Abstract
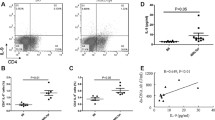
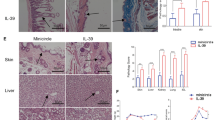
As has been reported previously, models of chronic graft-versus-host (GvH) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)-like diseases are characterized by high IgE and IgG1 immunoglobulin (Ig) levels in the serum. An IL-4 induced pathological expansion of Th2 helper cells has been described for both disease models. Due to the immunopharmacological profile of soluble recombinant interleukin-4 receptor (IL-4-R) to bind specifically the corresponding ligand IL-4 and thereby to modulate biological activity upon exogenous administration in various autoimmune disease models, we investigated the immunoregulatory activity of IL-4-R and anti-IL-4 monoclonal antibody (MAb) 11B11 on the development of SLE-like disease in MRL/lpr autoimmune mice and on chronic GvH reaction in BDF1 hybrid mice. Sensitized GvH-BDF1 hybrid mice and SLE in MRL/lpr autoimmune mice were treated in vivo with the IL-4 antagonists to alter the pattern of serum Ig production and to modulate the disease process. These animals were followed for proteinuria, autoantibody production (anti-dsDNA), serum IgE, IgG1 and IgG2a levels, and the survival was monitored. Treatment of these diseased animals resulted in an improved survival rate, lowered the percentage of animals with lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly, reduced the levels of autoantibodies and inhibited proteinuria of the developing glomerulonephritis in both mouse strains, even in the established diseases. In both models the increase in total IgE and IgG1 levels in serum was strongly inhibited by the IL-4 antagonists, even under therapeutic conditions. But there was no inhibitory activity observed on the IgG2a serum levels.
The available evidence suggests that in chronic GvH and SLE-like diseases, there is an increased production of IL-4 by Th2 helper T cells which enables B cells to switch to an enhanced production of IgE and IgG1 autoantibodies. Treatment with the IL-4 antagonists suppressed chronic GvH disease in BDF1 hybrid mice and reduced clinical symptoms of the spontaneous SLE-like disease in MRL/lpr autoimmune mice. Therefore, treatment with soluble recombinant IL-4-R may be beneficial in diseases with a dysregulation of Th2 helper T cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Claman HN, Spiegelberg HL. Immunoglobulin dysregulation in murine graft-vs-host disease: a hyper-IgE syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopath 1990;56:46–53.
Magilavy DB, Foys KM, Gajewski TF. Liver of MRL/lpr mice contain interleukin-4-producing lymphocytes and accessory cells that support the proliferation of Th2 helper T-lymphocyte clones. Eur J Immunol 1992;22:2359–65.
Dubey C, Bellon B, Druet P. TH1 and TH2 dependent cytokines in experimental autoimmunity and immune reactions induced by chemicals. Eur Cytokine Net 1991;2:147–52.
Gleichmann E, van Elven EH, van der Veen JPW. A systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)-like disease in mice induced by abnormal T-B cell cooperation. Preferential formation of autoantibodies characteristic of SLE. Eur J Immunol 1982;12:152–9.
Paul WE. Interleukin-4: a prototypic immunoregulatory lymphokine. Blood 1991;77:1859–70.
Mosley B, Beckmann MP, March CJ, Jolzerda RL, Gimpel SD, van den Bos T, et al. The murine Interleukin-4 receptor: molecular cloning and characterization of secreted and membrane bound forms. Cell 1989;59:335–48.
Umland SP, Razac S, Nahrebne DK, Seymour BW. Effects of in vivo administration of interferon (IFN γ ), anti IFN γ , or anti-interleukin-4 monoclonal antibodies in chronic autoimmune graft-versus-host disease. Clin Immunol Immunpath 1992;63:66–73.
Schorlemmer H-U, Lauffer L, Kanzy EJ, Enssle K. Immunoregulation by recombinant interleukin-4 receptor (IL-4-R) of murine GvH and SLE-like diseases in BDF1 hybrid mice and MRL/lpr autoimmune mice. Agents Actions 1994;41:180–2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schorlemmer, H.U., Dickneite, G., Kanzy, E.J. et al. Modulation of the immunoglobulin dysregulation in GvH- and SLE-like diseases by the murine IL-4 receptor (IL-4-R). Inflamm Res 44 (Suppl 2), S194–S196 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01778328
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01778328