat. In normal i.m. collagen the proportion of Type I collagen was considerably higher than Type III. Following injury there was a rapid increase in the proportion of Type III collagen reaching a maximum at 5 days after injury. After a further 2 days the proportion of Type I had increased significantly resulting in a decrease of the Type III/I ratio to below that of the control. However, as healing progressed there was a gradual shift back to the Type III/I ratio for normal i.m. collagen.
The collagen produced in response to an injury was initially stabilized by the stable keto-imine cross-link hydroxylysino-5-keto-norleucine, characteristic of embryonic collagenous tissues. The proportion of the stable ketoimine cross-link gradually decreased, and a reversion to the cross-link pattern of normal uninjured i.m. collagenous connective tissue occurred towards the end of the 42-day follow-up period.
The present biochemical study demonstrates that during the early phases of the repair process there is a reversion to the collagens typically present in high proportions in embryonic dermal connective tissue. This suggests that the fibroblasts have the ability to modify their product expression under varying circumstances. The study also demonstrates the importance of collagen cross-linking in determining the tensile strength of collagen fibre during the repair process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allbrook D, de Baker C, Kirkaldy-Willis WH (1966) Muscle regeneration in experimental animals and in man. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 48:153–169
Anttinen H, Orava S, Ryhänen L, Kivirikko K (1973) Assay of procollagen lysyl hydroxylase activity in the skin of human subjects and changes in the activity with age. Clin Chim Acta 47:289–295
Bailey AJ (1974) Tissue and species specificity in the cross-linking of collagen. Pathol Biol 22:675–680
Bailey AJ, Bazin S, Delaunay A (1973) Changes in the nature of the collagen during development and resorption of granulation tissue. Biochem Biophys Acta 328:383–390
Bailey AJ, Bazin S, Sims TJ, Le Lous M, Nicoletis C, Delaunay A (1975) Characterization of the collagen of human hypertrophic and normal scars. Biochem Biophys Acta 405:412–421
Bailey AJ, Robins SP, Balian G (1974) Biological significance of the intermolecular cross-links of collagen. Nature 251:105–109
Bailey AJ, Sims TJ (1976) Chemistry of the collagen cross-links. Nature of the cross-links in the polymorphic forms of dermal collagen during development. Biochem J 153:211–215
Bailey AJ, Sims TJ (1977) Meat tenderness: distribution of molecular species of collagen in bovine muscle. J Sci Food Agric 28:565–570
Bailey AJ, Sims TJ, Le Lous M, Bazin S (1975) Collagen polymorphism in experimental granulation tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 66:1160–1165
Barnes JM, Constable BJ, Morton LF, Royce PM (1974) Age-related variations in hydroxylation of lysine and proline in collagen. Biochim J 139:461–468
Barnes MJ, Morton LF, Bailey AJ, Bennett RC (1975) Studies on collagen synthesis in the mature dermal scar in the guinea pig. Br Biochem Soc Trans 3:917–918
Clore JN, Cohen IK, Diegelmann RF (1979) Quantitation of collagen Types I and III during wound healing in rat skin. Prog Soc Exp Biol Med 161:337–340
Duance VC, Restall DJ, Beard H, Bourne FJ, Bailey AJ (1977) The location of three collagen types in skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett 79:248–252
Epstein EH (1974) [α 1(III)]3 Human skin collagen. J Biol Chem 249:3225–3231
Foidart M, Foidart J-M, King-Engel W (1981) Collagen localization in normal and fibrotic human skeletal muscle. Arch Neurol 38:152–157
Gabbiani G, Le Lous M, Bailey AJ, Bazin S, Delaunay A (1976) Collagen and myofibroblasts of granulation tissue. A chemical, ultrastructural and immunologic study. Virchows Arch [Cell Pathol] 21:133–145
Gay S, Martin G, Müller P, Timpl R, Kühn K (1976) Simultaneous synthesis of Types I and III collagen by fibroblasts in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:4037–4040
Gay S, Viljanto J, Raekallio J, Penttinen R (1978) Collagen types in early phases of wound healing in children. Acta Chir Scand 144:205–211
Grant RA (1964) Estimation of hydroxyproline by the auto analyzer. J Clin Pathol 17:685–686
Hasselbach W, Schneider G (1951) L-Myosin and actin contents of rabbit muscle. Biochem Z 321:462–475
Jackson DW, Feagin JA (1973) Quadriceps contusions in young athletes. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 55:95–105
Järvinen M, Sorvari T (1975) Healing of a crush injury in rat striated muscle 1. Description and testing of a new method in inducing a standard injury to the calf muscles. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand [A] 83:259–265
Järvinen M (1975) Healing of a crush injury in rat striated muscle 2. A histological study of the effect of early mobilization and immobilization on the repair processes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand [A] 83:269–282
Järvinen M (1976) Healing of a crush injury in rat striated muscle 4. Effect of early mobilization and immobilization on the tensile properties of gastrocnemius muscle. Acta Chir Scand 142:47–56
Kurkinen M, Vaheri A, Roberts P, Stenman S (1980) Sequential appearance of fibronectin and collagen in experimental granulation tissue. Lab Invest 43:47–51
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–682
Laemmli UK, Favre M (1973) Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol 80:575–599
Lapière CM, Nusgens B, Pierard GE (1977) Interaction between collagen Type I and III in conditioning bundles organization. Connect Tiss Res 5:21–29
Light ND (1979) Bovine Type I collagen: a study in cross-linking in various mature tissues. Biochem Biophys Acta 581:96–105
Light ND (1982) Estimation of Types I and III collagens in whole tissues by quantitation of CNBr peptides on SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Acta 702:30–36
Light ND, Bailey AJ (1979) Changes in cross-linking during aging in bovine tendon collagen. FEBS Lett 97:183–188
Light ND, Bailey AJ (1980) The chemistry of the collagen cross-links. Purification and characterization of cross-linked polymeric peptide material from mature collagen containing unknown aminoacids. Biochem J 185:373–381
Millar AP, Salmon J (1967) Muscle tears. Aust J Sports Med 2:435–438
Robins SP, Bailey AJ (1977) Some observations on the aging in vitro of reprecipitated collagen fibres. Biochem Biophys Acta 492:408–414
Robins SP, Shimokomaki M, Bailey AJ (1973) The chemistry of the collagen cross-links age related changes in the reducible components of intact bovine collagen fibers. Biochem J 131:771–780
Wiedemann H, Chung E, Fujii E, Miller EJ, Kühn K (1975) Comparative electronmicroscope studies on Type III and Type I collagens. Eur J Biochem 51:363–368
Viljanto J (1976) Cellstric: a device for wound healing studies in man. Description of the method. J Surg Res 20:115–119
Woessner JF Jr (1961) The determination of hydroxyproline in tissue and protein samples containing small proportions of this imino acid. Arch Biochem Biophys 93:440–447
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the Research Council for Physical Education and Sport, Ministry of Education, Finland
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lehto, M., Sims, T.J. & Bailey, A.J. Skeletal muscle injury—molecular changes in the collagen during healing. Res. Exp. Med. 185, 95–106 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01854894
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01854894