Summary
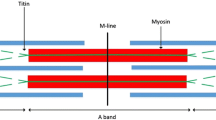
Structural features of the Z-lines of rabbit psoas muscle myofibrils have been studied in the electron microscope with a negative staining technique. The results obtained suggest the presence of about 20 nm periodicity in the structural organization of the Z-line region : a band pattern of five bands of extra density spaced about 20 nm apart was revealed in the Z-region and the Z-filaments connecting actin filaments from neighbouring sarcomeres often appeared to be positioned at intervals of 17–20 nm. An electron microscopic investigation of the interactionin vitro of two major Z-line proteins,α-actinin and F-actin, indicated that the positions ofα-actinin bridges between actin filaments are defined by relative azimuthal positions of actin subunits. A possible arrangement of actin-linking macromolecular bridges in the Z-region is considered. It is supposed that the arrangement of the Z-filaments is related to the helical symmetry of actin-containing filaments. Also, the banded appearance of the Z-region is interpreted as arising from the arrangement of crossbridges connecting thin filaments of the same sarcomeres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanchard, A., Ohanian, V. &Critchley, D. (1989) The structure and function of α-actinin.J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 10, 280–9.
Casella, J. F., Craig, S. W., Maack, D. J. &Brown, A. E. (1987) Cap Z36/32), a barbed end actin-capping protein, is a component of the Z-line of skeletal muscle.J. Cell Biol. 105, 371–9.
Chen, W. Y. J., Dhoot, G. K. &Perry, S. V. (1986) Characterization and fibre type distribution of a new myofibrillar protein of molecular weight 32 kDa.J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 7, 517–26.
Chowrashi, P. K. &Pepe, F. (1982) The Z-band 85 000-dalton amorphin and α-actinin and their relation to structure.J. Cell Biol. 94, 565–73.
Cooper, J. &Trinick, J. (1984) Binding and location of AMP deaminase in rabbit psoas muscle myofibrils.J. Mol. Biol. 177, 137–52.
Craig, R. (1977) Structure of A-segments from frog and rabbit skeletal muscle.J. Mol. Biol. 109, 69–81.
Derosier, D. J. &Tilney, L. G. (1982) How actin filaments pack into bundles.Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 46, 525–40.
Egelman, E. H., Francis, N. &Derosier, D. J. (1982) F-actin is a helix with a random variable twist.Nature 298, 131–5.
Egelman, E. H. &Padron, R. (1984) X-ray diffraction evidence that actin is a 100 Å filament.Nature 307, 56–8.
Franzini-Armstrong, C. (1973) The structure of a simple Z-line.J. Cell. Biol. 58, 630–42.
Fürst, D. O., Osborn, M., Nave, R. &Weber, K. (1988) The organization of titin filaments in the half sarcomere revealed by monoclonal antibodies in immunoelectron microscopy ; a map of ten non-repetitive epitopes starting at the Z-line extends to the M line.J. Cell Biol. 106, 1563–72.
Goldstein, M. A., Schroeter, J. P. &Sass, R. L. (1977) Optical diffraction of the Z lattice in canine cardiac muscle.J. Cell Biol. 75, 818–36.
Goldstein, M. A., Schroeter, J. P. &Sass, R. L. (1979) The Z-lattice in mammalian cardiac muscle.J. Cell Biol. 83, 187–204.
Goldstein, M. A., Stromer, M. H., Schroeter, J. P. &Sass, R. L. (1980) Optical reconstruction of nemaline rods.Exp. Neurol. 70, 83–97.
Goldstein, M. A., Schroeter, J. P. &Sass, R. L. (1982) The Z-band lattice in a slow skeletal muscle.J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 3, 333–48.
Goldstein, M. A., Michael, L. H., Schroeter, J. P. &Sass, R. L. (1986) The Z-band lattice in skeletal muscle before, during and after tetanic contraction.J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 7, 527–36.
Goldstein, M. A., Michael, L. H., Shroeter, J. P. &Sass, R. L. (1987) Z band dynamics as a function of sarcomere length and the contractile state of muscle.FASEB J. 1, 133–42.
Goldstein, M. A., Michael, L. H., Schroeter, J. P. &Sass, R. L. (1988) Structural states in the Z band of skeletal muscle correlate with states of active and passive tension.J. Gen. Physiol. 92, 113–19.
Hattori, A. &Takahashi, K. (1979) Studies on the post-mortem fragmentation of myofibrils.J. Biochem. Tokyo 85, 47–56.
Henderson, D. W., Goll, D. E. &Stromer, M. H. (1970) A comparison of shortening and Z-line degradation in postmortem bovine, porcine and rabbit muscle.Am. J. Anat. 128, 117–35.
Hirose, K. &Wakabayashi, T. (1988) Thin filaments of rabbit skeletal muscle are in helical register.J. Mol. Biol. 204, 797–801.
Kawamura, M., Masaki, T., Nonomura, Y. &Maruyama, K. (1970) An electron-microscopic study of action of the 6S-component of α-actinin on F-actin.J. Biochem. Tokyo 68, 577–80.
Kelly, D. E. (1967) Models of muscle Z band fine structure based on a looping filament configuration.J. Cell Biol. 34, 827–40.
Kelly, D. E. &Cahill, M. A. (1972) Filamentous and matrix components of skeletal muscle Z-discs.Anat. Rec. 172, 623–42.
Knappeis, G. G. &Carlsen, F. (1962) The ultrastructure of the Z-disc in skeletal muscle.J. Cell Biol. 13, 323–35.
Kossmann, T., Fürst, D. &Small, J. V. (1987) Structural and biochemical analysis of skinned smooth muscle preparations.J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 8, 135–44.
