Abstract
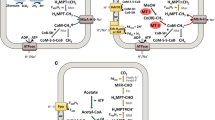
Methanogenic archaea are strictly anaerobic organisms that derive their metabolic energy from the conversion of a restricted number of substrates to methane. H2+CO2 and formate are converted to CH4 via the CO2-reducing pathway, while methanol and methylamines are metabolized by the methylotrophic pathway. A limited number of methanogenic organisms utilize acetate by the aceticlastic pathway. Redox reactions involved in these processes are partly catalyzed by membrane-bound enzyme systems that generate or, in the case of endergonic reactions, use electrochemical ion gradients. The H2:heterodisulfide oxidoreductase, the F420H2:heterodisulfide oxidoreductase and the CO:heterodisulfide oxidoreductase, are novel systems that generate a proton motive force by redox-potential-driven H+ translocation. The methyltetrahydromethanopterin:coenzyme M methyltransferase is a unique, reversible sodium ion pump that couples methyl transfer with the transport of Na+ across the cytoplasmic membrane. Formylmethanofuran dehydrogenase is a reversible ion pump that catalyzes formylation and deformylation, of methanofuran. In summary, the pathways are coupled to the generation of an electrochemical sodium ion gradient and an electrochemical proton gradient. Both ion gradients are used directly for ATP synthesis via membrane integral ATP synthases. The function of the above-mentioned systems and their components in the metabolism of methanogens are described in detail.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DCCD N,N′ :
-
dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
- F 420 :
-
(N-l-Lactyl-γ-l-glutamyl)-l-glutamic acid phosphodiester of 7,8 didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin-5′-phosphate
- H 4MPT:
-
Tetrahydromethanopterin
- HS-CoM :
-
2-Mercaptoethanesulfonate
- HS-HTP :
-
7-Mercaptoheptanoyl-O-phospho-l-threonine
- MF :
-
Methanofuran
- Ms :
-
Methanosarcina
- Mc :
-
Methanococcus
- Mb :
-
Methanobacterium
- SF 6847 :
-
3,5-Di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzylidene-malononitrile
- \(\Delta \tilde \mu _{Na^ + } \) :
-
Electrochemical sodium ion gradient
- \(\Delta \tilde \mu _{H^ + } \) :
-
Electrochemical proton gradient
References
Abbanat DR, Ferry JG (1991) Resolution of component proteins in an enzyme complex fromMethanosarcina thermophila catalyzing the synthesis or cleavage of acetyl CoA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:3272–3276
Aceti DJ, Ferry JG (1988) Purification and characterization of acetate kinase from acetate grownMethanosarcina thermophila. J Biol Chem 263:15444–15448
Al-Mahrouq HA, Carper SW, Lancaster, JR Jr (1986) Discrimination between transmembrane ion gradient-driven and electron transfer-driven ATP synthesis in the methanogenic bacteria. FEBS Lett 207:262–265
Becher B, Müller V, Gottschalk G (1992a) The methyltetrahydromethanopterin:coenzmye M methyltransferase ofMethanosarcina strain Göl is a primary sodium pump. FEMS Microbiol Lett 91:239–244
Becher B, Müller V, Gottschalk G (1992b)N 5-Methyltetrahydromethanopterin:coenzyme M methyltransferase ofMethanosarcina strain Göl is an Na+-translocating membrane protein. J Bacteriol 174:7656–7660
Becher B, Müller V (1994) 160-1 drives the synthesis of ATP via a Na+-translocating F1Fo ATP synthase in membrane vesicles of the archaeonMethanosarcina mazei strain Göl. J Bacteriol 176:2543–2550
Bertram PA, Thauer RT (1994) Thermodynamics of the formylmethanofuran dehydrogenase reaction inMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Eur J Biochem 226:811–818
Bertram PA, Schmitz RA, Linder D, Thauer RK (1994) Tungstate can substitute for molybdate in sustaining growth ofMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch Microbiol 161:220–228
