Summary
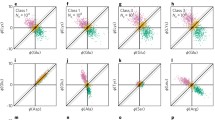
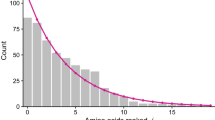
Transition probability matrices of amino acid substitution are calculated for hemoglobin, cytochrome c, fibrinopeptide, immunoglobulin and lysozyme, and for protein as a whole. When these matrices operate on the column vectors which represent the contemporary amino acid frequencies of the corresponding proteins, amino acid compositions change so as to increase their entropy. The entropy increase of amino acid sequences in proteins need not be interpreted as a random process. If we assume instead a selective process favoring randomness in protein, the biased nature of the genetic code can contribute to non-randomness in the DNA sequence. The entropy increase of protein as a whole is interpreted as a diversification of protein, and is reflected in DNA base sequence of higher organisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dayhoff,M.O., Eck,R.V., Park,C.M. (1969). Atlas of protein sequence and structure, M.O.Dayhoff, ed., p.75. Silver Spring: National Biomedical Research Foundation
Dayhoff,M.O. (1972). Atlas of protein sequence and structure. Silver Spring: National Biomedical Research Foundation
Gatlin,L.L. (1972a). Math.Biosci. 13, 213
Gatlin,L.L. (1972b). Information theory and the living system. New York: Columbia Univ. Press
Hasegawa,M., Yano,T. (1972). Origin of life, and evolution (in Japanese), p.134. Tokyo: Kyoritsu
Hasegawa,M., Yano,T. (in press,1974). The genetic code, and the entropy of protein. Math.Biosci.
Josse, J., Kaiser, A.D., Kornberg, A. (1961). J.Biol.Chem. 236, 864
King,J.L. (1972). Proc. 6-th Berkeley Symp.Math.Stat.Prob. Berkeley: University of California Press
Ohta,T., Kimura,M. (1971). Sci. 174, 150
Smith,M.H. (1966). J.Theor.Biol. 13, 261
Smith,T.F. (1969). Math.Biosci. 4, 179
Sueoka,N. (1965). Evolving genes and proteins, V.Bryson, H.J.Vogel, eds., p.480. New York: Academic Press
Swartz,M.N., Trautner,T.A., Kornberg,A. (1962). J.Biol.Chem. 237, 1961
Vogel, H., Zuckerkandl,E. (1971). Molecular evolution.II.Biochemical evolution and the origin of life, E.Schoffeniels, ed., p.352. Amsterdam: North-Holland
Watson,J.D. (1970). Molecular biology of the gene. New York: Benjamin
Zuckerkandl,E., Derancourt,J., Vogel,H. (1971). J.Mol.Biol. 59, 473
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yano, T., Hasegawa, M. Entropy increase of amino acid sequence in protein. J Mol Evol 4, 179–187 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01732022
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01732022