Summary
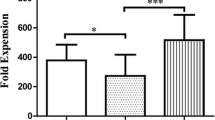
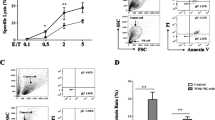
The effect of pretreatment with antitumor drugs on lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cell cytotoxic activity, determined by lactate-dehydrogenase(LDH)-release assay, was investigated. LAK cells were induced by incubating peripheral blood lymphocytes of healthy donors in medium containing interleukin-2 (IL-2) and monoclonal anti-CD3 antibody for 6–7 days. A human lung squamous carcinoma cell line, SQ-5, was used as an adherent target. After 24 h exposure of the target cells to cisplatin, doxorubicin, or mitomycin C, the drugs were washed off and LAK cells were added at an E/T ratio of 5. During further incubation for 48 h, LDH release from cisplatin- or doxorubicin-pretreated target cells was markedly higher than that from non-pretreated target cells. The combination of cisplatin and LAK cells has an additive cytotoxic effect and that of mitomycin C and LAK cells does not; there may also be an additive effect late in the toxicity mechanism between doxorubicin and LAK cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta D, Anuford DC, Smith RV (1980) Cytotoxicity of acetaminophen and papaverine in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 53: 306
Allavena P, Grandi M, D'Incalci M, Geri O, Giuliani FC, Mantovani A (1987) Human tumor cell lines with pleiotropic drug resistance are efficiently killed by interleukin-2 activated killer cells and by activated monocytes. Int J Cancer 40: 104
Carmicael J, Degraff WG, Gazdar AF, Minna JD, Mitchel JB (1987) Evaluation of the tetrazolium-based semiautomated colorimetric assay: assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer Res 47: 936
Decker T, Matthes ML (1988) A quick and simple method for the quantitation of lactate dehydrogenase release in measurements of cellular cytotoxicity and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) activity. J Immunol Methods 15: 61
Grimm EA, Mazunder A, Zhang HZ, Rosenberg SA (1983) Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon: lysis of natural killer-resistant fresh solid tumor cells by interleukin 2-activated autologous human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med 157: 884
Harker WG, Tom C, McGregor JR, Slade L, Samlowski WE (1990) Human tumor cell line resistance to chemotherapeutic agents does not predict resistance to natural killer or lymphokine-activated killer cell mediated cytolysis. Cancer Res 50: 5931
Heo DS, Park JG, Hata K, Day R, Herberman RB, Whiteside TL (1990) Evaluation of tetrazolium-based semiautomatic colorimetric assay for measurement of human antitumor-cytotoxicity. Cancer Res 50: 3681
Korzeniewski C, Callewaert DM (1983) An enzyme-release assay for natural cytotoxicity. J Immunol Methods 64: 313
Leroux JY, Mercier G, Oth D (1986) Enhancement of murine lymphoma cell lysability by CTL and by LAK cells, after treatments with mitomycin C and with Adriamycin. Int J Immunopharmacol 8: 369
Papa MZ, Yang JC, Vetto JT, Shiloni E, Eisenthal A, Rosenberg SA (1988) Combined effect of chemotherapy and interleukin 2 in the therapy of mice with advanced pulmonary tumor. Cancer Res 48: 122
Passerini CG, Radrizzani M, Erba E, Fossati G, Parmiani G (1987) Lysis by lymphocytes of melanoma and small cell lung cancer cells surviving in vitro treatment with mafosfamide. Cancer Res 47: 2547
Passerini CG, Rivoltini L, Supino R, Rodolfo M, Radrizzani M, Fossati G, Parmiani G (1988) Susceptibility of chemoresistant murine and human tumor cells to lysis by interleukin 2-activated lymphocytes. Cancer Res 48: 2372
Roper PR, Drewinko B (1976) Comparison of in vitro methods to determine drug-induced cell lethality. Cancer Res 36: 2182
Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Muul LM, Leitman S, Chang AE, Ettinghausen SE, Matory YL, Skiber JM, Shiloni E, Vetto JT, Seipp CA, Simpson C, Reichert CM (1985) Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med 313: 1485
Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Muul LM, Chang AE, Avis FP, Leitman S, Linehan M, Robertson GN, Lee RE, Rubin JT, Seipp CA, Simpson CG, White DE (1987) A progress report on the treatment of 157 patients with advanced cancer using lymphokine-activated killer cells and interleukin-2 or high-dose interleukin-2 alone. N Engl J Med 316: 889
Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Yang JC, Aebersold PM, Linehan WM, Seipp CA, White DE (1989) Experience with the use of high-dose interleukin-2 in the treatment of 652 cancer patients. Ann Surg 210: 474
Salup RR, Wiltrout RH (1986) Adjuvant immunotherapy of established murine renal cancer by interleukin 2-stimulated cytotoxic lymphocytes. Cancer Res 46: 3358
Scuderi P, Woo L, Chong AS, Liu R, Salmon SE (1990) Modification of the clonogenic assay for the detection of the lymphokine activated killer cell activity. J Immunol Methods 128: 119
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawai, K., Sasaki, T., Saijo-Kurita, K. et al. Additive effects of antitumor drugs and lymphokine-activated killer cell cytotoxic activity in tumor cell killing determined by lactate-dehydrogenase-release assay. Cancer Immunol Immunother 35, 225–229 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01789327
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01789327