Abstract
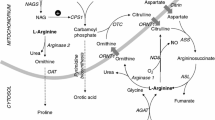
Argininosuccinic aciduria, due to deficiency of argininosuccinic acid lyase, is generally associated with severe neonatal hyperammonaemia and its neurological sequelae. The cases of two siblings with this autosomal recessive disorder are presented. Both infants were preterm and delivered by Caesarean section for maternal pre-eclampsia. The first infant was not diagnosed until after the development of severe hyperammonaemia and, despite adequate treatment with haemodialysis and arginine infusion, remained comatose for a prolonged period. At 20 months she has profound developmental delays and intellectual impairment. The second infant, whose diagnosis was made antenatally by amniotic fluid analysis, was treated with arginine infusion beginning at 32 h of life and never developed hyperammonaemia. We conclude that early recognition and prompt institution of arginine therapy is an effective regimen for the prevention of neonatal hyperammonaemia in argininosuccinic aciduria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batshaw, M. L. and Brusilow, S. W. Treatment of hyperammonemic coma caused by inborn errors of urea synthesis.J. Pediatr. 97 (1980) 893–900
Batshaw, M. L., Brusilow, S. W., Waber, L., Blom, W., Brubakk, A. M., Burton, B. K., Cann, H. M., Kerr, D., Mamunes, P., Matalon, R., Myerberg, D. and Schafer, I. A. Treatment of inborn errors of urea synthesis. Activation of alternative pathways of waste nitrogen synthesis and excretion.N. Engl. J. Med. 306 (1982) 1387–1392
Batshaw, M. L., Thomas, G. H. and Brusilow, S. W. New approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of inborn errors of urea synthesis.Pediatrics 68 (1981) 290–297
Brusilow, S. W. and Batshaw, M. L. Arginine therapy for argininosuccinic deficiency.Lancet 1 (1979) 134–136
Collins, F. S., Summer, G. K., Schwartz, R. P. and Parke, J. C., Jr. Neonatal argininosuccinic aciduria-survival after early diagnosis and dietary management.J. Pediatr. 96 (1980) 429–431
Donn, S. M., Swartz, R. D. and Thoene, J. G. Comparison of exchange transfusion, peritoneal dialysis, and hemodialysis for the treatment of hyperammonemia in an anuric newborn infant.J. Pediatr. 95 (1979) 67–70
Fleisher, L. D., Harris, C. J. and Mitchell, D. A. Citrullinemia: prenatal diagnosis of an affected fetus.Am. J. Hum. Genet. 35 (1983) 85–90
Goodman, S. I., Mace, J. W. and Turner, B. Antenatal diagnosis of argininosuccinic aciduria.Clin. Genet. 4 (1973) 236–239
Msall, M., Batshaw, M. L., Suss, R., Brusilow, S. W. and Mellits, E. D. Neurologic outcome in children with inborn errors of urea synthesis. Outcome of urea-cycle enzymopathy.N. Engl. J. Med. 310 (1984) 1500–1550
Van Anken, H. C. and Schiphorst, M. E. A kinetic determination of ammonia in plasma.Clin. Chem. Acta 56 (1974) 151–157
Wiegand, C., Thompson, T., Bock, G. H., Mathis, R. K., Kjellstrard, C. M. and Mauer, S. M. The management of life-threatening hyperammonemia: a comparison of several therapeutic modalities.J. Pediatr. 96 (1980) 142–144
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donn, S.M., Thoene, J.G. Prospective prevention of neonatal hyperammonaemia in argininosuccinic acidura by arginine therapy. J Inherit Metab Dis 8, 18–20 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01805478
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01805478