Summary
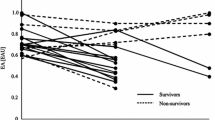
In patients with severe underlying disease and in polytraumatized patients, clinical signs of septicemia caused by infections with gram-negative bacteria are observed postoperatively with increasing frequency. Using a photometric LAL test, a longitudinal assessment of LAL reactivity on 41 intensive care patients was performed. Postoperatively, all patients developed a septicemia of different severity with body temperatures >38.5° C. Dividing the individual disease course, related to body temperatures, into three phases (A-C) it was found that independent of the severity of septicemia, the majority of patients (38/41) yielded a positive LAL reactivity. In phase B (body temperature >38.5° C) more plasma samples contained LAL-reactive material than in phase A and C (body temperature <38.5° C). A decline of fever (phase B to C) correlated significantly (P < 0.05) with the change from positive to negative LAL reactivity. In patients with high leukocyte counts (15–50 × 109/l) a positive LAL reactivity was found more frequently. The majority of patients (21/27) who survived were transferred with negative LAL reactivity to the general wards. The results suggest that single determinations of LAL reactivity are of limited clinical validity. Using the individual profile of LAL reactivity gained through a longitudinal assessment, data upon the development of the disease course can be obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LAL:
-
Limulus amebocyte lysate
- LPS-E:
-
Lipopolysaccharide-equivalent
References
McCabe WR, Jackson GG (1962) Gram-negative bacteremia. I. Etiology and ecology. Arch Int Med 110:83–91
Levin J, Poore TE, Young NS, Margolis S, Zauber NP, Townes AS, Bell WR (1972) Gram-negative sepsis: detection of endotoxemia with the limulus test. With studies of associated changes in blood coagulation, serum lipids, and complement. Ann Int Med 76:1–7
Hardaway RM (1980) Endotoxemic shock. Dis Colon Rectum 23:597–604
Weil MH, Shubin H, Biddle M (1964) Shock caused by gram-netative microorganisms. Analysis of 169 cases. Ann Intern Med 60:384–400
Christy JH (1971) Pathophysiology of gram-negative shock. Am Heart J 81:694–701
Eiseman B, Beart R, Norton L (1977) Multiple organ failure. Surg Gynecol Obstet 144:323–326
Vito L, Dennis RC, Weisel RD, Hechtman HB (1974) Sepsis presenting as acute respiratory insufficiency. Surg Gynecol Obstet 138:896–900
Wardle EN (1975) Endotoxinaemia and the pathogenesis of acute renal failure. Q J Med 44:389–398
McGowan JE Jr, Barnes MW, Finland M (1975) Bacteremia at Boston City Hospital: Occurrence and mortality during 12 selected years (1935–1972), with special reference to hospital-acquired cases. J Infect Dis 132:316–335
Maki DG (1981) Nosocomial bacteremia. An epidemiologic overview. Am J Med 70:719–732
Rose R, Huning KJ, Townsend TR, Wenzel RP (1977) Morbidity/mortality and economics of hospital-acquired blood stream infections: a controlled study. South Med J 70:1267–1269
Yin ET, Galanos C, Kinsky S, Bradshaw RA, Wessler S, Lüderitz O, Sarmiento ME (1972) Picogram-sensitive assay for endotoxin: Gelation of Limulus polyphemus blood cell lysate induced by purified lipopolysaccharides and lipid A from gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 261:284–289
Fink PC, Lehr L, Urbaschek RM, Kozak J (1981) Limulus amebocyte lysate test for endotoxemia: investigations with a femtogram sensitive spectrophotometric assay. Klin Wochenschr 59:213–218
Elin RJ, Knowles R, Barth WF, Wolff SM (1978) Lack of specificity of the Limulus lysate test in the diagnosis of pyogenic arthritis. J Infect Dis 137:507–513
Elin RJ, Wolff SM (1973) Nonspecificity of the Limulus amebocyte lysate test: positive reactions with polynucleotides and proteins. J Infect Dis 128:349–352
Pekarek R, Wannemacher R, Powanda M, Abeles F (1974) Further evidence that leukocytic endogenous mediator (LEM) is not endotoxin. Life Sci 14:1765–1776
Fink PC, Wolkersdorfer RG (1982) Leucoxyte activation of the Limulus amebocyte lysate. In: Watson SW, Levin J, Novitsky TJ (eds) Endotoxins and their detection with the Limulus amebocyte lysate test. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 281–285
Prytz H, Holst-Christensen J, Korner B, Liehr H (1976) Portal venous and systemic endotoxaemia in patients without liver disease and systemic endotoxaemia in patients with cirrhosis. Scand J Gastroenterol 11:857–863
Wildfeuer A, Heymer B, Schleifer KH, Haferkamp O (1974) Investigations on the specificity of the Limulus test for the detection of endotoxin. App Microbiol 28:867–871
Brunson KW, Watson DW (1976) Limulus amebocyte lysate reaction with streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. Infect Immun 14:1256–1258
Sullivan JD, Watson SW (1974) Factors affecting the sensitivity of Limulus lysate. Appl Environ Microbiol 28:1023–1026
