Abstract
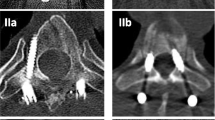
A prospective study of the accuracy of titanium pedicle screw placement in 30 low back operations was performed. The postoperative plain radiographs and CT reformation images were evaluated by two independent radiologists. Thirty-two out of 152 screws (21%) perforated the pedicle cortex. One-tenth of the perforations was detected with conventional radiography. In ten patients (33%) all the screws were located within the pedicle. The clinical significance of this study lies in the finding that pedicle perforations are more frequent than is generally believed and that, in spite of the many malplacements, no screw that perforated by less than 4.0 mm caused neurological problems. Only one nerve root lesion was detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castro WH, Halm H, Jerosch J, Malms J, Steinbeck J, Blasius S (1996) Accuracy of pedicle screw placement in lumbar vertebrae. Spine 21:1320–1324
Esses SI, Sachs BL, Dreyzin V (1993) Complications associated with the technique of pedicle screw fixation — a selected survey of ABS members. Spine 18:2231–2239
Farber GL, Place HM, Mazur RA, Jones C, Damiano TR (1995) Accuracy of pedicle screw placement in lumbar fusions by plain radiographs and computed tomography. Spine 20:1494–1499
George DC, Krag MH, Johnson CC, Van Hal ME, Haugh LD, Grobler LJ (1991) Hole preparation techniques for transpedicle screws — effect on pullout strength from human cadaveric vertebrae. Spine 16:181–184
Gertzbein SD, Robbins SE (1990) Accuracy of pedicular screw placement in vivo. Spine 15:11–14
Louis R (1983) Surgery of the spine. Surgical anatomy and operative approaches. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 114
Soini J, Laine T, Pohjolainen T, Hurri H, Alaranta H (1993) Spondylodesis augmented by transpedicular fixation in the treatment of olisthetic and degenerative conditions of the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop 297:111–116
Steinman JC, Herkowitz HN, El-Kommos H, Wesolowski P (1993) Spinal pedicle fixation: confirmation of an image-based technique for screw placement. Spine 18:1856–1861
Weinstein JN, Spratt KF, Spengler D, Brick C, Reid S (1988) Spinal pedicle fixation: reliability and validity of roentgenogram-based assessment and surgical factors on successful screw placement. Spine 13:1012–1018
Yoo J, Ghanayem A, Petersilge C, Lewin J (1996) Accuracy of identifying pedicle screw placement using CT scan images. Abstract 78. Proceedings of the Scoliosis Research Society, Annual Meeting, Ottawa
Zindric MR, Wiltse LL, Doornik A, Widell EH, Knight GW, Patwardhan AG, Thomas JC, Rothman SL, Fields BT (1987) Analysis of the morphometric characteristics of the thoracic and lumbar pedicles. Spine 12:160–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laine, T., Mäkitalo, K., Schlenzka, D. et al. Accuracy of pedicle screw insertion: A prospective CT study in 30 low back patients. Eur Spine J 6, 402–405 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01834068
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01834068