Kuroda, M., Tanaka, T. &Masaki, T. (1981) Eu-actinin, a new structural protein of the Z-line of striated muscle.J. Biochem. Tokyo 89, 297–310.
Landon, D. N. (1970a) Change in Z-disc structure with muscular contraction.J. Physiol. 211, 44P-45P.
Landon, D. N. (1970b) The influence of fixation upon the structure of the Z-disc of rat striated muscle.J. Cell Sci. 6, 257–76.
MacDonald, R. D. &Engel, A. G. (1971) Observation on organization of Z-disk components and on rod-bodies of Z-disk origin.J. Cell Biol. 48, 431–7.
Maher, P. A., Cox, G. F. &Singer, S. J. (1985) Zeugmatin: a new high molecular weight protein associated with Z-lines in adult and early embryonic striated muscle.J. Cell Biol. 101, 1871–83.
Masaki, T., Endo, M. &Ebashi, S. (1967) Localization of 6S-component of α-actinin at Z-band.J. Biochem. Tokyo 62, 630–2.
Meyer, R. K. &Aebi, U. (1990) Bundling of actin filaments by α-actinin depends on its molecular length.J. Cell Biol. 110, 2013–24.
Morris, E. P., Nneji, G. &Squire, J. M. (1990) The three-dimensional structure of the nemaline rod Z-band.J. Cell Biol. 111, 2961–78.
Muguruma, M., Kobayashi, K., Fukazawa, T., Ohashi, K. &Maruyama, K. (1981) A new 220000 dalton protein located in the Z-lines of vertebrate skeletal muscle.J. Biochem. Tokyo 89, 1981–4.
Offer, G., Moos, C &Starr, R. (1973) A new protein of thick filaments of vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Extraction, purification and characterization.J. Mol. Biol. 74, 653–76.
Ohashi, K. &Maruyama, K. (1979) A new structural protein located in the Z-lines of chicken skeletal muscle.J. Biochem. Tokyo 85, 1103–5.
Pardee, J. D. &Spudich, J. A. (1982) Purification of muscle actin. InMethods in Cell Biology 24, part A (edited byWilson, L.) pp. 271–89. New York: Academic Press.
Podlubnaya, Z. A., Tskhovrebova, L. A., Zaalishvili, M. M. &Stefanenko, G. A. (1975) Electron microscopic study of α-actinin.J. Mol. Biol. 92, 357–9.
Reedy, M. K. (1964) The structure of actin filaments and the origin of the axial periodicity in the I substance of vertebrate striated muscle.Proc. R. Soc. Series B 160, 458–60.
Rowe, R. W. (1971) Ultrastructure of the Z-line of skeletal muscle fibers.J. Cell Biol. 51, 674–85.
Rowe, R. W. (1973a) The ultrastructure of the Z discs from white, intermediate and red fibres of mammalian striated muscles.J. Cell. Biol. 57, 261–77.
Rowe, R. W. D. (1973b) Transverse striations in the Z-line of slow-twitch mammalian muscle fibres. InBasic Research in Myology (edited byKakulas, B. A.) pp. 49–55. New York: American Elsevier.
Squire, J. M. &Harford, J. J. (1988) Actin filament organization and myosin head labelling patterns in vertebrate skeletal muscles in the rigor and weak binding states.J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 9, 344–58.
Suzuki, A., Goll, D. E., Singh, I., Allen, R. E., Robson, R. M. &Stromer, M. H. (1976) Some properties of purified skeletal muscle α-actinin.J. Biol. Chem. 251, 6860–70.
Suzuki, A., Saito, M., Okitani, A. &Nonami, Y. (1981) Z-nin, a new high molecular weight protein required for reconstitution of the Z-disk.Agric. Biol. Chem. 45, 2535–42.
Suzuki, A. &Nonami, Y. (1982) A 34000 dalton protein located in the Z-disk.Agric. Biol. Chem. 46, 1977–8.
Takahashi, K., Kim, O. H. &Yano, K. (1987) Calcium-induced weakening of Z-disks in postmortem skeletal muscle.J. Biochem. Tokyo 101, 767–73.
Ullrick, W. C., Toselli, P. A., Saide, J. D. &Phear, W. P. C. (1977) Fine structure of the vertebrate Z-disc.J. Mol. Biol. 115, 61–74.
Wallraff, E., Schleicher, M., Modersitzki, M., Rieger, D., Isenberg, G. &Gerisch, G. (1986) Selection ofDictyostelium mutants defective in cytoskeletal proteins: use of an antibody that binds to the ends of α-actinin rods.EMBO J. 5, 61–7.
Wang, K. &Wright, J. (1988) Architecture of the sarcomere matrix of skeletal muscle: immunoelectron microscopic evidence that suggests a set of parallel inextensible nebulin filaments anchored at the Z-line.J. CellBiol. 107,2199–212.
Weeds, A. G. &Pope, B. (1977) Studies on the chymotryptic digestion of myosin. Effects of divalent cations on proteolytic susceptibility.J. Mol. Biol. 111, 129–57.
Yamaguchi, M., Izumimoto, M., Robson, R. M. &Stromer, M. H. (1985) Fine structure of wide and narrow vertebrate muscle Z-lines. A proposed model and computer simulation of Z-line architecture.J. Mol. Biol. 184, 621–44.
Yamaguchi, M., Robson, R. M. &Stromer, M. H. (1983) Evidence for actin involvement in cardiac Z-lines and Z-line analogues.J. Cell Biol. 96, 435–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tskhovrebova, L.A. Vertebrate muscle Z-line structure: An electron microscopic study of negatively-stained myofibrils. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 12, 425–438 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01738327
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01738327