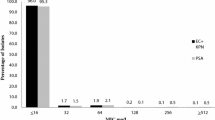
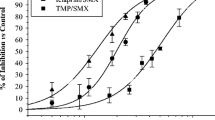
Abstract
The use of established fluoroquinolones, such as ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin, as empirical therapy for the treatment of moderate-to-severe respiratory tract infections is limited by their poor activity against gram-positive and atypical pathogens. Data from in vitro susceptibility studies and in vivo animal protection models suggest that the new fluoroquinolone, trovafloxacin, compared with ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin offers equivalent activity against gram-negative pathogens and improved activity against gram-positive pathogens. In particular, susceptibility data indicate that trovafloxacin is at least 16-fold more potent than either ciprofloxacin or ofloxacin against penicillin-susceptible and penicillin-resistant strains ofStreptococcus pneumoniae. Other susceptible pathogens includeStreptococcus pyogenes, vancomycin-susceptibleEnterococcus faecalis and the atypical respiratory pathogensLegionella pneumophila, Mycoplasma pneumoniae andChlamydia pneumoniae. In vivo studies involving models of protection against acute systemic infection and pneumococcal pneumonia in mice, and Legionnaires' disease in guinea pigs, indicate that the antibacterial spectrum observed for trovafloxacin in vitro extends to the in vivo setting. Together, these findings suggest that trovafloxacin may offer clinical efficacy against respiratory pathogens superior to that of ciprofloxacin and of ofloxacin, and may find a useful role as empiric therapy in both the community and hospital setting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baquero F: Epidemiology and management of penicillin-resistant pneumococci. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases (1996) 9:372–379
Brighty KE, Gootz TD: The chemistry and biological profile of trovafloxacin. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1997) 39, Supplement B:1–14
Gootz TD, Brighty KE: Fluoroquinolone antibacterials: SAR, mechanism of action, resistance, and clinical aspects. Medicinal Research Reviews (1996) 16:433–486
Wiedemann B, Heisig P: Mechanisms of quinolone resistance. Infection (1994) 22, Supplement 2:73–79
Hooper DC, Wolfson JS: Mechanisms of quinolone action and bacterial killing. In: Hooper DC, Wolfson JS (eds): Quinolone antimicrobial agents. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC (1993), pp 53–75
Hoshino K, Kitamura A, Morrissey I, Sato K, Kato J, Ikeda H: Comparison of inhibition ofEscherichia coli topoisomerase IV by quinolones with DNA gyrase inhibition. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1994) 38:2623–2627
Belland RJ, Morrisson SG, Ison C, Huang WM:Neisseria gonorrhoeae acquires mutations in analogous regions ofgyrA andparC in fluoroquinolone-resistant isolates. Molecular Microbiology (1994) 14:371–380
Ferrero L, Cameron B, Crouzet J: Analysis ofgyrA andgrlA mutations in stepwise-selected ciprofloxacin-resistant mutants ofStaphylococcus aureus. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1995) 39:1554–1558
Gootz TD, Zaniewski R, Haskell S, Schmieder B, Tankovic J, Girard D, Courvalin P, Polzer RJ: Activity of the new fluoroquinolone trovafloxacin (CP-99,219) against DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV mutants ofStreptococcus pneumoniae selected in vitro. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1996) 40:2691–2697
Gootz TD, Brighty KE, Anderson MR, Schmeider BJ, Haskell SL, Sutcliffe JA, Castaldi MJ, McGuirk PR: In vitro activity of CP-99,219, a novel 7-(3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexyl)naphthyridone antimicrobial. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease (1994) 19:235–243
Cohen SP, Hachler H, Levy SB: Genetic and functional analysis of the multiple antibiotic resistance (mar) locus inEscherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology (1993) 175:1484–1492
Kaatz GW, Seo SM, Ruble CA: Mechanisms of fluoroquinolone resistance inStaphylococcus aureus. Journal of Infectious Diseases (1991) 163:1080–1086
Trucksis M, Wolfson JS, Hooper DC: A novel locus conferring fluoroquinolone resistance inStaphylococcus aureus. Journal of Bacteriology (1991) 173:5854–5860