Blaut M (1994) Metabolism of methanogens. Antonie Van Leewenhoek 66:187–208
Blaut M, Gottschalk G (1984) Coupling of ATP synthesis and methane formation from methanol and molecular hydrogen inMethanosarcina barkeri. Eur J Biochem 141:217–222
Blaut M, Müller V, Gottschalk G (1987) Proton translocation coupled to methanogenesis from methanol + hydrogen inMethanosarcina barkeri. FEBS Lett 215:53–57
Bobik TA, Wolfe RS (1989) Activation of formylmethanofuran synthesis in cell extracts ofMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol 171:1423–1427
Börner G, Karrasch M, Thauer RK (1989) Formylmethanofuran dehydrogenase activity in cell extracts ofMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum and ofMethanosarcina barkeri. FEBS Lett 244:21–25
Börner G, Karrasch M, Thauer RK (1991) Molybdopterin adenine dinucleotide and molybdopterin hypoxanthine dinucleotide in formylmethanofuran dehydrogenase fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. FEBS Lett 290:31–34
Boone DR, Whitman WB, Rouvière P (1993) Diversity and taxonomy of methanogens. In: Ferry JG (ed) Methanogenesis. Chapman & Hall, New York London, pp 33–80
Bott M, Thauer RK (1989) Proton translocation coupled to the oxidation of carbon monoxide to CO2 and H2 inMethanosarcina barkeri. Eur J Biochem 179:469–472
Bott M, Eikmanns B, Thauer RK (1986) Coupling of carbon monoxide oxidation to CO2 and H2 with the phosphorylation of ADP in acetate-grownMethanosarcina barkeri. Eur J Biochem 159: 393–398
Carper SW, Lancaster JR Jr (1986) An electrogenic sodium-translocating ATPase inMethanococcus voltae. FEBS Lett 200:177–180
Chen W, Konisky J (1993) Characterization of a membrane-associated ATPase fromMethanococcus voltae, a methanogenic member of the Archaea. J Bacteriol 175:5677–5682
Coremans JMCC, Van der Zwaan JW, Albracht SPJ (1989) Redox behaviour of nickel in hydrogenase fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Correlation between nickel valence and enzyme activity. Biochim Biophys Acta 997:256–267
Daas PJH, Hagen WR, Keltjens JT, Vogels GD (1994) Characterization and determination of the redox properties of the 2[4Fe-4S] ferredoxin fromMethanosarcina barkeri strain MS. FEBS Lett 356:342–344
Deppenmeier U (1995) Different structure and expression of the operons encoding the membrane-bound hydrogenases fromMethanosarcina mazei Göl. Arch Microbiol 164:370–376
Deppenmeier U, Blaut M, Mahlmann A, Gottschalk G (1990a) Membrane-bound F420H2-dependent heterodisulfide reductase in methanogenic bacterium strain Göl andMethanolobus tindarius. FEBS Lett 261:199–203
Deppenmeier U, Blaut M, Mahlmann A, Gottschalk G (1990b) Reduced coenzyme F420H2-dependent heterodisulfide oxidoreductase: a proton-translocating redox system in methanogenic bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:9449–9453
Deppenmeier U, Blaut M, Gottschalk G (1991) H2:heterodisulfide oxidoreductase, a second energy-conserving system in the methanogenic strain Göl. Arch Microbiol 155:272–277
Deppenmeier U, Blaut M, Schmidt B, Gottschalk G (1992) Purification and properties of a F420-nonreactive membrane-bound hydrogenase fromMethanosarcina strain Göl. Arch Microbiol 157:505–511
Deppenmeier U, Blaut M, Lentes S, Herzberg C, Gottschalk G (1995) Analysis of thevhoGAC andvhtGAC operons fromMethanosarcina mazei strain Göl, both encoding a membrane-bound hydrogenase and a cytochromeb. Eur J Biochem 227:261–269
Dharmavaram RM, Konisky J (1987) Identification of a vanadatesensitive, membrane-bound ATPase in the archaebacteriumMethanococcus voltae. J Bacteriol 169:3921–3925
Dharmavaram RM, Konisky J (1989) Characterization of a P-type ATPase of the archaebacteriumMethanococcus voltae. J Biol Chem 264:14085–14089
