Summary
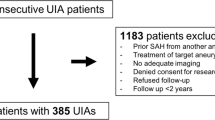
Of 1076 patients with intracranial ruptured aneurysms (RA) included in the Danish Aneurysm Study, 948 had the RA verified by angiography. Of these cases 908 RA had a maximum diameter less than 25 mm. 162 RA were <5 mm, 474 and 272 were between 5–10 mm and 11–24 mm, respectively. The average diameter of the RA according to the day of angiography after the aneurysm rupture did not differ significantly within the first 10 days. In these circumstances, using this indirect method for estimation of aneurysm rupture according to the size, we also recommend that unruptured aneurysms with a size 10 mm or less should be seriously considerated for operation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allcock JM, Canham PB (1976) Angiographic study of the growth of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 45: 617–621
Auer LM (1991) Unfavourable outcome following early surgical repair of ruptured cerebral aneurysms — a critical review of 238 patients. Surg Neurol 35: 152–158
Bailes JE, Spetzler RF, Hadley MN,et al (1990) Management morbidity and mortality of poor-grade aneurysm patients. J Neurosurg 72: 559–566
Bonita R, Thomson S (1985) Subarachnoid haemorrhage: epidemiology, diagnosis, management, and outcome. Stroke 4: 591–594
de Boulay GH (1965) Some observations on the natural history of intracranial aneurysms. Br J Radiol 38: 721–757
van Crevel H, Habbema JDF, Braakman R (1986) Decision analysis of the management of incidental intracranial saccular aneurysms. Neurology 36: 1335–1339
Cromptom MR (1966) Mechanism of growth and rupture in cerebral berry aneurysms. Br Med J 1: 1138–1142
Dell S (1982) Asymptomatic cerebral aneurysm: assessment of its risk of rupture. Neurosurgery 10: 162–166
Dion J, Gates P, Fox AJ,et al (1986) Clinical events following neuroangiography. Acta Radiol [Suppl] (Stockh) 369: 29–33
Drake CG, Girvin JP (1976) The surgical treatment of subarachnoid haemorrhage with multiple aneurysms. In: Morley TP (ed) Current controversies in neurosurgery. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 274–278
Drake CG (1981) Management of cerebral aneurysms. Stroke 3: 273–283
Earnest F, Forbes G, Sandok B,et al (1984) Complications of cerebral angiography: prospective assessment of risk. AJR 142: 247–253
Eskesen V, Rosenørn J, Schmidt K,et al (1987) Clinical features and outcome in 48 patients with unruptured intracranial saccular aneurysms: a prospective consecutive study. Br J Neurosurg 1: 47–52
Eskesen V, Rosenørn J, Schmidt K (1988) The influence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on life expectancy in relation to their size at the time of detection and age. Br J Neurosurg 2: 379–384
Eskesen V, Rosenørn J, Schmidt K (1989) The size of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. In: Bhatia R, Bhatia S (eds) Book of abstracts of 9th International Congress of Neurological Surgery. New Delhi, p 48
Ferguson GG (1972) Physical factors in the initiation, growth, and rupture of human intracranial saccular aneurysms. J Neurosurg 37: 666–667
Fogelholm R (1981) Subarachnoid haemorrhage in Middle-Finland: incidence, early prognosis, and indications for neurosurgical treatment. Stroke 3: 296–301
Garraway WM, Whisnant JP, Furlan AJ,et al (1979) The declining incidence of stroke. N Engl J Med 300: 449–452
Graf CJ (1971) Prognosis for patients with nonsurgically treated aneurysms. Analysis of the co-operative study of intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurosurg 35: 438–443
Hashimoto N, Handa H (1983) The size of cerebral aneurysms in relation to repeated rupture. Surg Neurol 19: 107–111
Hauerberg J, Andersen BB, Eskesen V,et al (1991) Importance of the recognition of a warning leak as a sign of a ruptured intracranial aneurysm. Acta Neurol Scand 83: 61–64
Heiskanen O, Marttila I (1970) Risk of rupture of a second aneurysm in patients with multiple aneurysms. J Neurosurg 32: 295–299
Heiskanen O (1981) Risk of bleeding from unruptured aneurysms in cases with multiple intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 55: 524–526
Heiskanen O (1986) Risks of surgery for unruptured intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 65: 451–453
Hijdra A, Braakman R, van Gijn J,et al (1987) Aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Complications and outcome in a hospital population. Stroke 18: 1061–1067
Jane JA, Kassell NF, Torner JC,et al (1985) The natural history of aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 62: 321–323
Jomin M, Lesion F, Lozes G (1984) Prognosis with 500 ruptured and operated intracranial aneurysms. Surg Neurol 21: 13–18
Kassell NF, Drake CG (1982) Timing of aneurysm surgery. Neurosurgery 10: 514–519
Kassell NF, Torner JC (1983) Size of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 12: 291–297
Kassell NF, Torner JC (1983) Aneurysmal rebleeding: a preliminary report from the cooperative aneurysm study. Neurosurgery 5: 479–481
Kassell NF, Torner JC, Haley EC Jr,et al (1990) The international cooperative study on the timing of aneurysm surgery. Part 1: overall management results. J Neurosurg 73: 18–36
Kassell NF, Torner JC, Jane JA,et al (1990) The international cooperative study on the timing of aneurysm surgery. Part 2: Surgical results. J Neurosurg 73: 37–47