Barry AL, Brown SD, Fuchs PC: In-vitro selection of quinolone-resistant staphylococcal mutants by a single exposure to ciprofloxacin or trovafloxacin (CP-99,219). Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1996) 38:324–327
Köhler T, Michéa-Hamzehpoor M, Plésiat P, Kahr AL, Pechère J-C: Differential selection of multidrug efflux systems of quinolones inPseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1997) 41:2540–2543
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards: Standard methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility test for bacteria that grow aerobically. Approved standard M7A3. NCCLS, Villanova, PA (1990)
Olsson-Liljequist B, Hoffman BM, Hedlund J: Activity of trovafloxacin against blood isolates ofStreptococcus pneumoniae in Sweden. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (1996) 15:671–675
Sefton AM, Maskell JP, Rafay AM, Whiley A, Williams JD: The in-vitro activity of trovafloxacin, a new fluoroquinolone against gram-positive bacteria. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1997) 39, Supplement B: 57–62
Felmingham D, Robbins MJ, Ingley K, Mathias I, Bhogal H, Leakey A, Ridgway GL, Grüneberg RN: In-vitro activity of trovafloxacin (CP-99,219), a new fluoroquinolone, against recent clinical isolates. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1997) 39, Supplement B: 43–49
Rolston KVI, Ho DH, LeBlanc B, Streeter H, Dvorak T: In-vitro activity of CP-99,219, a novel azabicyclo-naphthyridone, against clinical bacterial isolates from patients with cancer. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1997) 39, Supplement B: 15–22
Urbásková P, Trupl J, Hupková H, Appelbaum PC, Jacobs MR: In vitro susceptibility of pneumococci to trovafloxacin, penicillin G, and other antimicrobial agents in the Czech Republic and Slovakia. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (1996) 15:686–688
Crokaert F, Aoun M, Duchateau V, Grenier P, Vandermies A, Klastersky J: In vitro activity of trovafloxacin (CP-99,219), sparfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and fleroxacin against respiratory pathogens. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (1996) 15:696–698
Shonekan D, Handwerger S, Mildvan D: Comparative in-vitro activities of RP59500 (quinupristin/dalfopristin), CL 329.998, CL331.002, trovafloxacin, clinafloxacin, teicoplanin and vancomycin against gram-positive bacteria. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1997) 39:405–409
Eliopoulos GM, Klimm K, Eliopoulos CT, Ferraro MJ, Moellering RC Jr: In vitro activity of CP-99,219, a new fluoroquinolone against clinical isolates of gram-positive bacteria. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1993) 37:366–370
Child J, Andrews J, Boswell F, Brenwald N, Wise R: The in-vitro activity of CP-99,219, a new naphthyridone antimicrobial agent: a comparison with fluoroquinolone agents. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1995) 35:869–876
Verbist L, Verhaegen J: In vitro activity of trovafloxacin versus ciprofloxacin against clinical isolates. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (1996) 15:683–685
Thomson KS, Chartrand SA, Sanders CC, Block SL: Trovafloxacin, a new fluoroquinolone with potent activity againstStreptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1997) 41:478–480
Klugman K, Wasas A: In-vitro activity of the fluoroquinolone trovafloxacin against penicillin-susceptible and-resistantStreptococcus pneumoniae. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1995) 36:873–874
Pankuch GA, Jacobs MR, Appelbaum PC: Activity of CP-99,219 compared with DU-6859a, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, lomefloxacin, tosulfloxacin, sparfloxacin, and grepafloxacin against penicillin-susceptible and -resistant pneumococci. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1995) 35:230–232
Neu HC, Chin N: In vitro activity of the new fluoroquinolone CP-99,219. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1994) 38:2615–2622
Briggs-Gooding B, Jones RN: In vitro antimicrobial activity of CP-99,219, a novel azabicyclo-naphthyridone. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1993) 37:349–353
Cunha BA, Qadri SMH, Ueno Y, Walters EA, Domenico P: Antibacterial activity of trovafloxacin (CP-99,219) against nosocomial gram-positive and gram-negative isolates. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1997) 39, Supplement B: 29–34