Dross F, Geisler V, Lengler R, Theis F, Krafft T, Fahrenholz F, Kojro E, Duchene A, Tripier D, Juvenal K, Kröger A (1992) The quinone-reactive Ni/Fe-hydrogenase ofWolinella succinogenes. Eur J Biochem 206:93–102
Dybas M, Konisky J (1992) Energy transduction in the methanogenMethanococcus voltae is based on a sodium ion current. J Bacteriol 174:5575–5583
Eggen RIL, Geerling ACM, Jetten MSM, DeVos WM (1991) Cloning, expression, and sequence analysis of the genes for carbon monoxide dehydrogenase ofMethanothrix soehngenii. J Biol Chem 266:6883–6887
Fähnrich V (1994) Untersuchungen zum CO-abhängigen Elektronentransport in Vesikeln von Methanosarcina Stamm Göl. Diploma Thesis, University of Göttingen, Germany
Ferry JG (1992) Biochemistry of methanogenesis. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 27:473–503
Fischer R, Thauer RK (1988) Methane formation from acetyl phosphate in cell extracts ofMethanosarcina barkeri. FEBS Lett 228: 249–253
Fischer R, Thauer RK (1989) Methyltetrahydromethanopterin as an intermediate in methanogenesis from acetate inMethanosarcina barkeri. Arch Microbiol 151:459–465
Fischer R, Thauer RK (1990) Ferredoxin-dependent methane formation from acetate in cell extracts ofMethanosarcina barkeri (strain MS). FEBS Lett 269:368–372
Gärtner P, Ecker A, Fischer R, Linder D, Fuchs G, Thauer RK (1993) Purification and properties ofN 5-methyltetrahydromethanopterin: coenzyme M methyltransferase fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Eur J Biochem 213:537–545
Gärtner P, Weiss DS, Harms U, Thauer RK (1994)N 5-Methyltetrahydromethanopterin:coenzyme M methyltransferase fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Catalytic mechanism and sodium ion dependence. Eur J Biochem 226:465–472
Grahame DA (1991) Catalysis of acetyl CoA cleavage and tetrahydrosarcinapterin methylation by a carbon monoxide dehydrogenase-corrinoid enzyme complex. J Biol Chem 266:22227–22233
Grahame DA, Stadtman TC (1987) Carbon monoxide dehydrogenase fromMethanosarcina barkeri: disaggregation, purification, and physicochemical properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem 262:3706–3712
Haase P, Deppenmeier U, Blaut M, Gottschalk G (1992) Purification and characterization of F420H2-dehydrogenase fromMethanolobus tindarius. Eur J Biochem 203:527–531
Halboth S, Klein A (1992)Methanococcus voltae harbors four gene clusters potentially encoding two [NiFe] and two [NiFeSe] hydrogenases, each of the cofactor F420-reducing or F420-non-reducing types. Mol Gen Genet 233:217–224
Harms U, Weiss DS, Gärtner P, Linder D, Thauer RK (1995) The energy conservingN 5-methyltetrahydromethanopterin:coenzyme M methyltransferase complex fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum is composed of eight different subunits. Eur J Biochem 228:640–648
Hatchikian EC, Bruschi M, Forget N, Scandellari M (1982) Electron transport components from methanogenic bacteria: the ferredoxin fromMethanosarcina barkeri. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 109:1316–1323
Hedderich R, Berkessel A, Thauer RK (1990) Purification and properties of heterodisulfide reductase fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Eur J Biochem 193:255–261
Hedderich R, Albracht SPJ, Linder D, Koch J, Thauer RK (1992) Isolation and characterization of polyferredoxin fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. FEBS Lett 298:65–68
Hedderich R, Koch J, Linder D, Thauer RK (1994) The heterodisulfide reductase fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum contains sequence motifs characteristic of pyridine-nucleotide-dependent thioredoxin reductases. Eur J Biochem 225: 253–261
Heiden S, Hedderich R, Setzke E, Thauer RK (1993) Purification of a cytochromeb containing H2:heterodisulfide oxidoreductase complex from membranes ofMethanosarcina barkeri. Eur J Biochem 213:529–535
