Summary
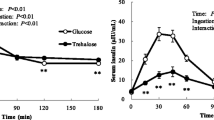
In blind studies the effects of a newα-glucosidase inhibitor (BAY g 5421) were tested in normal weight and overweight male volunteers after oral application of 75, 150, or 300 mg of BAY g 5421 or placebo per os before three standardized main meals of one day. Before and three hours after each meal blood glucose, serum insulin, and serum triglyceride levels were determined. In addition, safety studies were performed.
BAY g 5421 induced a statistically significant, in part dose-dependent inhibition of the postprandial increase of blood glucose- and serum insulin levels. The reduction of the postprandial increase of serum triglyceride levels was variable. Routine blood chemistry and hematology tests have revealed no adverse side effects; but the application of the drug was frequently associated with intestinal effects, such as flatulence and diarrhea, which were substrate (carbohydrate) and, in part, dose-dependent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berchtold, P., Hillebrand, I., Boehme, K., Frank, G., Fink, H.: Effects of the glycosidehydrolase inhibitor BAY g 5421 on postprandial blood glucose-, serum insulin- and triglyceride levels in normal and overweight subjects. Diabetologia15, 218 (1978)
Berchtold, P., Kiesselbach, N.: Unpublished results from clinical trials conducted by Bayer (1976)
Bryce, G. R., Carter, M. W.: MAD—The analysis of variance in unbalanced designs—a software package. In: Compstat 1974, Proc. computational statistics, pp. 447–456. Wien: Physica Verlag 1974
Caspary, W. F.: Sucrose malabsorption in man after ingestion ofα-glucosidehydrolase inhibitor. Lancet1978 I, 1231–1233
Caspary, W. F., Graf, S.: Hemmung Kohlenhydrat-verdauender Enzyme aus menschlichem Dünndarm durch ein komplexes Oligosaccharid. 13. Kongress Dtsch. Diabetesgesellschaft Düsseldorf 1978 (abstract)
Cleave, T. L., Campbell, D. G., Painter, N. S.: Diabetes, coronary thrombosis and the saccharine disease. Bristol: Wright and Sons 1969
Den Besten, L., Reyna, R. H., Connor, W. E., Stegink, L. D.: The different effects on the serum lipids and fecal steroids of high carbohydrate diets given orally or intravenously. J. Clin. Invest.52, 1284–1393 (1973)
Eggstein, M., Kreutz, F. H.: Eine neue Bestimmung der Neutralfette im Blutserum und Gewebe. Klin. Wschr.44, 262 (1966)
Gries, F. A., Koschinsky, Th., Berchtold, P.: Obesity, diabetes, and hyperlipoproteinemia. Atherosclerosis Rev., Vol. 4, pp. 71–95. New York: Raven Press 1979
Hillebrand, S. S. (ed.): Is the risk of becoming diabetic affected by sugar consumption? 8th Int. Sugar Research Symposium Washington D.C. Bethesda, Md.: Int. Sugar Res. Found. 1974
Huggett, A. St., Nixon, D. A.: Use of glucose oxidase, peroxidase and O-Dianisidine in determination of blood and urinary glucose. Lancet273, 363–370 (1957)
Jaeger, H., Krause, U., Wolf, E., Cordes, U., Beyer, J.: Nachweis der verbesserten Kohlehydrattoleranz bei insulinpflichtigen, stark schwankenden Diabetikern durch Einsatz eines neuen Saccharasehemmers. 84. Tagung Dtsch. Ges. Inn. Med. 1978 (Abstract 394)
Melani, F., Ditschuneit, F., Bartelt, K. M., Friedrich, H., Pfeiffer, E. F.: Über die radioimmunologische Bestimmung von Insulin im Blut. Klin. Wschr.43, 1000–1007 (1965)
Puls, W., Keup, U.: Metabolic studies with an amylase inhibitor in acute starch loading tests in rats and men and its influence on the amylase content of the pancreas. In: Recent advances in obesity research, A. Howard, ed., Vol. I, p. 391. London: Newman Publ. 1975
Puls, W., Keup, U., Krause, H. P., Thomas, G., Hoffmeister, F.: Glucosidase inhibition. A new approach to the treatment of diabetes, obesity, and hyperlipoproteinemia. Naturwissenschaften64, 536 (1977)
Roberts, A. M.: Dietary sucrose and serum triglyceride levels. Am. Heart J.88, 808–809 (1974)
Sachse, G., Willms, B.: Wirkung desα-Glucosidasehemmers BAY g 5421 auf die Stoffwechsellage sulfonylharnstoffbehandelter und insulinpflichtiger Diabetiker. 13. Kongress Dtsch. Diabetesges. Düsseldorf 1978 (Abstract)
Schmidt, D. D., Frommer, W., Junge, B., Müller, L., Wingender, W., Truscheit, E., Schäfer, D.:α-glucosidase inhibitors. New complex oligosaccharides of microbial origin. Naturwissenschaften64, 535–536 (1977)
Walton, R. I., Alberti, K. G. M. M., Goulder, T. J., Noy, G. A., Sterif, I. T.: Modification of glycaemic and metabolic responses to meals in insulin-dependent diabetics by alterations in digestion and absorption of sugars. Paediat. Adolesc. Endocrinol. 1978 (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hillebrand, I., Boehme, K., Frank, G. et al. The effects of theα-glucosidase inhibitor BAY g 5421 (Acarbose) on meal-stimulated elevations of circulating glucose, insulin, and triglyceride levels in man. Res. Exp. Med. 175, 81–86 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01851236
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01851236