Abstract
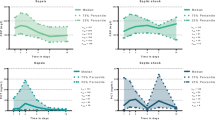
In order to assess if an oxidant/antioxidant imaalance is involved in human septic shock and its outcome, we measured plasma levels of the lipid peroxides malondialdehyde—as thiobarbituric acid reactive substance—conjugated dienes and fluorescent products, together with the antioxidants alpha-tocopherol, glutathione peroxidase activity and selenium in 12 patients with septic shock and compared them with values of normal controls. At first measurements, malondialdehyde (median 3.9 μmol/l; range 2–38.8) and fluorescent products (median 21.2%; range 9.4–134) were elevated (p<0.05), alpha-tocopherol (median 15 μmol/l; range 7–25) and selenium (median 0.76 μg/ml; range 0.49–1.09) were depressed (p<0.05). Conjugated dienes and glutathione peroxidase activity were in the normal range. In non-survivors (n=5) initial levels of malondialdehyde and fluorescent products (median 11 versus 3.1 μmol/l; 74 versus 135 respectively) were higher than in survivors (p<0.05) and initial selenium levels were lower (median 0.58 versus 0.92 μg/l;p<0.05). These results are consistent with the concept that an oxidant/antioxidant imbalance—as indicated by elevated plasma lipid peroxides and depressed antioxidants—is involved in human septic shock and a fatal outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kunimoto F, Morita T, Ogawa R, Fujita T (1987) Inhibition of lipid peroxidation improves survival rate of endotoxemic rats. Circ Shock 21:15–22
Broner CW, Shenep JL, Stidham GL, Stokes DC, Hildner WK (1988) Effect of scavengers of oxygen-derived free, radicals on mortality in endotoxin-challenged mice. Crit Care Med 16:848–851
Morgan RA, Manning PB, Coran AG, Drongowski RA, Till GO, Ward PD, Oldham KT (1988) Oxygen free radical activity during live E. coli septic shock in the dog. Circ Shock 25:319–323
Demling R, Lalonde C, Seekamp A, Fiore N (1988) Endotoxin causes hydrogen peroxide-induced lung lipid peroxidation and prostanoid production. Arch Surg 123:1337–1341
Takeda K, Shimada Y, Okada T, Amono M, Sakai T, Yoshiya I (1986) Lipid peroxidation in experimental septic rats. Crit Care Med 14:719–723
Yoshikawa T, Takemura T, Tanigawa T, Miyagawa H, Yoshida N, Sugino S, Kondo M (1987) Role of lipid peroxidation and free radical scavengers on endotoxin shock. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 18:295–300
Powell RJ, Machiedo GW, Rush B, Dikdar G (1989) Effect of alpha tocopherol on red cell deformability and survival in sepsis. Curr Surg 46:381–383
Sakaguchi O, Kanda N, Sakaguchi S, Hsu C-C, Abe H (1981) Effect of alpha-tocopherol on endotoxicosis. Microbiol Immunol 25:787–799
Warner BW, Hasselgren PO, Fischer JE (1986) Effect of allopurinol and superoxide dismutase on survival rate in rats with sepsis. Curr Surg 43:292–293
McKechnie K, Furman BL, Parrat JR (1986) Modification by oxygen free radical scavengers of the metabolic and cardiovascular effects of endotoxin infusion in conscious rats. Circ Shock 19:429–439
Peavy DL, Fairchild EJ (1986) Evidence for lipid peroxidation in endotoxin-poisoned mice. Infect Immun 52:613–616
Novotny MJ, Laughlin H, Adams HR (1988) Evidence for lack of importance of oxygen free radicals in Escherichia coli endotoxemia in dogs. Am J Physiol 254:H954-H962
Broner CW, Shenep JL, Stidham GL, Stokes DC, Fairclough D, Schonbaum GR, Rehg JE, Hildner WK (1989) Effect of antioxidants in experimentalEscherichia coli septicemia. Circ Shock 29:77–92
Henson PM, Johnston Jr RB (1987) Tissue injury in inflammation. J Clin Invest 79:669–674
Cross CE, moderator (1987) Oxygen radicals and human disease (Davis Conference). Ann Intern Med 107:526–545
Takeda K, Shimada Y, Amano M, Sakai T, Okada T, Yoshiya I (1984) Plasma lipid peroxides and alpha locopherol in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 12:957–959
Baldwin SR, Grum CM, Boxer LA, Simon RH, Ketai LH, Devall LJ (1986) Oxidant activity in expired breath of patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet I:11–14
Szajder JI, Fraiman A, Hall JB, Sanders W, Schmidt G, Crawford G, Nahum A, Factor P, Wood LDH (1989) Increased hydrogen peroxide in the expired breath of patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. Chest 96:606–612
Richard C, Lemonnier F, Tibault M, Couturier M, Auzepy P (1990) Vitamin E deficiency and lipoperoxidation during adult respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med 18:4–9
Grum CM, Ragsdale RA, Ketai LH, Simon RH (1987) Plasma xanthine oxidase activity in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. J Crit Care 2:22–26
Machiedo GW, Powell RJ, Rush BF, swislocki NI Dikdan G (1989) The incidence of decreased red blood cell deformability in sepsis and the association with oxygen free radical damage and multiplesystem organ failure. Arch Surg 124:1386–1389
Bertrand Y, Pincemail J, Hanique G, Denis B, Leenaerts L, Vankeerberghen L, Deby C (1989) Differences in tocopherol-lipid ratios in ARDS and non-ARDS patients. Intensive Care Med 15:87–93
Fantone JC, Ward PA (1982) Role of oxygen-derived free radicals and metabolites in leukocyte-dependent inflammatory reactions. Am J Pathol 107:397–418
Thomson CD, Steven SM, van Rij AM, Wade CR, Robinson MF (1988) Selenium and vitamin E supplementation: activities of glutathione peroxidase in human tissues. Am J Clin Nutr 48:316–323
Groeneveld ABJ, Kester ADM, Nauta JJP, Thijs LG (1987) Relation of arterial blood lactate to oxygen delivery and haemodynamic variables in human shock states. Circ Shock 22:35–53
Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE (1985) APACHE II: A severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med 13:818–829
Wong SHY, Knight JA, Hopfer SM, Zaharia O, Leach CN Jr, Sunderman FW (1987) Lipoperoxides in plasma as measured by liquid-chromatographic separation of malondialdehyde-thiobarbituric acid adduct. Clin Chem 33:214–220
Ward PA, Till GO, Hatherill JR, Anesley TM, Kunkel RG (1985) Systemic complement activation, lung injury, and products of lipid peroxidation. J Clin Invest 76:517–527
Miller KW, Yang CS (1985) An isocratic HPLC method for the simultancous analysis of plasma retinol, alpha-tocopherol, and various carotenoids. Anal Biochem 145:21–26
Beutler E (1971) Red cell metabolism. A Manual of Biochemical Methods. Grune and Stratton, New York London, pp 66–68
Watkinson JH (1966) Simple fluorometric determination of selenium in food and biological material with 2,3-diamino-naphtalene. Anal Chem 38:92–96
Halliwell B (1984) Oxygen radicals: a commonsense look at their nature and medical importance. Med Biol 62:71–77
Ohkawa H, Oshihi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Hawkey FY, Stewart PM, Snitch PJ (1990) Effects of acute illness on selenium homeostasis. Crit Care Med 18:442–446
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogilvie, A.C., Groeneveld, A.B.J., Straub, J.P. et al. Plasma lipid peroxides and antioxidants in human septic shock. Intensive Care Med 17, 40–44 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01708408
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01708408