Heiden S, Hedderich R, Setzke E, Thauer RK (1994) Purification of two subunit cytochrome b containing heterodisulfide reductase from methanol-grownMethanosarcina barkeri. Eur J Biochem 221:855–861
Hughes PE, Tove SB (1982) Occurrence of α-tocopherolquinone and α-tocopherolquinol in microorganisms. J Bacteriol 151:1397–1402
Inatomi KI, Eya S, Maeda M, Futai M (1989a) Amino acid sequence of the α and β subunit ofMethanosarcina barkeri ATPase deduced from cloned genes. J Biol Chem 264:10954–10959
Inatomi KI, Maeda M, Futai M (1989b) Dicyclohexylcarbodimide-binding protein is a subunit of theMethanosarcina barkeri ATPase complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 162:1585–1590
Jablonski PE, Ferry JG (1991) Purification and properties of methyl coenzyme M methylreductase from acetate-grownMethanosarcina thermophila. J Bacteriol 173: 2481–2487
Jetten MSM, Stams AJM, Zehnder AJB (1989a) Purification and characterization of an oxygen-stable carbon monoxide dehydrogenase ofMethanothrix soehngenii. Eur J Biochem 181:437–441
Jetten MSM, Stams AJM, Zehnder AJB (1989b) Isolation and characterization of acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase fromMethanothrix soehngenii. J Bacteriol 171:5430–5435
Jetten MSM, Hagen WR, Pierik AJ, Stams AJM, Zehnder AJB (1991) Paramagnetic centers and acetyl CoA/CO exchange activity of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase fromMethanothrix soehngenii. Eur J Biochem 195:385–391
Jin SLC, Blanchard DK, Chen JS (1983) Two hydrogenases with distinct electron carrier specificity and subunit composition inMethanobacterium formicicum. Biochim Biophys Acta 748:8–20
Jussofie A, Gottschalk G (1986) Further studies on the distribution of cytochromes in methanogenic bacteria. FEMS Lett 37:15–18
Kaesler B, Schönheit P (1989a) The role of sodium ions in methanogenesis. Formaldehyde oxidation to CO2 and 2H2 in methanogenic bacteria is coupled with primary electrongenic Na+ translocation at a stoichiometry of 2–3 Na+/CO2. Eur J Biochem 184:223–232
Kaesler B, Schönheit P (1989b) The sodium cycle in methanogenesis-CO2 reduction to the formaldehyde level in methanogenic bacteria is driven by a primary electrochemical potential of Na+ generated by formaldehyde reduction to CH4. Eur J Biochem 186:309–316
Kamlage B, Blaut M (1992) Characterization of cytochromes fromMethanosarcina Strain Göl and their involvement in electron transport during growth on methanol. J Bacteriol 174:3921–3927
Karrasch M, Börner G, Enssle M, Thauer RK (1989) Formylmethanofuran dehydrogenase from methanogenic bacteria, a molybdoenzyme. FEBS Lett 253:226–230
Karrasch M, Börner G, Enssle M, Thauer RK (1990) The molybdoenzyme formylmethanofuran dehydrogenase fromMethanosarcina barkeri contains a pterin cofactor. Eur J Biochem 194:367–372
Keltjens JT, Vogels GD (1993) Conversion of methanol and methylamines to methane and carbon dioxide. In: Ferry JG (ed) Methanogenesis. Chapman & Hall, New York London, pp 209–252
Kemner JM, Zeikus JG (1994a) Purification and characterization of membrane-bound hydrogenase fromMethanosarcina barkeri MS. Arch Microbiol 161:47–54
Kemner JM, Zeikus JG (1994b) Regulation and function of ferredoxin-linked versus cytochromeb-linked hydrogenase in electron transfer and energy metabolism ofMethanosarcina barkeri MS. Arch Microbiol 162:26–32
Kemner JM, Krzycki JA, Prince RC, Zeikus JG (1987) Spectroscopic and enzymatic evidence for membrane-bound electron transport carriers and hydrogenase and their relation to cytochrome b function inMethanosarcina barkeri. FEMS Lett 48:267–272
Kojima N, Fox JA, Hausinger RP, Daniels L, Orme-Johnson A, Walsh C (1983) Paramagnetic centers in nickel-containing, deazaflavin-reducing hydrogenase fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:378–382