Fuchs PC, Barry AL, Brown SD: Tentative interpretative criteria for testing the susceptibility ofStreptococcus pneumoniae to eight fluoroquinolones. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease (1996) 26:23–27
Fuchs PC, Barry AL, Brown SD, Sewell DL: In vitro activity and selection of disk content for disk diffusion susceptibility tests with trovafloxacin. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (1996) 15:678–682
Dembry LM, Farrell PA, Orcutt DR, Gerrity LA, Andriole VT: In-vitro activity of trovafloxacin (CP-99,219 against sensitive and resistant aerobic bacteria using the standard microdilution broth method and E-test. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1997) 39, Supplement B: 35–42
Mulazimoglu L, Drenning SD, Yu VL: In vitro activities of two novel oxazolidinones (U100592 and U100766), a new fluoroquinolone (trovafloxacin), and dalfopristin-quinupristin againstStaphylococcus aureus andStaphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1996) 40:2428–2430
Coque TM, Singh KV, Murray BE: Comparative in-vitro activity of the new fluoroquinolone trovafloxacin (CP-99,219) against gram-positive cocci. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1996) 37:1011–1016
Jones RN: In vitro antimicrobial activity of CP-99,219-99, a new 7-azabicyclonaphthyridone. Drugs (1995) 49, Supplement 21:205–207
Cormican MG, Jones RN: In-vitro activity of trovafloxacin (CP-99,219) tested by two methods against 150 vancomycin-resistant enterococcal isolates. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1996) 37:847–849
Freeman C, Robinson A, Cooper B, Mazens-Sullivan M, Quintiliani R, Nightingale C: In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of glycopeptide-resistant enterococci. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease (1995) 21:47–50
Visalli MA, Bajaksouzian S, Jacobs MR, Appelbaum PC: Comparative activity of trovafloxacin, alone and in combination with other agents, against gram-negative nonfermentative rods. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1997) 41:1475–1478
Fass RJ, Barnishan J, Solomon MC, Ayers LW: In vitro activities of quinolones, β-lactams, tobramycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole against nonfermentative gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1996) 40:1412–1418
Roblin PM, Kutlin A, Hammerschlag MR: In vitro activity of trovafloxacin againstChlamydia pneumoniae. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1997) 41:2033–2034
Edelstein PH, Edelstein MAC, Ren J, Polzer R, Gladue RP: Activity of trovafloxacin (CP-99,219) againstLegionella isolates: in vitro activity, intracellular accumulation and killing in macrophages, and pharmacokinetics and treatment of guinea pigs withL. pneumophila pneumonia. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1996) 40:314–319
Kenny GE, Cartwright FD: Susceptibilities ofMycoplasma pneumoniae, Mycoplasma hominis andUreaplasma urealyticum to a new quinolone, trovafloxacin (CP-99,219). Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1996) 40:1048–1049
Girard AE, Girard D, Gootz TD, Faiella JA, Cimochowski CR: In vivo efficacy of trovafloxacin (CP-99,219), a new quinolone with extended activities against gram-positive pathogens,Streptococcus pneumoniae andBacteroides fragilis. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1995) 39:2210–2216
Andrews JM, Honeybourne D, Brenwald NP, Bannerjee D, Iredale M, Cunningham D, Wise R: Concentrations of trovafloxacin in bronchial mucosa, epithelial lining fluid, alveolar macrophages and serum after administration of single or multiple oral doses to patients undergoing fibre-optic bronchoscopy. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1997) 39:797–802
Bedos J-P, Rieux V, Bauchet J, Muffat-Joly M, Carbon C, Azoulay-Dupuis: Efficacy of trovafloxacin against penicillinsusceptible and multiresistant strains in a mouse pneumonia model. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1998) 42:862–867
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pechère, J.C., Gootz, T.D. Bacteriological activity of trovafloxacin, a new quinolone, against respiratory tract pathogens. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 17, 405–412 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01691573
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01691573