Rastogi SC, Seligmann EB, Hochstein HD, Dawsom JH, Farag LG, Marquina RE (1979) Statistical procedure for evaluating the sensitivity of Limulus amebocyte lysate by using a reference lysate. Appl Environ Microbiol 38:911–915
Tsuji K, Steindler KA (1983) Use of magnesium to increase sensitivity of Limulus amebocyte lysate for detection of endotoxin. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:1342–1350
Weary ME, Donohue G, Pearson FC, Story K (1980) Relative potencies of four reference endotoxin standards as measured by the Limulus amebocyte lysate and USP Rabbit Pyrogen Tests. Appl Environ Microbiol 40:1148–1151
Levin J, Tomasulo PA, Oser RS (1970) Detection of endotoxin in human blood and demonstration of an inhibitor. J Lab Clin Med 75:903–911
Cooperstock MS, Tucker RP, Baublis JV (1975) Possible pathogenic role of endotoxin in Reye's syndrome. Lancet 1:1272–1274
Reinhold RB, Fine J (1971) A technique for quantitative measurement of endotoxin in human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 137:334–340
Stumacher RJ, Kovnat MJ, McCabe WR (1973) Limitations of the usefulness of the Limulus assay for endotoxin. N Engl J Med 288:1261–1264
Elin RJ, Robinson RA, Levine AS, Wolff SM (1975) Lack of clinical usefulness of the Limulus test in the diagnosis of endotoxemia. N Engl J Med 293:521–524
Harris NS, Feinstein R (1977) A new Limulus assay for the detection of endotoxin. J Trauma 17:714–718
Dixon WJ, Mood AM (1946) The statistical sign test. J Am Statist Assoc 41:557–566
McNemar Q (1947) Note on sampling error of the differences between correlated proportions or percentages. Psychometrika 12:153–154
Feldman S, Pearson TA (1974) The Limulus test and gram-negative bacillary sepsis. Am J Dis Child 128:172–174
Elin RJ (1978) Clinical utility of the Limulus test with blood, CSF and synovial fluid. In: Cohen E (ed) Biomedical applications of the horseshoe crab (Limulidae). Alan R Liss, New York, pp 279–292
Harris NS, Feinstein R (1977) Relationship of endotoxemia with clinically defined gram-negative septicemia. Surg Forum 28:23–25
Garibaldi RA, Allman GW, Larsen DH, Smith CB, Burke JP (1973) Detection of endotoxemia by the Limulus test in patients with indwelling urinary catheters. J Infect Dis 128:551–554
Skarnes RC (1966) The inactivation of endotoxin after interaction with certain proteins of normal serum. Ann NY Acad Sci 133:644–662
Freudenberg MA, Bøg-Hansen TC, Back U, Galanos C (1980) Interaction of lipopolysaccharides with plasma high-density lipoprotein in rats. Infect Immun 28:373–380
Freudenberg MA, Freudenberg N, Galanos C (1982) Time course of cellular distribution of endotoxin in liver, lungs and kidney of rats. Br J Exp Pathol 63:56–65
Bränemark PI, Urbaschek B (1967) Endotoxins in tissue injury. Vital microscopic studies on the effect of endotoxin from E. coli on the microcirculation. Angiology 18:667–671
Cuevas P, Fine J (1972) Role of intraintestinal endotoxin in death from peritonitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet 134:953–957
Levin J (1982) The Limulus test and bacterial endotoxins: some perspectives. In: Watson SW, Levin J, Novitsky TJ (eds) Endotoxins and their detection with the Limulus amebocyte lysate test. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 7–24
Andersen BM, Solberg O (1980) The endotoxin-liberating effect of antibiotics on meningococci in vitro. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand [B] 88:231–236
Goto H, Nakamura S (1980) Liberation of endotoxin from Escherichia coli by addition of antibiotics. Jpn J Exp Med 50:35–43
Gelfand JA, Elin RJ, Berry FW, Frank MM (1976) Endotoxemia associated with the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. N Engl J Med 295:211–213
Nolan JP, Camara DS (1982) Endotoxin, sinusoidal cells, and liver injury. In: Popper H, Schaffner F (eds) Progress in Liver Diseases Vol VII. Grune Stratton, New York, pp 361–376
Fink PC, Schultze KD (1982) The polyethylene glycol precipitation technique and the particle-counting immunoassay for detection of circulating immune complex-like material in liver cirrhosis and septicemia. J Lab Clin Med 99:852–865
Ruiter DJ, v der Meulen J, Wisse E (1980) Some cell biological and pathological aspects of the endotoxin uptake by the liver. In: Liehr H, Grün M (eds) The Reticuloendothelial System and the Pathogenesis of Liver Disease. Elsevier North-Holland Amsterdam, pp 267–277
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by grant Fi 281/3-3 from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fink, P.C., Grunert, J.H. Endotoxemia in intensive care patients: A longitudinal study with the limulus amebocyte lysate test. Klin Wochenschr 62, 986–991 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01728429
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01728429