Krzycki JA, Mortenson LE, Prince RC (1989) Paramagnetic centers of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase from acetoclasticMethanosarcina barkeri. J Biol Chem 264:7217–7221
Kühn W, Gottschalk G (1983) Characterization of the cytochromes occurring inMethanosarcina species. Eur J Biochem 135:89–94
Kühn W, Fiebig K, Hippe H, Mah RA, Huser BA, Gottschalk G (1983) Distribution of cytochromes in methanogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 20:407–410
Kumazawa Y, Fujiwara T, Fukumori Y, Koga Y, Yamanaka T (1994) Cytochromebc purified from the methanogenMethanosarcina barkeri. Curr Microbiol 29:53–56
Laubinger W, Dimroth P (1987) Characterization of the Na+-stimulated ATPase ofPropiongenium modestum as an enzyme of the F1F0 type. Eur J Biochem 168:475–480
Lienard T (1995) Reinigung und Charakterisierung derN 5-Methyltetrahydromethanopterin:Coenzym M Methyltransferase ausMethanosarcina mazei Stamm Göl. Diploma thesis, University of Göttingen, Germany
Lovley DR, Ferry JG (1985) Production and consumption of H2 during growth ofMethanosarcina spp. on acetate. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:247–249
Lu WP, Becher B, Gottschalk G, Ragsdale SW (1995) Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopic and electrochemical characterization of the partially purifiedN 5-methyltetrahydromethanopterin:coenzym M methyltransferase fromMethanosarcina mazei Göl. J Bacteriol 177:2245–2250
Lünsdorf H, Niedrig M, Fiebig K (1991) Immunocytochemical localization of the coenzyme F420-reducing hydrogenase inMethanosarcina barkeri Fusaro. J Bacteriol 173:978–984
Lundie LL, Ferry JG (1989) Activation of acetate byMethanosarcina thermophila. Purification and characterization of phosphotransacetylase. J Biol Chem 264:18392–18396
Mahlmann A, Deppenmeier U, Gottschalk G (1989) Methanofuran-b is required for CO2 formation from formaldehyde byMethanosarcina barkeri. FEMS Microbiol Lett 61:115–120
Mayer F, Jussofie A, Salzmann M, Lübben M, Rohde M, Gottschalk G (1987) Immunoelectron microscopic demonstration of ATPase on the cytoplasmic membrane of the methanogenic bacterium strain Göl. J Bacteriol 169:2307–2309
Mountfort DO (1978) Evidence for ATP synthesis driven by a proton gradient inMethanosarcina barkeri. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 85:1346–1350
Moura I, Moura JJG, Huynh BH, Santos H, LeGall, J, Xavier AV (1982) Ferredoxin fromMethanosarcina barkeri: evidence for the presence of a three-iron cluster. Eur J Biochem 126:95–98
Müller V, Kozianowski G, Blaut M, Gottschalk G (1987a) Methanogenesis from trimethylamine+H2 byMethanosarcina barkeri is coupled to ATP synthesis by a chemiosmotic mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 892:207–212
Müller V, Blaut M, Gottschalk G (1987b) Oxidation of trimethylamine to the level of formaldehyde byMethanosarcina barkeri is dependent on the proton motive force. FEMS Microbiol Lett 43:183–186
Müller V, Blaut M, Gottschalk G (1987c) Generation of a transmembrane gradient of Na+ inMethanosarcina barkeri. Eur J Biochem 162:461–466
Müller V, Blaut M, Gottschalk G (1988a) The transmembrane electrochemical gradient of Na+ as driving force for the methanol oxidation inMethanosarcina barkeri. Eur J Biochem 172:601–606
Müller V, Winner C, Gottschalk G (1988b) Electron-transport-driven sodium extrusion during methanogenesis from formaldehyde+H2 byMethanosarcina barkeri. Eur J Biochem 178:519–525
Müller V, Blaut M, Gottschalk G (1993) Bioenergetics of methanogenesis. In: Ferry JG (ed) Methanogenesis. Chapman & Hall, New York, pp 360–406
Muth E (1988) Localization of the F420-reducing hydrogenase inMethanococcus voltae cells by immunogold technique. Arch Microbiol 150:205–207
