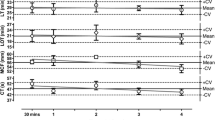
Summary
In 22 patients with suspected pulmonary embolism and 19 patients with suspected deep vein thrombosis, thrombin-antithrombin III complex (TAT) as an indicator of thrombin activation was measured using a newly developed ELISA. For comparison fibrinopeptide A (FPA), as a marker of an activated coagulation, as well as platelet factor 4 (PF4), and β-thromboglobulin (β-TG), as markers of platelet activation, were determined. In all patients in whom pulmonary embolism was confirmed by perfusion lung scan and in 15 of 16 patients in whom deep vein thrombosis was confirmed by phlebography, TAT exceeded the upper limit of normal (3.0 ng/ml). FPA was increased in 71% of the pulmonary embolism patients, PF 4 in 53%, and β-TG in 59%. The data for the patients with deep vein thrombosis were comparable. PF 4 and β-TG were increased in more than 25% of the normal controls, FPA in 17%, and TAT in 9%.
TAT is very sensitive in detecting an activation of the coagulation system in patients with suspected thromboembolic events. The test, however, is not specific for thrombembolism; it only indicates an activation of the coagulation system. Acute pulmonary embolism or deep vein thrombosis would appear to be unlikely if TAT is normal. The measurement of TAT is easier and less susceptible to disturbances than that of FPA, PF4, and β-TG.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FPA:
-
Fibrinopeptid A
- LE:
-
Lungenembolie
- PF 4:
-
Plättchenfaktor 4
- TAT:
-
Thrombin-Antithrombin III-Komplex
- β-TG:
-
β-Thromboglobulin (beta-Thromboglobulin)
- VT:
-
tiefe Venenthrombose
Literatur
Blanke H, Kaiser H, Karsch KR, Kreuzer H (1978) Die Diagnostik der Lungenembolie. In: Köstering H (Ed) Die Thrombembolien. Editions Roche, S 21
Cella G, Jahavi J, de Haas HA, Kakkar VV (1979) β-Thromboglobulin, Platelet Production Time and Platelet Function in Vascular Disease. Brit J Haematol 43:127–136
Dewar HA, Marshall T, Weightman D, Prakash V, Boon PJ (1979) β-Thromboglobulin in Antecubital Vein Blood — The Influence of Age, Sex and Blood Group. Thrombos Haemostas 42:1159–1163
Doyle DJ, Chesterman CN, Cade JF, McGready JR, Rennie GC, Morgan FJ (1980) Plasma Concentrations of Platelet-Specific Proteins Correlated with Platelet Survival. Blood 55:82–84
Flies JC, Malpass TW, Yee EK, Ritchie JL, Harker LA (1981) Studies of Human Platelet alpha-Granule Release In Vivo. Blood 58:607–618
Hirsh J (1981) Blood Tests for the diagnosis of Venous and Arterial Thrombosis. Blood 57:1–8
van Hulsteiyn H, Briet E, Bertina R (1981) Simplified Procedure for the Assay of Fibrinopeptide A in Plasma. Thromb Res 21:207–213
van Hulsteiyn H, Briet E, Koch C, Hermans J, Bertina R (1982) Diagnostic Value of Fibrinopeptide A and beta-Thromboglobulin in Acute Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism. Acta Med Scan 211:323–330
Kaplan KL, Owen J (1981) Plasma Levels of β-Thromboglobulin and Platelet Factor 4 as Indices of Platelet Activation In Vivo. Blood 57:199–202
Ludlam CA, Bolton AE, Moore S, Cash JD (1975) New Rapid Method for Diagnosis of Deep Venous Thrombosis. Lancet II:259–260
Ludlam CA, Cash JD (1976) Studies on the Liberation of β-Thromboglobulin from Human Platelets In Vitro. Brit J Haematol 33:239–247
Ludlam CA (1979) Evidence for the Platelet Specificity of β-Thromboglobulin and Studies on its Plasma Concentration in Healthy Individuals. Brit J Haematol 41:271–278
Nossel HL, Yudelman I, Canfield RE, Butler VP jr, Spanondis K, Wilner GD, Qureshi GD (1974) Measurement of Fibrinopeptide A in Human Blood. J Clin Invest 54:43–53
Nossel HL, Butler VP jr, Canfield RE, Yudelman I, Ti M, Spanondis K, Soland T (1975) Potential Use of Fibrinopeptide A Measurements in the Diagnosis and Management of Thrombosis. Thrombos Diathes Haemorrh 33:426–434
Nossel HL (1976) Radioimmunoassay of Fibrinopeptides in Relation to Intravascular Coagulation and Thrombosis. New Engl J Med Aug 19:428–432
Nossel HL, Ti M, Kaplan KL, Spanondis K, Soland T, Butler VP jr (1976) The Generation of Fibrinopeptide A in Clinical Blood Samples. Evidence for thrombin activity. J Clin Invest 58:1136–1144
Pelzer H, Fuhge P, Bleyl H, Heimburger N (1985) Enzyme Immunoassay for Determination of Human Thrombin-Antithrombin III Complex. Thrombos Haemostas P142:24
Pelzer H, Schwarz A, Heimburger N (1986) Enzyme Immunoassay for Determination of Human Thrombin-Antithrombin III Complex. Thromb Res Suppl VI:51
Peuscher FW, van Aken WG, Flier OTN, Stoepman-van Dalen EY, Cremer-Goote TM, van Mourik JA (1980) Effect of Anticoagulant Treatment Measured by Fibrinopeptide A (fpA) in Patients with Venous Thrombo-Embolism. Thromb Res 18:33–43
Smith RC, Duncanson J, Ruckley CV, Webber RG, Allan NC, Dawes J, Bolton AE, Hunter WM, Pepper DS, Cash JD (1978) β-Thromboglobulin and Deep Vein Thrombosis. Thrombos Haemostas 39:338–345
White GC, Marouf AA (1981) Platelet Factor 4 Levels in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. J Lab Clin Med 97:369–378
Yudelman IM, Nossel HL, Kaplan KL, Hirsh J (1978) Plasma Fibrinopeptide A Levels in Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism. Blood 51:1189–1195
Zahavi J, Kakkar VV (1980) β-Thromboglobulin — a Specific Marker of In Vivo Platelet Release Reaction. Thrombos Haemostas 43:23–29
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blanke, H., Praetorius, G., Leschke, M. et al. Die Bedeutung des Thrombin-Antithrombin III-Komplexes in der Diagnostik der Lungenembolie und der tiefen Venenthrombose — Vergleich mit Fibrinopeptid A, Plättchenfaktor 4 und β-Thromboglobulin. Klin Wochenschr 65, 757–763 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01743250
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01743250