Summary
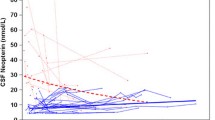
The HIV-1 RNA in plasma and CSF samples from 40 HIV-1 infected patients was measured by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique. The possible implication of cytokines in HIV-1 replication was investigated by measuring the concentrations of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), macrophage colony stimulation factor (M-CSF) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in these fluids. HIV-1 RNA was quantified in all plasma samples and in 87.5% of the CSF samples. CSF HIV-1 RNA titers did not correlate with the stage of disease or the CD4+ T cell counts, unlike the plasma HIV-1 RNA titers. These results were confirmed when patients with a blood brain barrier damage, as assessed by the CSF/plasma albumin ratio, were excluded from the analysis. TNF-α levels were statistically correlated with the HIV-1 RNA in plasma and CSF. These data demonstrate that HIV-1 replication in the CSF at each clinical stage can be accurately measured with PCR and, although the titers of HIV-1 RNA copies in the CSF are correlated with those in the plasma, the magnitude of HIV-1 replication in CSF is not directly linked to the stage of disease, or to the CD4+ T cell count. The significance of early high levels of HIV-1 RNA in CSF is now being studied prospectively.
Zusammenfassung
HIV-1-RNA wurde mittels Polymerasekettenreaktion (PCR) in Plasma- und Liquorproben von 40 HIV-1-infizierten Patienten quantifiziert. Um mögliche Einflüsse durch Zytokine auf die HIV-1-Replikation zu erfassen, wurden Tumornekrosefaktor-α (TNF-α), Makrophagen-Kolonie-stimulierender Faktor (M-CSF) und Interleukin-6 (IL-6) in diesen Flüssigkeiten ebenfalls bestimmt. Eine Quantifizierung von HIV-1 RNA war in allen Plasmaproben und in 87,5% der Liquorproben möglich. Im Gegensatz zu den HIV-1-RNA-Titern im Plasma fand sich zwischen HIV-1-RNA-Titern im Liquor und dem Krankheitsstadium oder den CD4+-T-Zell-Zahlen keine Korrelation. Diese Ergebnisse bestätigten sich auch bei Patienten, bei denen gemessen am Liquor-Ausschluß von Plasma-Albumin-Quotienten eine Blut-Liquor-Schrankenstörung bestand. Die HIV-1-Replikation kann in allen klinischen Stadien mittels PCR exakt quantifiziert werden. Obwohl die Liquor-Titer an HIV-1-RNA-Kopien mit den Plasmatitern korrelieren, besteht dennoch keine direkte Beziehung zum Krankheitsstadium oder zur CD4+-Zellzahl. In einer prospektiven Studie wird derzeit die Bedeutung frühzeitig auftretender HIV-1-RNA-Spiegel im Liquor untersucht.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Piatak, M., Saag, M. S., Yang, L. C., Clark, S. J., Kappes, J. C., Luk, K. C., Hahn, B. H., Shaw, G. M., Lifson, J. D. High levels of HIV-1 in plasma during all stages of infection determined by competitive PCR. Science 259 (1993) 1749–1754.
Price, R. W. Understanding the AIDS dementia complex. The challenge of HIV and its effects on the central nervous system. In:Price, R. W., Perry, S. W. (eds.): HIV, AIDS and the brain: Raven Press, New York 1994, pp. 1–45.
Ait Khaled, M., McLaughlin, J. E., Johnson, M. A., Emery, V. C. Distinct HIV-1 long terminal repeat quasispecies present in nervous tissues compared to that in lung, blood and lymphoid tissues of an AIDS patient. AIDS 9 (1995) 675–683.
Di Stefano, M., Sabri, F., Leitner, T., Svennerholm, B., Hagberg, L., Norkrans, G., Chiodi, F. Reverse transcriptase sequence of paired isolates of cerebrospinal fluid and blood from patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 during zidovudine treatment. J. Clin. Microbiol. 33 (1995) 352–355.
Brettle, R. P., Gore, S. M., Bird, A. G., McNeil, A. J. Clinical and epidemiological implications of the Centers for Disease Control/World Health Organization reclassification of AIDS cases. AIDS 7 (1993) 531–539.