Muth E, Mörschel E, Klein A (1987) Purification and characterization of an 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin-reducing hydrogenase from the archaebacteriumMethanococcus voltae. Eur J Biochem 169: 571–577
Naumann E, Fahlbusch K, Gottschalk G (1984) Presence of a trimethylamine:HS-coenzyme M methyltransferase inMethanosarcina barkeri. Arch Microbiol 138:79–83
Patel GB (1984) Characterization and nutritional properties ofMethanothrix concilli sp. nov., a mesophilic, acetoclastic methanogen. Can J Microbiol 30:1383–1396
Peer CW, Painter MH, Rasche ME, Ferry JG (1994) Characterization of a CO:heterodisulfide oxidoreductase system from acetategrownMethanosarcina thermophila. J Bacteriol 176:6974–6979
Peinemann S, Müller V, Blaut M, Gottschalk G (1988) Bioenergetics of methanogenesis from acetate byMethanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol 170:1369–1372
Peinemann S, Blaut M, Gottschalk G (1989) ATP synthesis coupled to methane formation from methyl CoM and H2 catalyzed by vesicles of the methanogenic bacterial strain Göl. Eur J Biochem 186:175–180
Raybuck SA, Ramer SE, Abbanat DR, Peters JW, Orme-Johnson WH, Ferry JG, Walsh CT (1991) Demonstration of carbon-carbon bound cleavage of acetyl CoA by using isotopic exchange catalyzed by the CO dehydrogenase complex from acetategrownMethanosarcina thermophila. J Bacteriol 173:929–932
Reeve JN (1993) Structure and organization of genes. In: Ferry JG (ed) Methanogenesis. Chapman & Hall, New York London, pp 493–527
Reeve JN, Beckler GS, Cram DS, Hamilton PT, Brown JW, Krzycki JA, Kolodziej AF, Alex L, Orme-Johnson WH, Walsh CT (1989) A hydrogenase-linked gene inMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum strain ΔH encodes a polyferredoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:3031–3035
Reidlinger J, Müller V (1994) Purification of the ATP synthase ofAcetobacterium woodii and identification as a Na+-translocating F1F0-type enzyme. Eur J Biochem 223:275–283
Schäfer G, Meyering-Vos M (1992) F-Type or V-Type — the chimeric nature of the archaebacterial ATP synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1101:232–235
Schmitz RA, Richter M, Linder D, Thauer RK (1992) A tungstencontaining active formylmethanofuran dehydrogenase in the thermophilic archaeonMethanobacterium wolfei. Eur J Biochem 207:559–565
Schwörer B, Thauer RK (1991) Activities of formylmethanofuran dehydrogenase, methylene-H4MPT dehydrogenase, methylene-H4MPT reductase, and heterodisulfide reductase in methanogenic bacteria. Arch Microbiol 155:459–465
Setzke E, Hedderich R, Heiden S, Thauer RK (1994) H2:heterodisulfide oxidoreductase complex fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Eur J Biochem 220:139–148
Shah NN, Clark DS (1990) Partial purification and characterization of two hydrogenases from the extreme thermophileMethanococcus jannaschii. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:858–863
Smigan P, Horovska L, Greksak M (1989) Na+-driven ATP synthesis inMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum can be modulated with sodium ion concentrations in the growth medium. FEBS Lett 242:85–88
Smigan P, Rusnak P, Greksak M, Zhilina TN, Zavarzin GA (1992) Mode of sodium ion action on methanogenesis and ATPase of the moderate halophilic methanogenic bacteriumMethanohalophilus halophilus. FEBS Lett 300:193–196
Smigan P, Majernik A, Greksak M (1994) Na+-driven ATP synthesis inMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum and its differentiation from H+-driven ATP synthesis by rhodamine 6G. FEBS Lett 349:424–428
Sorgenfrei O, Linder D, Karas M, Klein A (1993) A novel small subunit of a selenium containing [NiFe] hydrogenase ofMethanococcus voltae is posttranslationally processed by cleavage at a defined position. Eur J Biochem 213:1355–1358
