Summary
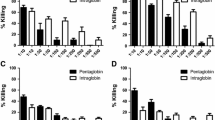
Thein vitro effect of subinhibitory and inhibitory concentrations of ofloxacin and G-CSF on the bactericidal activity of polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMNL) againstEscherichia coli was investigated. PMNL obtained from healthy volunteers were incubated with different concentrations of G-CSF and ofloxacin for 180 min. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of ofloxacin and even 1/4 × MIC enhanced the bactericidal activity of PMNL. G-CSF at a concentration of 6,000 units/ml led to a significant improvement of the bactericidal activity of PMNL. The combination of 6,000 units/ml of G-CSF and ofloxacin in inhibitory as well as subinhibitory concentrations, however, showed a significant synergistic effect on the antibacterial activity of PMNL during the complete incubation period. Combinations of G-CSF and antibiotics could therefore be beneficial for infected patients, especially those with impaired cellular host defense.
Zusammenfassung
Wir untersuchtenin vitro die bakterizide Wirkung von neutrophilen Granulozyten in Kombination mit subinhibitorischen und inhibitorischen Konzentrationen von Ofloxacin und G-CSF aufEscherichia coli. Neutrophile Granulozyten wurden dazu zusammen mit unterschiedlichen Konzentrationen von G-CSF und Ofloxacin inkubiert. Die minimale Hemmkonzentration und sogar ein Viertel der minimalen Hemmkonzentration von Ofloxacin verstärkten die bakterizide Aktivität, 6.000 Einheiten/ml G-CSF führten zu einer signifikanten Verbesserung der bakteriziden Wirkung der neutrophilen Granulozyten. Die Kombination von 6.000 Einheiten/ml von G-CSF mit Ofloxacin in inhibitorischen und subinhibitorischen Konzentrationen zeigten einen synergistischen Effekt während der gesamten Inkubationszeit auf neutrophile Granulozyten. Die Gabe von G-CSF in Kombination mit Antibiotika könnte daher bei Infektionen, insbesondere bei immunsupprimierten Patienten, vorteilhaft sein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Groopman, J. E., Molina, J. M., Scadden, D. T. Hematopoetic growth factors. Biology and clinical applications. N. Engl. J. of Med. 321 (1989) 1449–1459.
Kitagawa, S., Yuo, A., Souza, L. M., Saito, M., Miura, Y., Takadu, F. Recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances superoxide release in human granulocytes stimulated by chemotactic peptide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 14 (1987), 1143–1146.
Cohen, A. M., Hines, D. K., Korach, E. S., Ratzkin, B. J. In vivo activation of neutrophil function in hamsters by recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Infect. Immun. 56 (1988) 2861–2865.
Wang, J. M., Chen, Z. G., Colella, S., Bonilla, M. A., Welte, K., Mantovani, A. Chemotactic activity of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood 72 (1988) 1456–1460.
Roilides, E., Walsh, T. J., Pizzo, P. A., Rubin, M. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances the phagocytic and bactericidal activity of normal and defective human neutrophils. J. Inf. Dis. 163 (1991) 579–583.
Fabian, I., Kletter, Y., Bleiberg, I., Gadish, M., Naparsteck, E., Slavin, S. Effect of exogenous recombinant human granulocyte and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on neutrophil function following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Exp. Hematol. 19 (1991) 868–873.
Anding, K., Kropec, A., Schmidt-Eisenlohr, E., Benzing, A., Geiger, K., Daschner, P. Enhancement ofin vitro bactericidal activity of neutrophils from trauma patients in the presence of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Inf. Dis. 12 (1993) 121–124.
Böyum, A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood: isolation of mononuclear cells by one centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 × g. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 21 (Suppl. A) (1968) 77–89.
Daschner, F. D., Langmaack, H., Grehn, M., Steffens, A., Just, H. M. Combination effect of piperacillin with four aminoglycosides on nonfermenting gram-negative bacteria. Chemotherapy 27 (1981) 39–43.
Guffini, A. M., Carlone, N. A., Cimino, F. Enhancedin vitro macrophage phagocytosis of β-lactamase producingEscherichia coli in the presence of cefazolin. Microbiologica 3 (1980) 393–405.
Cuffini, A. M., Carlone, N. A., Xerri, L.: Effect of ceftazidime on the macrophage phagocytosis ofPseudomonas aeruginosa. 3rd Mediterranean Congress of Chemotherapy, Dubrovnik (1982), abstr. 422.
Gemell, C. G. Potentiation of phagocytosis of pathogenic bacteria by exposure to low concentrations of antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 13 (1984) 407–415.
Cuffini, A. M., Carlone, N. A., Xerri, L., Pizzoglio, M. F. Synergy of ceftazidime and human macrophages on phagocytosis and killing ofStaphylococcus aureus andPseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 20 (1987) 261–271.
Silver, G. M., Gamelli, R. L., O'Reilly, M. O. The beneficial effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) in combination with gentamycin on survival after Pseudomonas burn wound infection. Surgery 106 (1989) 452–456.
Yasuda, H., Ajiki, Y., Shimozato, T., Kasahara, M., Kawada, H., Shimizo, K. Therapeutic efficacy of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor alone and in combination with antibiotics againstPseudomonas aeruginosa infections in mice. Infect. Immun. 58 (1990) 2502–2509.
Matsumoto, M., Matsubara, S., Yokota, T. Effect of combination therapy with recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rG-CSF) and antibiotics in neutropenic mice unresponsive to antibiotics alone. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 28 (1991) 447–453.
Broek, van den, P. J. Antimicrobial drugs, microorganisms, and phagocytes. Clin. Inf. Dis. 11 (1989) 213–245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kropec, A., Lemmen, S.W., Grundmann, H.J. et al. Synergy of simultaneous administration of ofloxacin and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in killing ofEscherichia coli by human neutrophils. Infection 23, 298–300 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01716290
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01716290