Mulder, J., McKinney, N., Christopherson, C., Sninsky J., Greenfield, L., Kwok, S. Rapid and simple PCR assay for quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in plasma: application to acute retroviral infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 32 (1994) 292–300.
Blank, A., Dekker, C., Schieven, G., Sugiyama, R., Thelen, M. Human body fluid ribonucleases: detection, interrelationships and significance. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 10 (1981) 203–209.
Pantaleo, G., Graziosi C, Demarest, J. F., Butini, L., Montroni, M., Fox, C., Orenstein, J. M., Kotler, D. P., Fauci, A. S. HIV infection is active and progressive in lymphoid tissue during the clinically latent stage of disease. Nature 362 (1993) 355–358.
Embretson, J., Zupancic, M., Ribas, J. L., Burke, A., Racz, P., Tenner-Racz, K., Haase, A. T. Massive covert infection of helper T lymphocytes and macrophages by HIV during the incubation period of AIDS. Nature 362 (1993) 359–362.
Chiodi, F., Keys, B., Albert, J., Hagberg, L., Lundeberg, J., Uhlen, M., Fenyö, E. M., Norkrans, G. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is present in the cerebrospinal fluid of a majority of infected individuals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 30 (1992) 1768–1771.
Donaldson, Y. K., Bell, J. E., Ironside, J. W., Brettle, R. P., Robertson, J. R., Busuttil, A., Simmonds, P. Redistribution of HIV outside the lymphoid system with onset of AIDS. Lancet 343 (1994) 382–385.
Schmid, P., Conrad, A., Syndulko, K., Singer, A. J., Handley, D., Li, X., Tao, G., Fahy-Chandon, B., Tourtellotte, W. W. Quantifying HIV-1 proviral DNA using the polymerase chain reaction on cerebrospinal fluid and blood of seropositive individuals with and without neurologic abnormalities. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 7 (1994) 777–778.
Conrad, A. J., Schmid, P., Syndulko, K., Singer, E. J., Nagra, R. M., Russell, J. J., Tourtellotte, W. W. Quantifying HIV-1 RNA using the polymerase chain reaction on cerebrospinal fluid and serum of seropositive individuals with and without neurologic abnormalities. J. Acquir. Def. Syndr. and Hum. Retrovir. 10 (1995) 425–435.
Falangola, M. F., Hanly, A., Galvaocastro, B., Petito, C. K. HIV infection of human chorioid plexus: a possible mechanism of viral entry into the CNS. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 54 (1995) 497–503.
Wei, X., Ghosh, S. K., Taylor, M. E., Johnson, V. A., Emini, E. A., Deutsch, P., Lifson, J. D., Bonhoeffer, S., Nowak, M. A., Hahn, B. H., Saag, M. S., Shaw, G. M. Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature 373 (1995) 117–122.
Power, C., Johnson, R. T. HIV-1 associated dementia: clinical features and pathogenesis. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 22 (1995) 92–100.
Wyakarnam, A., McKeating, J., Meager, A., Beverley, P. C. Tumour necrosis factors (α, β) induced by HIV-1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells potentiate virus replication. AIDS 4 (1990) 21–27.
Perrella, O., Carrieri, P. B., Guarnaccia, D., Soscia, M. Cerebrospinal fluid cytokines in AIDS dementia complex. J. Neurol. 239 (1992) 387–388.
Gallo, P., De Rossi, A., Sivieri, S., Chieco-Bianchi, L., Tavolato, B. M-CSF production by HIV-1-infected monocytes and its intrathecal synthesis: implications for neurological HIV-1 related disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 51 (1994) 193–198.
Bilello, J. A., Stellrecht, K., Drusano, G. L., Stein, D. S. Soluble tumor necrosis factor-α receptor type II (sTNF α RII) correlates with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) RNA copy number in HIV-infected patients. J. Infect. Dis. 173 (1996) 464–467.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lafeuillade, A., Pellegrino, P., Poggi, C. et al. HIV-1 replication in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. Infection 24, 367–371 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01716081
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01716081