Kristensen MØ (1983) Increased incidence of bleeding intracranial aneurysms in Greenlandic Eskimos. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 67: 37–43
Ljunggren B, Säveland H, Brandt L,et al (1985) Early operation and overall outcome in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurosurg 62: 547–551
Locksley HB (1966) Report on the cooperative study of intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid haemorrhage. Section V, part II. Natural history of subarachnoid haemorrhage, intracranial aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 25: 321–368
McCaughey WTE (1956) Ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Ulster Med J 25: 111–118
Marttila I, Heiskanen O (1970) Value of neurological and angiographic signs as indicators of the ruptured aneurysm in patients with multiple intracranial aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 23: 95–102
McCormick WF, Acosta-Rua GJ (1970) The size of intracranial saccular aneurysms. An autopsy study. J Neurosurg 33: 422–427
Mount LA, Brisman R (1974) Treatment of multiple aneurysms — symptomatic and asymptomatic. Clin Neurosurg 21: 166–170
Ojemann RG (1981) Management of the unruptured intracranial aneurysm. N Engl J Med 304: 725–726
Olivecrona H (1977) Complications of cerebral angiography. Neuroradiology 14: 175–181
Pakarinen S (1967) Incidence, aetiology, and prognosis of primary subarachnoid haemorrhage: a study based on 589 cases diagnosed in a defined urban population during a defined period. Acta Neurol Scand 43 [Suppl 29]: 1–128
Philips LH, Whisnant JP, O'Fallon WM,et al (1980) The unchanging pattern of subarachnoid haemorrhage in a community. Neurology 30: 1034–1040
Rosenørn J, Astrup J, Duel P,et al (1986) The risk of haemorrhage from non-ruptured sacculate intracranial aneurysms. J Danish Med Ass 148: 3363–3365 [English summary]
Rosenørn J, Eskesen V, Schmidt K,et al (1987) Clinical features and outcome in 1076 patients with ruptured intracranial saccular aneurysms: a prospective consecutive study. Br J Neurosurg 1: 33–46
Rosenørn J, Eskesen V, Schmidt K,et al (1987) The risk of rebleeding from ruptured intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 67: 329–332
Rosenørn J (1988) Unfavourable prognostic factors in patients with intracranial aneurysms and the possibilities to improve the overall outcome. Prog Clin Neurosci 2: 179–186
Rosenørn J, Eskesen V, Schmidt K (1988) Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: an assessment of the annual risk of rupture based on epidemiological and clinical data. Br J Neurosurg 2: 369–378
Rosenørn J, Eskesen V, Madsen F,et al (1993) The importance of cerebral pan-angiography for detection of multiple aneurysms in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Acta Neurol Scand (accepted)
Säveland H, Hillman J, Brandt L,et al (1992) Overall outcome in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurosurg 76: 729–734
Salazar JL (1980) Surgical treatment of asymptomatic and incidental intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 53: 20–21
Samson DS, Hodosh RM, Clark WK (1977) Surgical management of unruptured asymptomatic aneurysms. J Neurosurg 46: 731–734
Sarwar M, Batnitzky S, Schreckter MM,et al (1976) Growing intracranial aneurysms. Radiology 120: 603–607
Seiler RW, Reulen HJ, Huber P,et al (1988) Outcome of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage in a hospital population: a prospective study including early operation, intravenous nimodipine, and transcranial Doppler ultrasound. Neurosurgery 23: 598–604
Solomon RA, Fink ME, Lennihan L (1988) Early aneurysm surgery and prophylactic hypervolemic hypertensive therapy for the treatment of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Neurosurgery 23: 699–704
Stehbens WE (1963) Aneurysms and anatomical variations of cerebral arteries. Arch Pathol 75: 45–64
Sundt TM, Kobayashi S, Fode NC,et al (1982) Results and complications of surgical management of 809 intracranial aneurysms in 722 cases. J Neurosurg 56: 753–765
Suzuki J, Ohara H (1978) Clinicopathological study of cerebral aneurysms. Origin, rupture, repair, and growth. J Neurosurg 48: 505–514
Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Sundt TM,et al (1987) The significance of unruptured intracranial saccular aneurysms. J Neurosurg 66: 23–29
Winn HR, Almaani WS, Berga SL,et al (1983) The long-term outcome in patients with multiple aneurysms. J Neurosurg 59: 642–651
Wirth FP, Laws ER, Piepgras DS (1983) Surgical treatment of incidental intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 12: 507–511
Wood EH (1964) Angiographic identification of the ruptured lesion in patients with multiple cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 21: 182–198
Zacks DJ, Russell DB, Miller JDR (1980) Fortuitously discovered intracranial aneurysms. Arch Neurol 37: 39–41
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenørn, J., Eskesen, V. Does a safe size-limit exist for unruptured intracranial aneurysms?. Acta neurochir 121, 113–118 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01809260
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01809260