Abstract
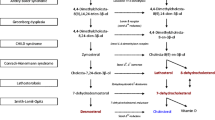
We measured the activity of dihydroxyacetone phosphate acyltransferase (DHAP-AT) in fibroblasts of controls and patients with classical Refsum's disease (RD), infantile Refsum's disease (IRD) and Zellweger's syndrome (ZS). We confirmed that DHAP-AT activity is severely reduced in ZS fibroblasts and amniocytes. We also demonstrated a partial deficiency of DHAP-AT activity in RD and IRD fibroblast cultures. These diseases are probably distinct but related entities in which peroxisomal biogenesis is affected to varying degrees.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boltshauser, E., Spycher, M. A., Steinmann, B., Briner, J., Isler, W., Kuster, T., Poulos, A. and Pollard, A. C. Infantile phytanic acid storage disease, a variant of Refsum's Disease?Eur. J. Pediatr. 139 (1982) 317
Bowen, P., Lee, C. S. N., Zellweger, H. and Lindenberg, R. A familial syndrome of multiple congenital defects.Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 114 (1964) 402–414
Bradford, M. M. A rapid sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.Analyt. Biochem. 72 (1976) 248
Brown, F. R., McAdams, A. J., Cullins, J. W., Konkol, R., Singh, I., Moser, A. B. and Moser, H. W. Cerebro-hepato-renal (Zellweger) syndrome and neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy. Similarities in phenotype and accumulation of very long chain fatty acid.Johns Hopkins. Med. J. 151 (1982) 344–351
Danks, D. M., Tippett, P., Adams, C. and Campbell, P. Cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome of Zellweger. A report of eight cases with comments upon the incidence, the liver lesion, and a fault in pipecolic acid metabolism.J. Pediatr. 86 (1975) 382–387
Datta, N. S., Wilson, G. N. and Hajra, A. K. Deficiency of enzymes catalyzing the biosynthesis of glycerol-ether lipids in Zellweger syndrome. A new category of metabolic disease involving the absence of peroxisomes.N. Engl. J. Med. 311 (1984) 1080–1083
Eldjarn, L., Stokke, O. and Try, K. Biochemical aspects of Refsum's disease and principles for the dietary treatment. In Vinkens, P. J. and Bruyn, G. W. (eds.),Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Vol. 27, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1976, pp. 519–541
Goldfischer, S. Peroxisomes and human metabolic disease. The cerebrohepatorenal syndrome, cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis and Schilder's disease (adrenoleukodystrophy).Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 386 (1982) 526–529
Goldfischer, S., Moore, C. L., Johnson, A. B., Spiro, A. J., Valsamis, M. P., Wisniewski, H. K., Ritch, R. H., Norton, W. T., Rapin, I. and Gartner, L. M. Peroxisomal and mitochondrial defects in the cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome.Science 182 (1973) 62–64
Goldfischer, S. and Reddy, J. K. Peroxisomes (microbodies) in cell pathology. InInternational Review of Experimental Pathology, Vol. 26, Academic Press, New York, 1984, pp. 45–84
Hajra, A. K., Burke, C. L. and Jones, C. L. Subcellular localisation of acyl coenzyme A: dihydroxyacetone phosphate acyltransferase in rat liver peroxisomes (microbodies).J. Biol. Chem. 254 (1979) 10896–10900
Heymans, H. S. A., van den Bosch, H., Schutgens, R. B. H., Tegelaers, W. H. H., Walther, J.-V., Muller-Hocker, J and Borst, P. Deficiency of plasmalogens in the cerebro-hepatorenal (Zellweger) syndrome.Eur. J. Pediatr. 142 (1984) 10–15
Kelley, R. I. Review: The cerebrohepatorenal syndrome of Zellweger, morphologic and metabolic aspects.Am. J. Med. Genet. 16 (1983) 503–517
Kolodney, E. H., Hass, W. K., Lane, B. and Drucker, W. D. Refsum's syndrome: report of a case including electron microscopic studies of liver.Arch. Neurol. 12 (1965) 583–596
Lazarow, P. B. Rat liver peroxisomes catalyze the β-oxidation of fatty acids.J. Biol. Chem. 253 (1978) 1522–1528
Monnens, L., Bakkeren, J., Parmentier, G., Janssen, G., van Haelst, U., Trijbels, F. and Eyssen, H. Disturbances in bile acid metabolism of infants with the Zellweger (cerebrohepato-renal) syndrome.Eur. J. Pediatr. 133 (1980) 31–35
Moser, H. W., Moser, A. E., Singh, I. and O'Neill, B. P. Adrenoleukodystrophy: Survey of 303 cases: Biochemistry, diagnosis and therapy.Ann. Neurol. 16 (1984) 628–641
Poulos, A. and Sharp, P. Plasma and skin fibroblast C26 fatty acids in infantile Refsum's Disease.Neurology 34 (1984) 1606–1609
Poulos, A., Pollard, A. C., Mitchell, J. D., Wise, G. and Mortimer, G. Patterns of Refsum's disease. Phytanic acid oxidase deficiency.Arch. Dis. Child. 59 (1984a) 222–229
Poulos, A., Sharp, P. and Whiting, M. Infantile Refsum's Disease (phytanic acid storage disease), a variant of Zellweger's syndrome?Clin. Genet. 26 (1984b) 579–586
Refsum, S. Heredopathia atactica polyneuritiformis. Phytanic acid storage disease (Refsum's disease). In Vinken, P. J. and Bruyn, G. W. (eds.)Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Vol. 22, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1975, p. 181
Schutgens, R. B. H., Heymans, H. S. A., Wanders, R. J. A., van den Bosch, H. and Schrakamp, G. Prenatal detection of Zellweger syndrome.Lancet ii (1984a) 1339–1340
Schutgens, R. B. H., Romeyn, G. J., Wanders, R. J. A., van den Bosch, H., Schrakamp, G. and Heymans, H. S. A. Deficiency of acyl-CoA: dihydroxyacetone phosphate acyltransferase in patients with Zellweger (cerebro-hepato-renal) syndrome.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 120 (1984b) 179–184
Scotto, J. M. Hadchouel, M. and Odieure, M. Infantile phytanic acid storage disease, a possible variant of Refsum's Disease: Three cases, including ultrastructural studies of the liver.J. Inher. Metab. Dis. 5 (1982) 83–90
Steinberg, D. Phytanic acid storage disease: Refsum's syndrome. In Stanbury, J. B., Wyngaarden, J. B. and Fredrickson, D. S. (eds.)The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease, 3rd Edn., McGraw-Hill, New York, 1978, pp. 688–706
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Crugten, J.T., Paton, B. & Poulos, A. Partial deficiency of dihydroxyacetone phosphate acyltransferase activity in both classical and infantile Refsum's diseases. J Inherit Metab Dis 9, 163–168 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01799453
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01799453