Sowers KR, Baron SF, Ferry JG (1984)Methanosarcina acetivorans sp. nov., an acetotrophic methane-producing bacterium from marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:971–978
Steigerwald VJ, Beckler GS, Reeve JN (1990) Conservation of hydrogenase and polyferredoxin structures in the hyperthermophilic archaebacteriumMethanothermus fervidus. J Bacteriol 172:4715–4718
Steigerwald VJ, Pihl TD, Reeve JN (1992) Identification and isolation of the polyferredoxin fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum strain ΔH. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:6929–6933
Stupperich E, Juza A, Hoppert M, Mayer F (1993) Cloning, sequencing, and immunological characterization of the corrinoid-containing subunit of theN 5-methyltetrahydromethanopterin: coenzyme M methyltransferase fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Eur J Biochem 217:115–121
Sumi M, Sato MH, Denda K, Date T, Yoshida M (1992) A DNA fragment homologous to F1-ATPase β subunit was amplified from genomic DNA ofMethanosarcina barkeri. FEBS Lett 314:207–210
Terlesky KC, Ferry JG (1988a) Ferredoxin requirement for electron transport from the carbon monoxide dehydrogenase complex to a membrane-bound hydrogenase in acetate-grownMethanosarcina thermophila. J Biol Chem 263:4075–4079
Terlesky KC, Ferry JG (1988b) Purification and characterization of a ferredoxin from acetate-grownMethanosarcina thermophila. J Biol Chem 263:4080–4082
Thauer RK, Jungermann K, Decker K (1977) Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 41:100–180
Thauer RK, Hedderich R, Fischer R (1993) Reactions and enzymes involved in methanogenesis from CO2 and H2. In: Ferry JG (ed) Methanogenesis. Chapman & Hall, New York London, pp 209–252
Unemoto T, Hayashi M (1989) Sodium-transport NADH-quinone reductase of a marineVibrio alginolyticus. J Bioenerg Biomembr 21:649–662
Van der Meijden P, Heythuysen HT, Pouwels A, Houwen FP, Van der Drift C, Vogels GD (1983) Methyltransferases involved in methanol conversion byMethanosarcina barkeri. Arch Microbiol 134:238–242
Wasserfallen A (1994) Formylmethanofuran synthesis by formylmethanofuran dehydrogenase fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum Marburg. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 199:1256–1261
Weiss DS, Gärtner P, Thauer RK (1994) The energetics and sodium ion dependence ofN 5-methyltetrahydromethanopterin: coenzyme M methyltransferase studied with cob(I)alamin as methyl acceptor and methylcob(III)alamin as methyl donor. Eur J Biochem 226:799–809
Wilms R (1992) Die ATPase des methanogenen Bakteriums Stamm Göl: Analyse von Struktur und Funktion des Gesamtkomplexes mit Hilfe von biochemischen, immunologischen und elektronenmikroskopischen Methoden. PhD dissertation, University of Göttingen, Germany
Winner C, Gottschalk G (1989) H2 and CO2 production from methanol or formaldehyde by the methanogenic bacterium strain Göl treated with 2-bromoethanesulfonic acid. FEMS Microbiol Lett 65:259–264
Woo GJ, Wasserfallen A, Wolfe RS (1993) Methylviologen hydrogenase II, a new member of the hydrogenase family fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum ΔH. J Bacteriol 175: 5970–5977
Zimniak L, Dittrich P, Gogarten JP, Kibak H, Taiz L (1988) The cDNA sequence of the 69-kDa subunit of the carrot vacuolar H+-ATPase. Homology to the β-chain of F1Fo ATPases. J Biol Chem 263:9102–9112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deppenmeier, U., Müller, V. & Gottschalk, G. Pathways of energy conservation in methanogenic archaea. Arch. Microbiol. 165, 149–163 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01692856
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01692856