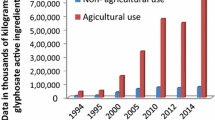
Conclusions
Under the experimental conditions used, 2, 2′ -dichlorobiphenyl proved to be non-persistent. It is metabolized (Fig. 1) to at least two monohydroxy derivatives and probably one dihydroxy derivative and a dechlorinated product. The monohydroxy derivatives occur in free form, as well as conjugated in the plant tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DUKE, T. W., LOWE, J.I., and WILSON, A.J., Jr., Bull. Environ. Contain, and Toxicol. 5, 171 (1970).
MUELLER, W., et al., unpublished.
MOZA, P., WEISGERBER, I., KLEIN, W., and KORTE, F., Chemosphere 2, 217 (1973).
ATTAR, A., ISMAIL, R., BIENIEK, D., KLEIN, W., KORTE, F., Chemosphere, submitted for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moza, P., Weisgerber, I., Klein, W. et al. Metabolism of 2, 2′ -dichlorobiphenyl-14c in two plant-water-soil-systems. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 12, 541–546 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01684916
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01684916