Abstract
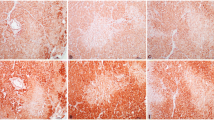
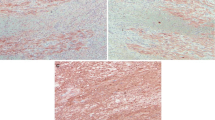
Antibodies (abs) against the terminal complement complex (C5b-9) were used on routinely processed post mortem myocardial tissue in parallel with conventional staining methods. Both monoclonal and polyclonal abs were tested using the avidin biotin peroxidase complex (ABC), alkaline phosphatase anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP) methods and an ab-bridge with alkaline phosphatase. Enhancement of the diaminobenzene (DAB) end product with cobalt-nickel (ABC method) was also done. The polyclonal ab gave the most satisfactory results and the alkaline phosphate conjugated ab-bridge had a slight advantage over the ABC method. Cobalt-nickel enhancement of DAB improved the visualization, but with higher background staining. APAAP was the least satisfactory method. Comparing the immunohistochemical method with the conventional staining methods, the former showed positive reaction in 97% of areas of coagulation necrosis and in 65% of contraction band necrosis. On the other hand coagulation necrosis was seen in 44% and contraction band necrosis in 68% of C5b-9 positive areas indicating that C5b-9 abs react with ischemically damaged myocytes before visible alterations are seen in hematoxilin-eosin staining. Moreover, using C5b-9 abs, it seems possible to exclude agonal/artefactual contraction bands which show a negative reaction. Immunohistochemical detection of C5b-9, using an adequate technique could increase the possibility to demonstrate early ischemic myocardial damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JC (1981) Heavy methal intensification of DAB-based HRP reaction product. J Histochem Cytochem 29:775
Baroldi G, Falzi G, Mariano F (1979) Sudden coronary death. A postmortem study in 208 selected cases compared to 97 “control” subjects. Am Heart J 98:20–31
Bhakdi S, Tranum-Jensen J (1983) Membrane damage by complement. Biochem Biophys Acta 731:343–372
Brinkmann B, Sepulchre MA, Fechner G (1993) The application of selected histochemical and immunocytochemical markers and procedures to the diagnosis of early myocardial damage. Int J Legal Med 106: 135–141
Hugo F, Hamdoch T, Mathey D, Schäfer H, Bhakdi S (1990) Quantitative measurement of SC5b-9(m) in infarcted myocardium. Clin Exp Immunol 81:132–136
Karch SB, Billingham ME (1984) Morphologic effect of defibrillation: a preliminary report. Crit Care Med 12:920–921
Karch SB, Billingham ME (1986) Myocardial contraction bands revisited. Hum Pathol 17:9–13
Kloner RA, Ganote CE, Whalen DA, Jennings RB (1974) Effect of a transient period of ischemia on myocardial cells. II. Fine structure during the first few minutes of reflow. Am J Pathol 74: 399–422
Leadbetter S, Wawman HM, Jasani B (1989) Immunocytochemical diagnosis of early myocardial ischaemic/hypoxic damage. Forensic Sci Int 40:171–180
Leadbetter S, Wawman HM, Jasani B (1990) Further evaluation of immunocytochemical staining in the diagnosis of early myocardial ischaemic/hypoxic damage. Forensic Sci Int 45: 135–141
Schäfer H, Mathey D, Hugo F, Bhakdi S (1986) Deposition of the terminal C5b-9 complement complex in infarcted areas of human myocardium. J Immunol 137:1945–1949
Thomsen H, Held H (1995) Immunohistochemical detection of C5b-9(m) in myocardium: an aid in distinguishing infarctioninduced ischemic heart muscle necrosis from other forms of lethal injury. Forensic Sci Int 71: 87–95
Thomsen H, Schulz A, Bhakdi S (1990) Immunhistochemische C5b-9-komplement-komplex-darstellung in Frdhstadien der Herzmuskelnekrosen am Paraffinschnitt. Z Rechtsmed 103: 199–206
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edston, E., Kawa, K. Immunohistochemical detection of early myocardial infarction. An evaluation of antibodies against the terminal complement complex (C5b-9). Int J Leg Med 108, 27–30 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01845613
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01845613