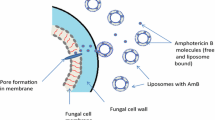
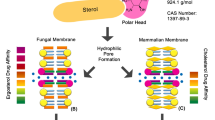
Summary
Amphotericin B is the only antifungal drug which, despite its dose-limiting toxicity, can be given intravenously when an aggressive treatment is required. In an attempt to reduce the drug toxicity while retaining its therapeutic efficacy, new formulations of amphotericin B have been developed. The most promising have employed lipid vehicles such as liposomes. Three lipid-based amphotericin B formulations have been developed by pharmaceutical companies and are under active clinical investigation. Efficacy and safety data of these derivatives in animals and humans are reviewed, with particular concern to cryptococcal infection. The authors' experience with a small unilamellar liposomal amphotericin B formulation, AmBisome, in the primary therapy of cryptococcosis is reported. Nine AIDS patients affected with cryptococcosis, seven of whom had meningitis, were given AmBisome (3 mg/kg/day) for 3–6 weeks. Complete response was obtained in six patients, marked improvement in two, and failure in one. AmBisome was well tolerated and shortened the time to clinical and mycological response suggesting a further improvement in the management of cryptococcosis in AIDS patients.
Zusammenfassung
Amphotericin B ist die einzige antimykotisch wirkende Substanz, die trotz ihrer dosislimitierenden Toxizität intravenös gegeben werden kann, wenn eine aggressive Behandlung erforderlich ist. In der Absicht, die medikamentös-toxischen Nebenwirkungen bei gleichbleibender therapeutischer Wirksamkeit zu reduzieren, wurden neue Formulierungen von Amphotericin B entwickelt. Am erfolgversprechendsten erwies sich bisher die Verwendung von Lipiden als Trägersubstanzen. Bis jetzt wurden drei lipid-gebundene Amphotericin-B-Formulierungen von pharmazeutischen Unternehemen entwickelt, die zur Zeit klinisch geprüft werden. Es werden Angaben zur Wirksamkeit und Verträglichkeit dieser Derivate bei Tieren und Menschen zusammenfassend dargestellt, insbesondere unter Berücksichtigung der Kryptokokken-Infektion. Die Autoren berichten über ihre Erfahrungen mit einer kleinen unilamellären liposomalen Amphotericin-B-Formulierung (AmBisome™) in der Primärtherapie der Kryptokokkose. Neun Patienten mit AIDS und Kryptokokken-Infektion (sieben Patienten hiervon mit Meningitis) erhielten AmBisome™ (3 mg/kg/Tag) über 3–6 Wochen. Vollständige Remissionen wurden bei sechs Patienten erreicht, eine deutliche Besserung bei zwei Patienten. Bei einem Patienten versagte die Therapie. AmBisome™ wurde gut vertragen und verkürzte das Zeitintervall bis zur klinischen und mykologischen Besserung, was eine weitere Verbesserung in der Therapie der Kryptokokkose bedeuten kann.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brajtburg, J., Powderly, G., Kobayashi, G. S., Medoff, G. Amphotericin B: delivery systems. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 34 (1990) 381–384.
Janknegt, R., de Marie, S., Bakker-Woudenberg, I. A. J. M., Crommelin, D. J. A. Liposomal and lipid formulations of amphotericin B. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 23 (1992) 279–291.
Ringdén, O., Meunier, F., Tollemar, J., Ricci, P., Tura, S., Kuse, E., Viviani, M. A., Gorin, N. C., Klastersky, J., Fenaux, P., Prentice, H. G., Ksionski, G. Efficacy of amphotericin B encapsulated in liposomes (AmBisome) in the treatment of invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 28 (Suppl. B) (1991) 73–82.
Meunier, F., Prentice, H. G., Ringdén, O. Liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome): safety data from a phase II/III clinical trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 28 (Suppl. B) (1991) 83–91.
Bowden, R., Cays, M.: Phase I study of amphotericin B colloidal dispersion (ABCD) for the treatment of invasive fungal infection after marrow transplant. ICAAC, 1992, abstract no. 621.
Hostetler, J. S., Caldwell, J. W., Johnson, R. H., Munoz, A. D., Einstein, H. E., Larsen, R. A., Stevens, D. A.: Coccidioidal infections treated with amphotericin B colloidal dispersion (Amphocil or ABCD). ICAAC, 1992, abstract no. 628.
Graybill, J. R., Craven, P. C., Taylor, R. L., Williams, D. M., Magee, W. E. Treatment of murine cryptococcosis with liposomal-associated amphotericin B. J. Infect. Dis. 145 (1982) 748–752.
Clark, J. M., Whitney, R. R., George, R. J., Kunselman, L., Swerdel, M., Feldman, A., Olsen, S. J., Bonner, D. P.: Amphotericin B lipid complex: efficacy in systemic candida infections in mice. ICAAC, 1988, abstract no. 316.
McManus, E. J., Rahman, A., Gondal, J., Bennett, J. E.: Liposomal amphotericin B in murine cryptococcosis. ICAAC, 1988, abstract no. 318.
Albert, M., Stahl-Carroll, T., Graybill, J.: Comparison of AmBisome to amphotericin B in cryptococcal meningitis (CM). ICAAC, 1992, abstract no. 178.
Hostetler, J. S., Clemons, K. V., Hanson, L. H., Stevens, D. A. Efficacy and safety of amphotericin B colloidal dispersion compared with those of amphotericin B deoxycholate suspension for treatment of disseminated murine cryptococcosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36 (1992) 2656–2660.
Perfect, J. R., Wright, K. A.: Efficacy of amphotericin B lipid complex in the treatment of experimental fungal infections. ASM, 1992, abstract no. F-96.
Graybill, J. R., Sharkey, P. K., Vincent, D., Johnson, E., Fan Havard, P., Eng, R., Kolokathis, A., Mildvan, D., Pollard, R., Kerr, L., Zalewska, B., Gupta, R.: Amphotericin B lipid complex in treatment of cryptococcal meningitis in patients with AIDS. ICAAC, 1991, abstract no. 289.
Coker, R., Tomlinson, D., Harris, J. Successful treatment of cryptococcal meningitis with liposomal amphotericin B after failure of treatment with fluconazole and conventional amphotericin B. AIDS 5 (1991) 231–232.
Schürmann, D., de Matos Marques, B., Grünewald, Th., Pohle, H. D., Hahn, H., Ruf, B. Safety and efficacy of liposomal amphotericin B in treating AIDS-associated disseminated cryptococcosis. J. Infect. Dis. 164 (1991) 620–622.
Coker, R., Horner, P. J. Short-course treatment and response to liposomal amphotericin B in AIDS-associated cryptococcosis. J. Infect. Dis. 165 (1992) 593.
Viviani, M. A., Tortorano, A. M., Grancini, A., Santagostino, E., Fasan, M., Capetti, A., Vigevani, G. M.: Liposomal amphotericin B in primary therapy of cryptococcosis in AIDS patients. SIDA 92, Paris, March 12–13, 1992, abstract 027.
Coker, R., Viviani, M. A., Gazzard, B. G., Dupont, B., Pohle, H. D., Murphy, S. M., Atouguia, J., Champalimaud, J. L., Harris, J. Treatment of cryptococcosis with liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome) in 23 patients with AIDS. AIDS 7 (1993) 829–835.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viviani, M.A., Tortorano, A.M., Roverselli, A.M. et al. Lipid-based amphotericin B in the treatment of cryptococcosis. Infection 22, 137–142 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01739025
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01739025